Is the target protein effectively degraded?
Poly-ubiquitination of the POI is followed by its recruitment by the proteasome and its proteolytic degradation. When the degradation rate of a target protein is faster than the rate at which it is being expressed, its net intracellular level decreases. If the target protein is also a pharmacological target, the effects of this decrease can be observed through downstream pathway effects. A reliable assessment of degradation is therefore an indirect measure of a PROTAC molecule’s binding efficacy and ultimately, its usefulness as a degrader.
Poly-ubiquitination of the POI is followed by its recruitment by the proteasome and its proteolytic degradation. When the degradation rate of a target protein is faster than the rate at which it is being expressed, its net intracellular level decreases. If the target protein is also a pharmacological target, the effects of this decrease can be observed through downstream pathway effects. A reliable assessment of degradation is therefore an indirect measure of a PROTAC molecule’s binding efficacy and ultimately, its usefulness as a degrader.
We offer a wide range of detection solutions for assessing protein degradation which ensure selectivity, sensitivity, and reproducibility and are ideal for replacing Western Blotting. Our AlphaLISA SureFire® Ultra™ total protein kits and HTRF total protein kits are alternatives to Western Blots for monitoring protein expression levels with precision. Our vast phospho protein kit portfolio offers a way to characterize the mechanism of action, to measure the functionality or effect of a degrader downstream.
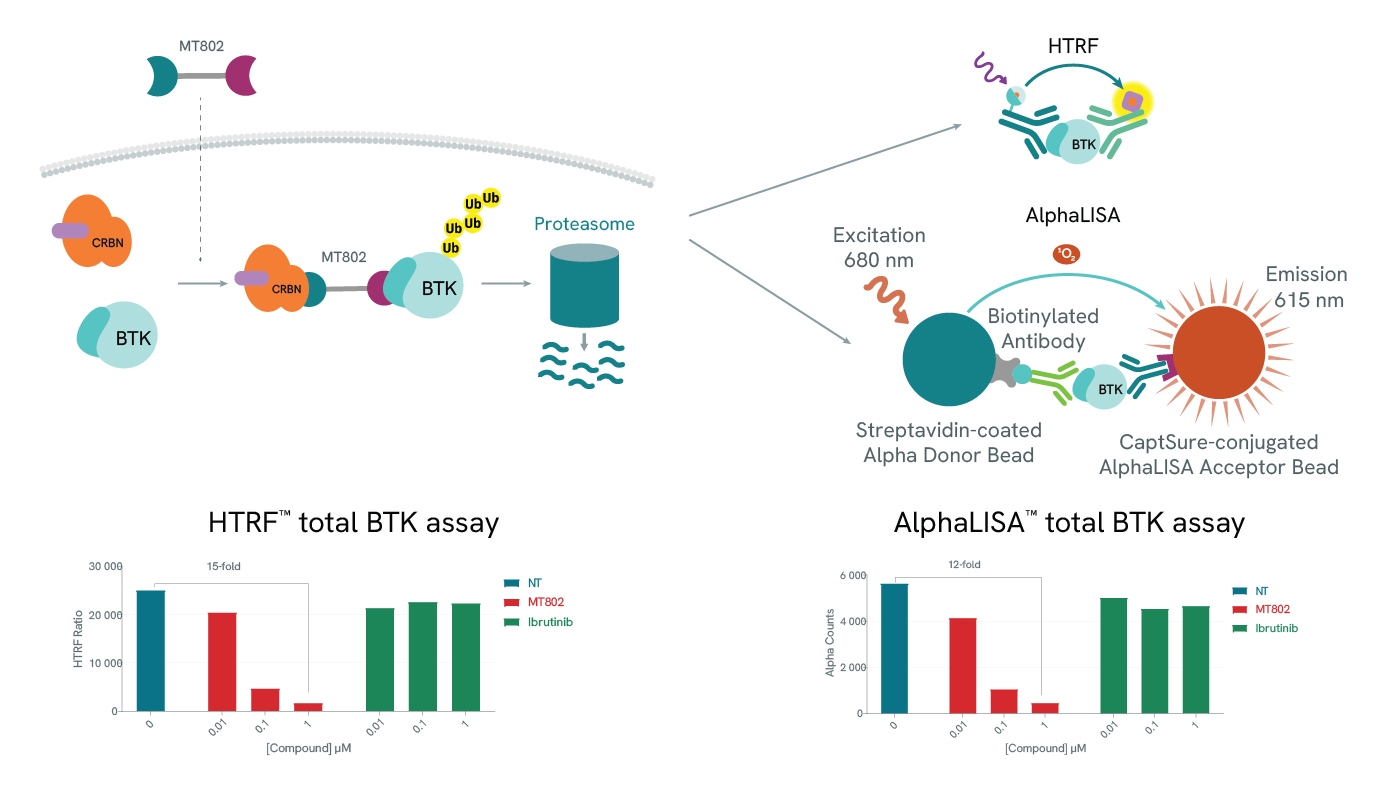
Protein degradation can be easily assessed using our total protein assays. In both examples (HTRF and AlphaLISA), use of a BTK-specific PROTAC, MT-802 leads to a drastic reduction of the detected levels of BTK. As expected, BTK levels are not affected by increasing concentrations of Ibrutinib, a BTK inhibitor.

PROTAC targeting EGFR assessed with total and phospho kits.
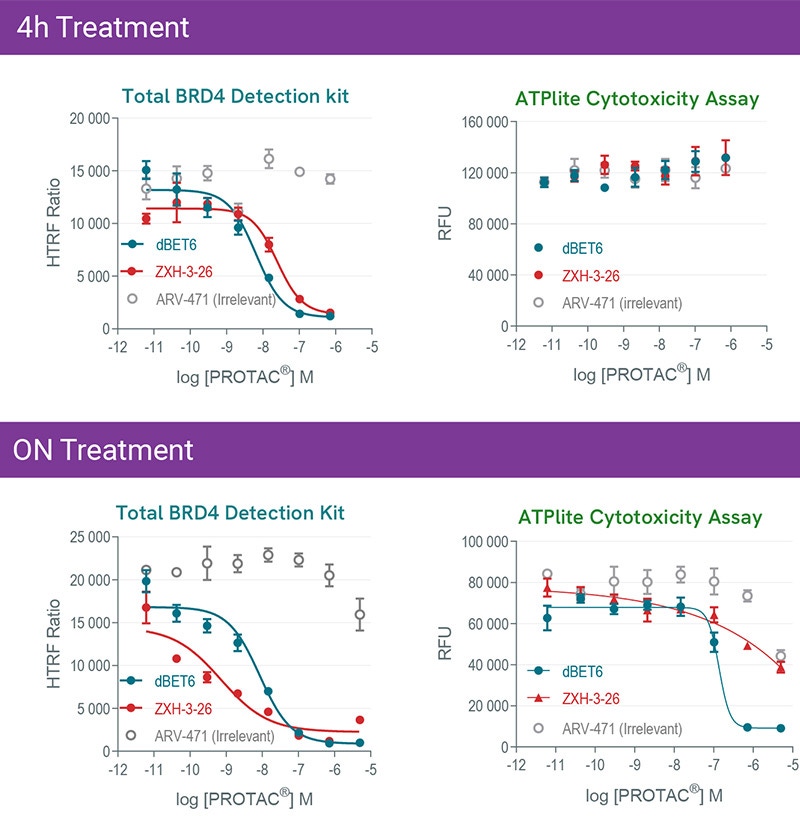
Kinetics of dBET6 and ZXH-3-26 PROTAC®s mediated degradation and cytotoxicity effects. HeLa cells were treated 4h or overnight with increasing concentrations of PROTAC®s. Experiments were carried out following instruction of each kit to monitor BRD4 expression level with HTRF total BRD4 kit, and Cytotoxicity with ATPlite kit.
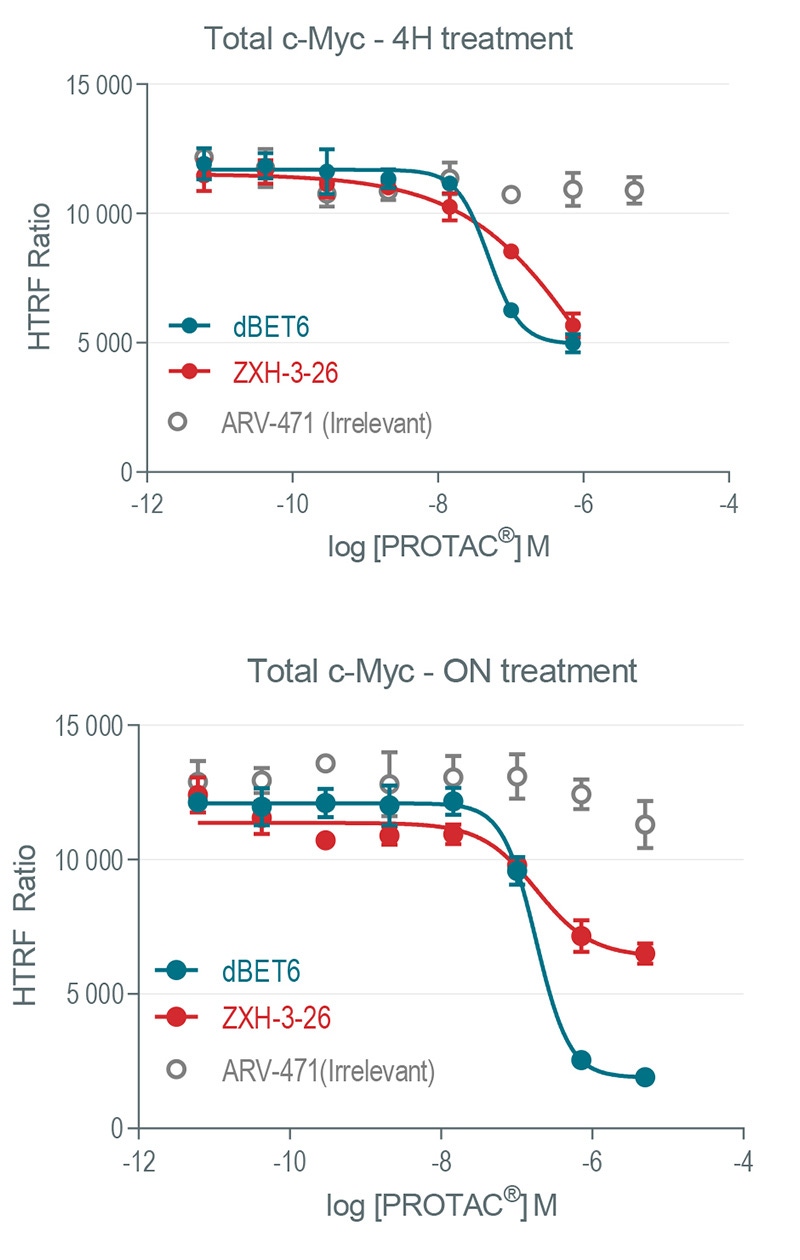
Modulation of c-Myc expression as a downstream BRD4 readout after PROTAC® treatment. HeLa cells were treated with increasing concentrations of dBET6 (pan BET family), ZXH-3-26 (selective BRD4 PROTAC®) as well as ARV-471 irrelevant PROTAC®) for 4h or overnight.
Is the degrader binding to the protein of interest?
Affinity for the POI is not the only consideration when designing a PROTAC molecule. As a therapeutic agent, the first three barriers it must overcome in an in vivo environment are chemical stability, solubility and membrane permeability.
Affinity for the POI is not the only consideration when designing a PROTAC molecule. As a therapeutic agent, the first three barriers it must overcome in an in vivo environment are chemical stability, solubility and membrane permeability.
Once in the cellular environment, the PROTAC first forms a binary complex with either the POI or the specific E3 ligase. Successful engagement of both binding partners signals the formation of the ternary complex.
Efficient and fast compound optimization is of paramount importance in the drug discovery process. Revvity offers many tools that can be used in PROTAC characterization studies.
Kinase-binding assays
If your POI is a kinase, Revvity’s biochemical offering includes three kinase activity assay kits that allow the measuring of the binding affinity of your PROTAC binder and are compatible with 80% of the human kinome. The assays are based on the competitive dissociation of a known kinase-binding inhibitor by the compound under study.

HTRF® kinase binding kits from Revvity are sandwich immunoassays based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) between a FRET donor (a conjugated anti-6HIS, anti-GST or anti-biotin antibody) and a fluorescent acceptor tracer. Competitive displacement of the tracer by the PROTAC reduces the fluorescent signal allowing the calculation of a dissociation constant.
Is the degrader binding to the E3 Ligase?
With only 2 E1 enzymes and 30-50 E2 enzymes encoded in the human genome, E3 ligases exhibit remarkable diversity, with over 600 genes. This variety is key in PROTAC (PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras) design, as different ligases can be recruited to target specific proteins for degradation. A common E3 ligase in PROTAC design is Cereblon (CRBN), which forms an E3 ligase complex with DDB1 (DNA Damage Binding protein 1), Cullin-4A (CUL4A), and ROC1 (Regulator of Cullins 1).
With only 2 E1 enzymes and 30-50 E2 enzymes encoded in the human genome, E3 ligases exhibit remarkable diversity, with over 600 genes. This variety is key in PROTAC (PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras) design, as different ligases can be recruited to target specific proteins for degradation. A common E3 ligase in PROTAC design is Cereblon (CRBN), which forms an E3 ligase complex with DDB1 (DNA Damage Binding protein 1), Cullin-4A (CUL4A), and ROC1 (Regulator of Cullins 1).
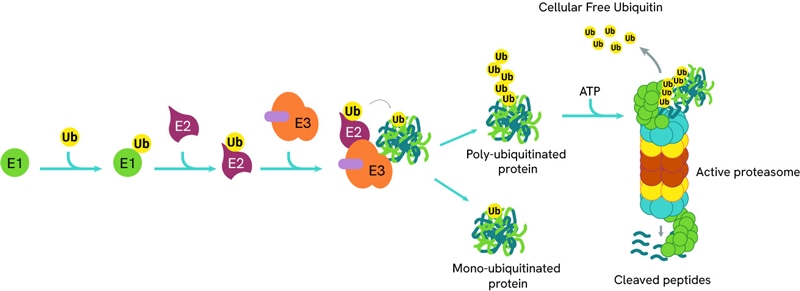
The process of ubiquitination can be sequentially repeated resulting in poly-ubiquitinated proteins which are then directed to the proteasome for degradation.
Assessing PROTAC binding to E3 ligases
With only 2 E1 enzymes and 30-50 E2 enzymes encoded in the human genome, E3 ligases exhibit remarkable diversity, with over 600 genes. This variety is key in PROTAC (PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras) design, as different ligases can be recruited to target specific proteins for degradation. A common E3 ligase in PROTAC design is Cereblon (CRBN), which forms an E3 ligase complex with DDB1 (DNA Damage Binding protein 1), Cullin-4A (CUL4A), and ROC1 (Regulator of Cullins 1).
Revvity supports PROTAC development with a suite of AlphaLISA and HTRF E3 ligase binding kits, which facilitate precise binding studies. Sample data generated using the AlphaLISA Cereblon Binding Kit illustrate the competitive binding of various molecules to Cereblon. For example, the PROTAC dBRD9 and the IMiDs (Immunomodulatory imide drugs), Pomalidomide and Lenalidomide, all competitively bind to Cereblon, displacing a biotinylated Cereblon ligand and generating dose-response inhibition curves that allow IC50 determination. However, VH032, a ligand that recruits the VHL (Von Hippel-Lindau) E3 ligase rather than Cereblon, does not displace the Cereblon ligand.
Similarly, HTRF assays demonstrate that the PROTAC MT-802 and Pomalidomide compete with a fluorescently labeled Thalidomide ligand for Cereblon binding, whereas VH032 (specific to VHL) does not. MT-802, a PROTAC targeting BTK (Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase) for degradation, and Pomalidomide produce dose-dependent inhibition, enabling IC50 calculations that align with established literature values. These kits offer valuable insights into PROTAC-E3 ligase interactions and support precise PROTAC design for targeted protein degradation.
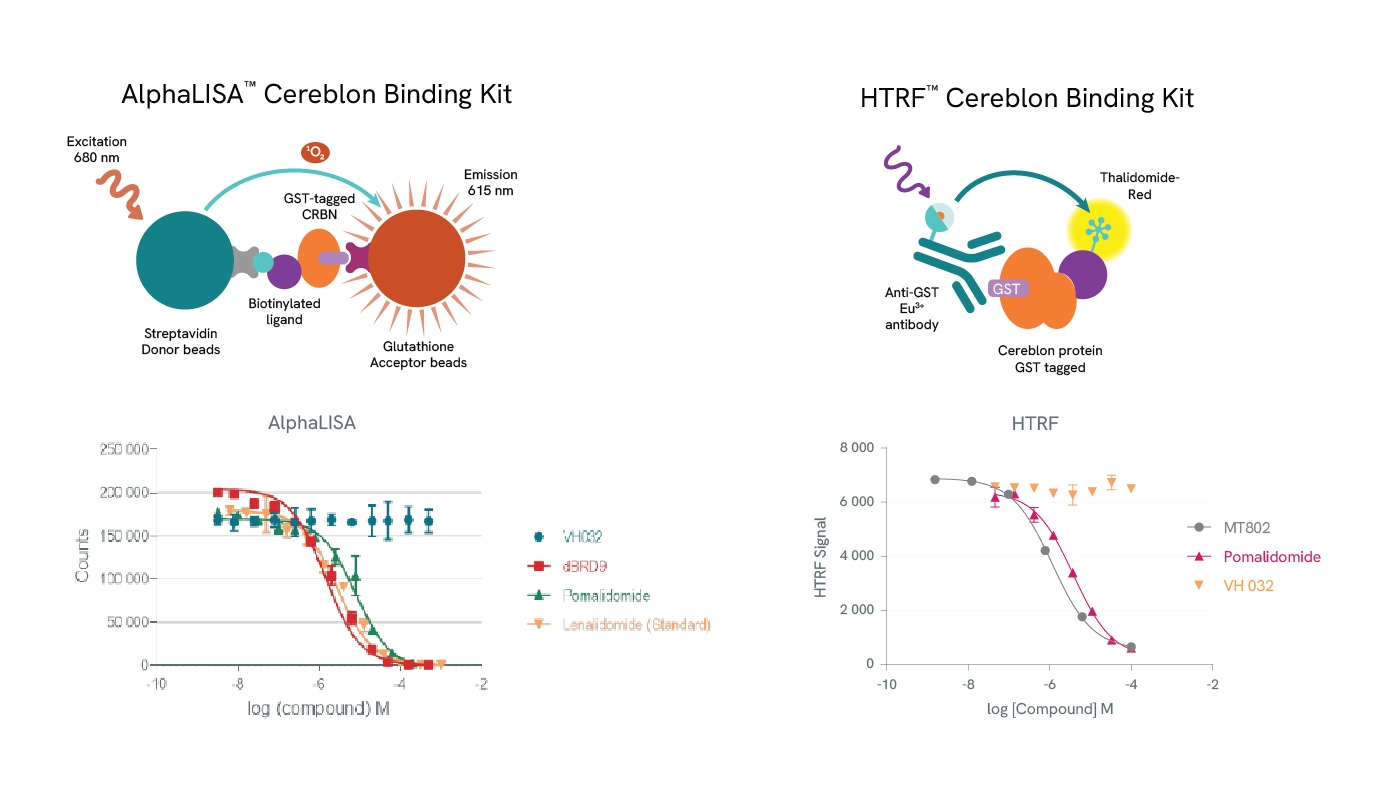
Top row: The AlphaLISA detection of Cereblon binding uses glutathione acceptor beads to capture GST-tagged Cereblon and Streptavidin-coated donor beads to capture the biotinylated ligand. Donor beads and acceptor beads come into proximity through ligand binding to Cereblon. In the HTRF assay Cereblon binding is detected using a specific GST antibody labeled with Europium Cryptate (donor) which binds to GST-tagged Cereblon and Thalidomide-Red labelled with XL665 (acceptor). Addition of a Cereblon binding compound leads to competitive displacement of the biotinylated ligand/Thalidomide red respectively, and a reduction of light emission inversely proportional to the compound’s concentration.
Bottom row: Binding of dBRD9, Pomalidomide or Lenalidomide to Cereblon reduces the signal of the AlphaLISA assay in a concentration-dependent fashion compared to the negative control VH032. Similarly for the HTRF assay, MT802 and Pomalidomide induce a reduction of FRET, whereas VH032 doesn’t.
Is the ternary complex formed correctly?
The binding efficacy and affinity of the PROTAC molecule for the POI and the E3 ligase in the context of a binary complex cannot predict the stability of the ternary complex. Increasing evidence suggests that the degradation activity of a PROTAC is highly dependent on the stability of ternary complexes and the cooperativity of protein-protein interactions.
The binding efficacy and affinity of the PROTAC molecule for the POI and the E3 ligase in the context of a binary complex cannot predict the stability of the ternary complex. Increasing evidence suggests that the degradation activity of a PROTAC is highly dependent on the stability of ternary complexes and the cooperativity of protein-protein interactions.
Characterizing the ternary complex
Any pharmaceutical development workflow will need to scrutinize extensively the formation, population, stability, binding affinities, cooperativity, and kinetics of PROTAC ternary complexes. Alpha and HTRF protein-protein interaction assay kits are ideal companions for such studies. By titrating a PROTAC molecule with its target protein and E3 ligase, a bell-shaped curve can be produced by plotting Alpha and HTRF signals against PROTAC concentrations, as high PROTAC concentrations result in binary complexes (PROTAC-POI or PROTAC-E3 Ligase} which compete for the ternary complex (hook effect). The height of the curve is dependent on ternary complex concentration, enabling the classification of PROTACs by their ability to form ternary complexes. In addition to ternary complex formation, Alpha and HTRF assay kits can also be repurposed to determine the affinity of these complexes.
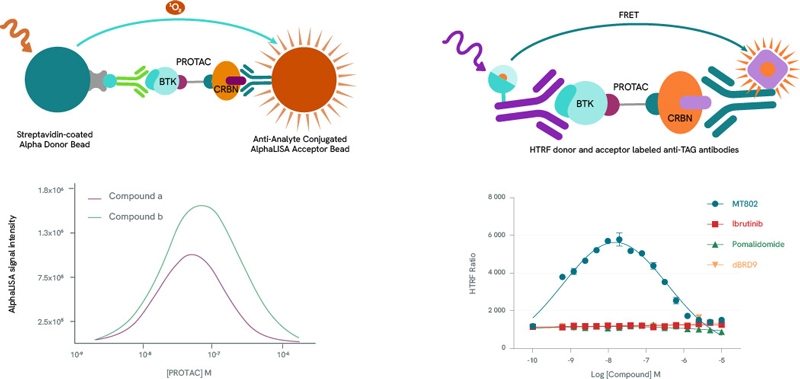
Left panel: Example bell curves constructed using an AlphaLISA protein-protein interaction assay. Compound a is more efficient than compound b in the formation of ternary complexes with BTK and Cereblon.
Right panel: Example bell-shaped curve obtained using an HTRF protein-protein interaction assay in the presence of BTK and Cereblon. Data from MT-802 demonstrate the formation of the ternary complex. As expected, the BTK inhibitor Ibrutinib, the Cereblon inhibitor Pomalidomide and the BRD9-specific PROTAC dBRD9 do not form ternary complexes.
What does the future hold for Targeted Protein Degradation?
PROTAC technology is by no means the only player in the targeted protein technology field. A number of alternative methods have been developed that utilise both the UPS (TRAFTAC, molecular glues) as well as the ALS (LYTAC, AUTAC, ATTEC). Targeting the ALS in particular, offers some distinct advantages as it allows for the degradation of large proteins, macromolecular complexes or aggregates.
PROTAC technology is by no means the only player in the targeted protein technology field. A number of alternative methods have been developed that utilise both the UPS (TRAFTAC, molecular glues) as well as the ALS (LYTAC, AUTAC, ATTEC). Targeting the ALS in particular, offers some distinct advantages as it allows for the degradation of large proteins, macromolecular complexes or aggregates.
Molecular glues
In contrast to the PROTAC technology that relies on bifunctional degradation activation compounds (biDACs), molecular glues (or glue degraders) are monofunctional degradation activation compounds (monoDACs). These bind to either the E3 ligase or the target protein and chemically modify its surface, prompting protein-protein interactions that ultimately cause the E3 ligase to bind to the target protein, resulting in degradation. MonoDACs tend to be smaller molecules than biDACs, which could simplify optimization with respect to bioavailability and compliance with drug development guidelines. However, monoDACs’ reliance on single protein-protein interactions can weaken their ability to select the target of interest.
TRAFTAC
TRAnscription Factor TArgeting Chimeras (TRAFTACs) are heterobifunctional chimeric oligonucleotides. They consist of a double-stranded DNA moiety that recruits the transcription factor of interest (TOI), covalently linked to a Cas9 CRISPR-binding RNA. The latter binds to an ectopically expressed dCas9-HaloTag7 fusion protein. Combining the TRAFTAC with a PROTAC molecule specific for HaloTag7 and an E3 Ligase (VHL in the original study) brings into proximity the E3 Ligase and the DNA-bound TOI, resulting in the latter’s ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation.

ATTEC
An AuTophagosome TEthering Compound (ATTEC) is a bifunctional molecule capable of binding simultaneously to a target protein as well as the phagophore protein LC3. By doing so, the POI-ATTEC-LC3 complex is incorporated in a phagophore membrane, leading to its engulfment and proteolytic degradation once the phagophore merges with a lysosome to form an autophagosome.
AUTAC
The AUtophagy-TArgeted Chimera (AUTAC) consists of a specific binder for an intracellular target of interest and a guanine tag connected by a flexible linker. This induces S-guanylation of the target, and has been applied in the selective autophagic degradation of proteins as well as mitochondria. In the case of mitochondria, the guanine tag induced K63 poly-ubiquitination, which facilitated of mitophagy in a Parkin and PINK1-independent fashion.
LYTAC
Designed specifically to target cell membrane-bound and extracellular proteins, LYsosome-TArgeted Chimeras (LYTACs) make use of the lysosome degradation pathway by recruiting proteins to lysosome-shuttling receptors located at the cell surface. LYTACs consist of a POI-binding element linked to a moiety that allows transport into the cell via lysosome-shuttling receptors, where it will get degraded by the endosome/lysosome pathway. The first example of such a moiety consisted of a chemically synthesized glycopeptide ligand, an agonist of the cation-independent mannose-6- phosphate receptor (CI−M6PR). Another study focusing on Human hepatocytes (HCC) used the liver-specific asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR) using a triantenerrary N-acetylgalactosamine (tri-GalNAc) motif as it displayed more efficient uptake than M6Pn-LYTAC owing to the higher surface expression of ASGPR in hepatocytes.

LYTAC, AUTAC and ATTEC mechanisms of action
As with PROTACs, our AlphaLISA and HTRF reagents can help research on the development of the other targeted degradation technologies, either in conjunction with the CETSA method, or standalone kits for transcription factors, kinases and protein-protein interactions.
Featured resources
































