Overview
Folate receptors (FR) are a family of cell surface receptors that bind the essential vitamin folic acid (folate, vitamin B9). These receptors are upregulated in highly metabolic cells due to the high need of this vital nutrient. IVISense™ Folate Receptor 680 (formerly FolateRSense) is a near infrared fluorescent probe that can be used to noninvasively quantify FR expression in vivo. It binds specifically to the folate receptor in vivo and can be used to image folate receptor expression.

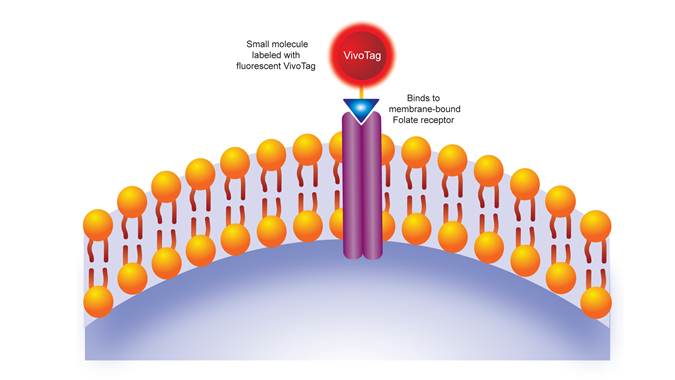
Figure 1: IVISense Folate Receptor 680 mechanism of action. IVISense Folate Receptor 680 is a fluorescent targeted probe that specifically binds to the folate receptor alpha (FRA) protein- a biomarker for tumor metabolism.
Products and catalog numbers
| Product | Catalog Number | Ex/Em wavelength (nm) | Molecular weight (g/mol) | Validated Experiments | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVISense Folate Receptor 680 | NEV10040 | 670/690 | 1605.7 | In vivo/Ex vivo Flow cytometry In vitro microscopy |
Oncology Acute Inflammation Arthritis |
Using IVISense Folate Receptor 680 probe for in vivo/ex vivo studies
In Vivo imaging
The generally recommended procedure for in vivo imaging with IVISense Folate Receptor 680 is administration via intravenous injection and imaging 6-24 hours post injection.
View instructions on setting up an in vivo mouse experiment with IVISense Folate Receptor 680 fluorescent probe.
| Route of Injection | Mouse Dose (25 g) | Rat Dose (250 g) | Blood t 1/2 | Tissue t 1/2 | Optimal imaging time | Optimal Re-injection Time (complete clearance) | Route of Metabolism/ background tissue | FMT and IVIS settings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IV | 2 nmol | 6-20 nmol | 5 min | >168 h | 6 h (6-24 h) | 6-7 days | Kidneys | FMT 680/700 IVIS 675/720 |
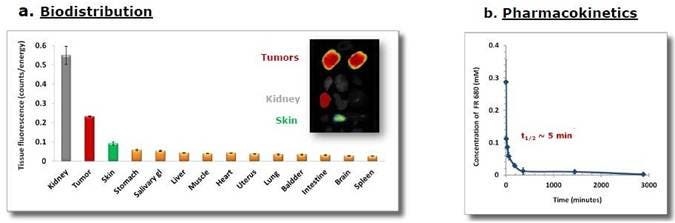
Figure 2: Biodistribution and Pharmacokinetics A) KB cells were injected into the mammary fat pads of Nu/Nu female mice. Mice were injected intravenously with 2 nmoles IVISense Folate Receptor 680 once tumors reached the desired size. Tissue samples were collected 4 hours later, and fluorescence assessed by planar imaging (ex vivo). Mean counts/energy for each tissue were determined as a measure of tissue brightness. B) The pharmacokinetic profile was assessed by injecting CD1 mice, then collecting plasma at multiple times post-injection and measuring the plasma fluorescence. The t ½ was determined to be 5 minutes.
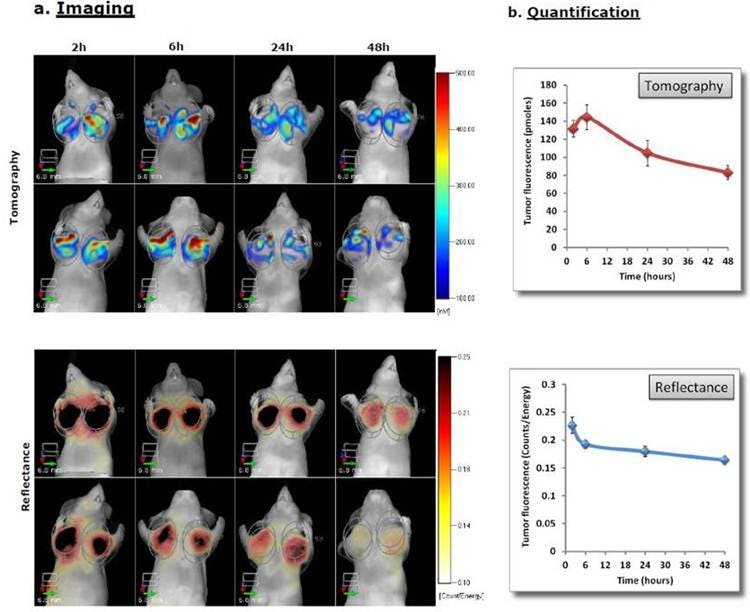
Figure 3: In Vivo Imaging and Quantification A) KB cells were injected into the mammary fat pads of Nu/Nu female mice. Once tumors reached the desired size, the mice were injected intravenously with 2 nmoles IVISense Folate Receptor 680 and imaged by tomographically (top) and by reflectance (bottom) at 2 hours and then at different times thereafter. Panels show two representative mice. B) Quantification of the tumor site signal (pmoles by tomography) and relative tumor brightness (mean counts/energy by reflectance) were determined over time.
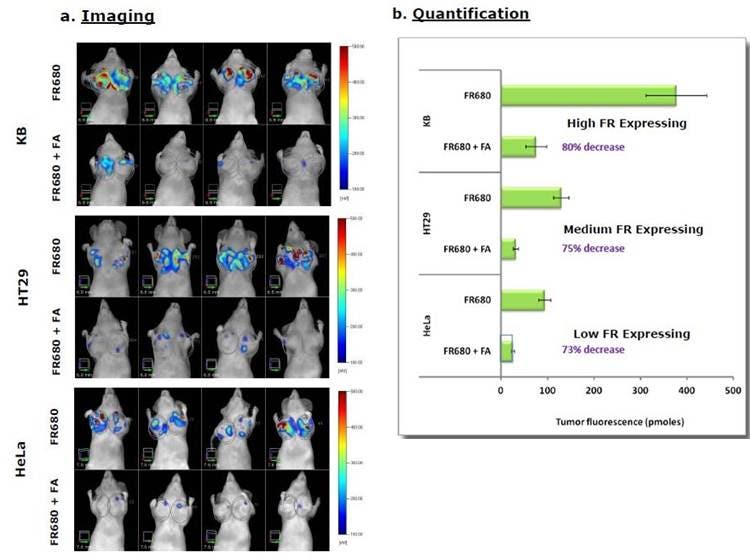
Figure 4: In Vivo Imaging and Quantification. Mice were implanted with KB, HeLa or human colorectal HT-29 tumors. A) Once tumors reached the desired size, mice were injected with IVISense Folate Receptor 680 in the absence or presence of 100x excess folic acid and imaged tomographically 4 hours later. Four representative mice per group are shown. B) The quantification of the signal in the different tumors with and without competitive folic acid is shown.
Ex Vivo Imaging:
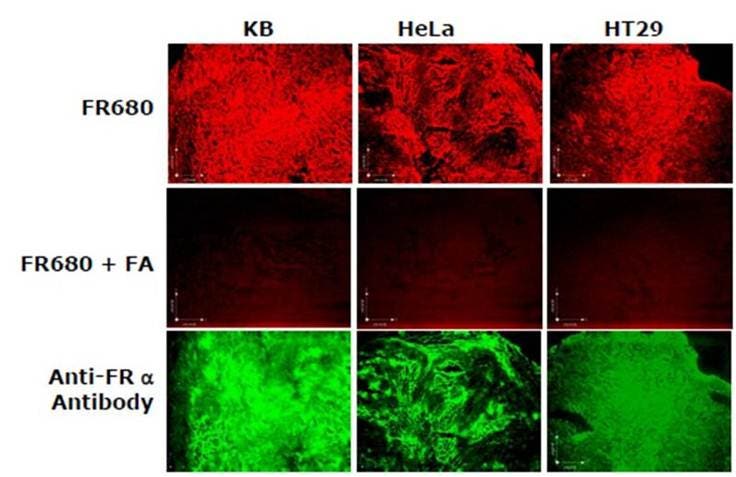
Figure 5: Ex Vivo Imaging. KB, HeLa or HT-29 tumors-bearing mice were injected with IVISense Folate Receptor 680, with or without excess folic acid as a competitor. The tumors were excised 4 hours later and then snap frozen. Using fluorescence microscopy, labeling of the tumor cells and effective competition by free folic acid can be seen. The FITC-conjugated anti-folate receptor antibody validates the results in the lower panel. In blue: DAPI nuclear stain, red: IVISense Folate Receptor 680, green: FITC-anti-folate receptor antibody. The acquisition time was the same for IVISense Folate Receptor 680 with and without the free folic acid.
IVISense Folate Receptor 680 probe for in vitro studies
Flow cytometry and in vitro microscopy
- We have validated IVISense Folate Receptor 680 for use with fluorescence microscopes and flow cytometers. Here is a brief protocol with a recommended concentration of probe to use:
- Culture tumor cells (such as KB) in standard TC plate or chamber slide
- Incubate cells with 1 µM IVISense Folate Receptor 680 for 1 hour at 37 °C
- Wash 3 times in PBS
- Flow cytometry filter settings: 712/21
Fluorescence micrsocopy filter: Cy 5.5
In Vitro Imaging:
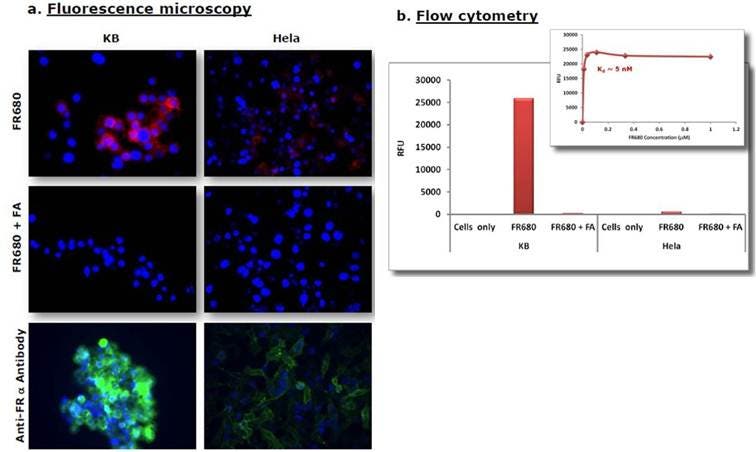
Figure 6: Fluorescence Microscopy and Flow Cytometry. KB or HeLa cells were incubated with 1mM IVISense Folate Receptor 680 in the presence or absence of excess unlabeled Folic acid (FA) for 1 hour at 37 °C. After washing, cells were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. A) The fluorescence microscopy shows labeling of positive cells and the second panel shows IVISense Folate Receptor 680 is effectively competed off by free folic acid. In the third panel, a FITC-conjugated anti-folate receptor antibody was used to validate the results. In blue: DAPI nuclear stain, red: IVISense Folate Receptor 680, green: FITC-anti-folate receptor antibody. B) The flow cytometry results confirm significantly higher labeling of folate receptor positive cells over negative cells. The binding experiments using increasing concentrations of IVISense Folate Receptor 680 were used to determine an approximate dissociation constant of 5 nM.
Application notes and posters
- Poster: Quantitative assessment of folate receptor expression by FMT imaging with a NIR fluorescent folate probe
FAQs
Q. Can I use IVISense Folate Receptor 680 in humans?
A. No, IVISense Folate Receptor 680 is intended for animal research use only, is not intended for use in diagnostic procedures and is not intended for use in humans.
Q. What cancer cell lines have Folate receptors overexpressed?
A. In a variety of cancers (including breast, ovarian, lung, kidney, colon, and brain) and in tumor associated macrophages, folate receptors (FR) are overexpressed. Folic acid has been successfully used as a cancer specific targeting moiety for the efficient delivery of chemotherapeutic agents and diagnostic reporters. The determination of the level of FR expression for a given tumor is critical to the success of such agents, and therefore, specific and quantitative imaging probes and methods for the determination of FR expression in vivo are imperative.
Q. Does IVISense Folate Receptor 680 bind to Folate Receptor alpha or beta?
A. The R&D team has tested the specificity of this probe for Folate receptor protein. We have not done studies to show whether it specifically binds to alpha or beta or both.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. The information provided above is solely for informational and research purposes only. The information does not constitute medical advice and must not be used or interpreted as such. Consult a qualified veterinarian or researcher for specific guidance or use information. Revvity assumes no liability or responsibility for any injuries, losses, or damages resulting from the use or misuse of the provided information, and Revvity assumes no liability for any outcomes resulting from the use or misuse of any recommendations. The information is provided on an "as is" basis without warranties of any kind. Users are responsible for determining the suitability of any recommendations for the user’s particular research. Any recommendations provided by Revvity should not be considered a substitute for a user’s own professional judgment. Users are solely responsible for complying with all relevant laws, regulations, and institutional animal care and use committee (IACUC) guidelines in their use of the information provided.




























