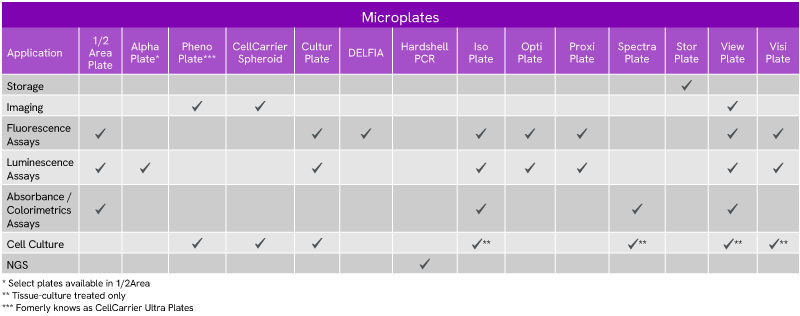
Microplates for storing reagents, biomolecules, or other samples.

Cell imaging
Microplates for microscopy and high-content screening offering the lowest plate bottom for superior image acquisition.
Microplates for microscopy and high-content screening offering the lowest plate bottom for superior image acquisition.

Assays
Microplates for TR-FRET, HTRF, Alpha, Radiometric, luminescence, fluorescence, and others for general research.
Microplates for TR-FRET, HTRF, Alpha, Radiometric, luminescence, fluorescence, and others for general research.

Cell culture
Microplates designed to improve consistency and reliability of cell growth for general cell culture as well as 3D cell culture.
Microplates designed to improve consistency and reliability of cell growth for general cell culture as well as 3D cell culture.

Microplates for genomic analysis used in sample preparation workflows.

Microplates for a range of high-throughput radiometric assays.