

HTRF Human & Mouse Total NF-κB Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points


HTRF Human & Mouse Total NF-κB Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points






The total-NFkB kit detects cellular NFkB, and can be used as a normalization assay for the p-NFkB kit. It is a leading product in cancer and inflammatory research.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Cell Signaling |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |
The total-NFkB kit detects cellular NFkB, and can be used as a normalization assay for the p-NFkB kit. It is a leading product in cancer and inflammatory research.



HTRF Human & Mouse Total NF-κB Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points



HTRF Human & Mouse Total NF-κB Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points



Product information
Overview
Total NFkB kit serves as a normalization assay with our Phospho-NFkB kits. NFkB (Nuclear Factor Kappa B) is of great interest in cancer research and a key player in the inflammatory response. The buffers of both HTRF phospho- and total NFkB assays are compatible, enabling an analysis of the phosphorylated and the total protein populations from one lysate sample.
Specifications
| Application |
Cell Signaling
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Lysis Buffer Compatibility |
Lysis Buffer 3
Lysis Buffer 4
Lysis Buffer 5
|
| Molecular Modification |
Total
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Phosphoproteins
|
| Target Species |
Human
Mouse
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
NASH/Fibrosis
Neuroscience
Oncology & Inflammation
|
| Unit Size |
10,000 Assay Points
|
Video gallery

HTRF Human & Mouse Total NF-κB Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points

HTRF Human & Mouse Total NF-κB Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points

How it works
Total-NFkB assay principle
The Total-NFkB assay quantifies the expression level of NFkB in a cell lysate. Contrary to Western Blot, the assay is entirely plate-based and does not require gels, electrophoresis or transfer. The Total-NFkB assay uses two labeled antibodies: one coupled to a donor fluorophore, the other to an acceptor. Both antibodies are highly specific for a distinct epitope on the protein. In presence of NFkB in a cell extract, the addition of these conjugates brings the donor fluorophore into close proximity with the acceptor and thereby generates a FRET signal. Its intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of the protein present in the sample, and provides a means of assessing the proteins expression under a no-wash assay format.

Total-NFkB 2-plate assay protocol
The 2 plate protocol involves culturing cells in a 96-well plate before lysis then transferring lysates to a 384-well low volume detection plate before adding Total NFkB HTRF detection reagents. This protocol enables the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored.

Total-NFkB 1-plate assay protocol
Detection of total NFkB with HTRF reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, stimulation and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS designed protocol enables miniaturization while maintaining robust HTRF quality.

Assay validation
Detection of total NFkB in various human/mouse cells
Human and murine cells in serum-deprived cell culture medium were plated at 40,000 cells per well in a 96-well plate and incubated for 24h at 37°C, 5% CO2. The phosphorylation state was induced by a 10 min stimulation time with 10 nM TNFalpha or 2 nM IL1beta. After stimulation, medium was removed and cells were lysed with 50 µL of lysis buffer for 30 min at RT under gentle shaking. 16 µL of lysate were transferred into 384-well sv white microplate, and 4 µL of the HTRF total NFkB detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation.

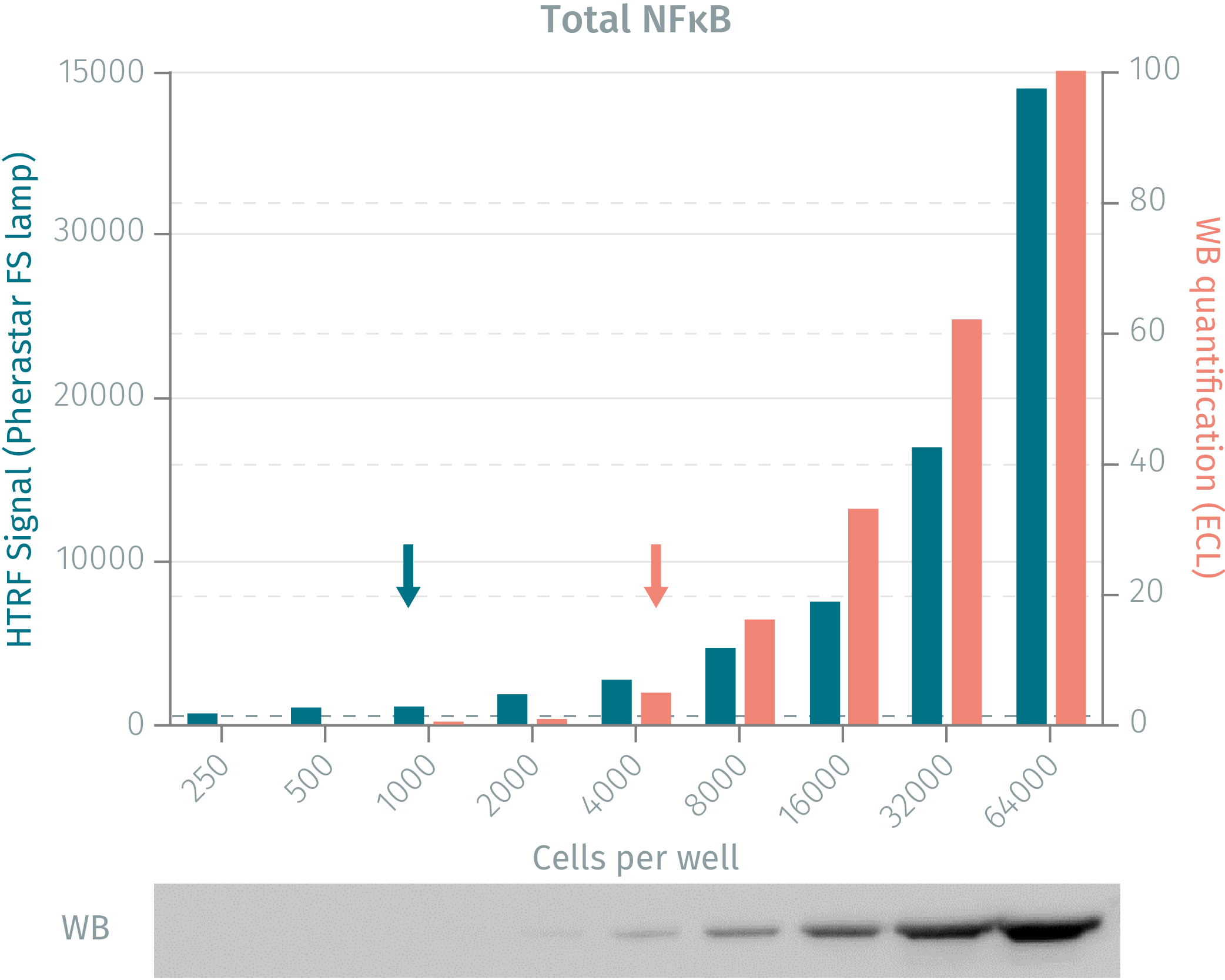
HTRF assay vs WB using total-NFkB assay
Human HeLa cells were cultured for 48 followed by TNFalpha stimulation. Following lysis, soluble fractions were collected after centrifugation. Serial dilutions of the cell lysate were analyzed side-by-side by Western Blot and by HTRF. Results show that HTRF total-NFkB cellular assays is more sensitive than the Western Blot, as 1 000 cells are sufficient for minimal signal detection when using the HTRF total-NFkB assay while 4 000 are needed for a Western Blot signal.
TNFa dose-response on HeLa cells using phospho and total NFkB kit
HeLa cells were plated and cultured for 24h before being exposed to increasing concentrations of TNFalpha. Following cell lysis, 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well sv white microplate and 4 µL of the phospho-NFkB (Ser536) or total NFkB detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation. Stimulation with increasing concentration of TNFa induces phosphorylation of NFkB, while the total amount of protein, unphosphorylated and phosphorylated, remains stable.


Pharmacological response on Phospho and total NFkB of BAY 11-7085
Prolonged exposure to BAY 11-7085 induces a downregulation of the NFkB expression level, as shown by the decrease of the HTRF total NFKB signal. Phosphorylation of NFKB also declines with increasing BAY concentrations. Consequently, the normalization signal calculated from phospho- & total NFkB level remains stable. 40,000 cells of the U937 cell line were stimulated by increasing concentrations of BAY 11-7085 for a 3 hours, and co-stimulated for 10 min with 10 nM TNFalpha. Cells were lysed and transferred into a 384-well sv white microplate for detection of both HTRF phospho and total NFkB.



Simplified pathway
Regulation of the NFkB pathway
NFkB is in a super-family with 5 members and consists of two subunits of either homo- or heterodimers that are involved in the regulation immune response. Two main NFkB pathways exist. The classical pathway involves p65 & p50 and is stimulated by cytokines or TLR activation. The alternative pathway is mainly activated in lymphocyte generation. Inactive NFkB dimers are sequestered in the cytoplasm. Upon stimulation, the IB proteins are phosphorylated, ubiquitinylated and degraded, which activates the NF-B complex, causing it to translocate into the nucleus. Activated NFkB helps mediate gene expression, inflammatory response, cell survival and cellular proliferation. Deregulation of NFkB pathways have been found in several auto-immune disorders but also in some types of cancer.

Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
This guide provides you an overview of HTRF applications in several therapeutic areas.
Dive deeper into astrocyte cell research
The release of pro-inflammatory factors by activated astrocytes has been shown to be...
An in-depth review of molecular and cellular pathways
The maintenance of proteostasis, the biological mechanisms that control the...
SDS, COAs, Manuals and more
Are you looking for technical documents related to the product? We have categorized them in dedicated sections below. Explore now.
- LanguageEnglishCountryUnited States
- LanguageFrenchCountryFrance
- LanguageGermanCountryGermany
- Resource TypeManualLanguageEnglishCountry-


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.




































