Overview
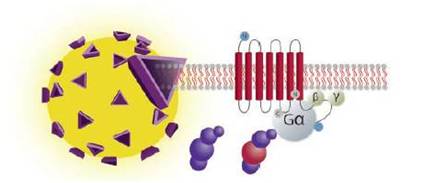
In the SPA format, cell membranes are captured onto SPA scintillant beads. When the fGPCR is activated 35S-labeled GTP will bind to the membrane. This puts the radiochemical into proximity of the SPA bead. When the radiochemical is close to the bead, the beta energy from the 35S can interact with scintillant in the bead, producing a signal that can be measured. 35S-GTP that is not bound to the cell membrane will not be close enough to the SPA bead to interact strongly with the scintillant.

What do I need to run this assay?
- Cell membrane expressing receptor of interest. (Revvity carrie receptor-transfected cell membranes)
- 35S-gamma GTP (NEG030H or NEG030X)
- Unlabeled non-hydrolyzable GTP-gamma-S control for non-specific binding
- GDP, agonists, antagonists, test compounds as appropriate
- WGA-coated SPA beads (See SPA bead options section for more information. We do not recommend using a PEI-coated bead (polyethyleneimine-coated bead) when working with 35S-gamma GTP.)
- Microplates (We recommend Revvity white or white-walled, clear-bottom for bottom reads.)
- TopSeal™-A (Cat. No. 6050185)
- Appropriate detection instrument. (We recommend a MicroBeta™ or Tri-Carb™ liquid scintillation counter)
*Revvity also sells a GTP binding SPA kit, Cat. No. RPNQ0210. This kit contains WGA PVT SPA beads and assay buffer.
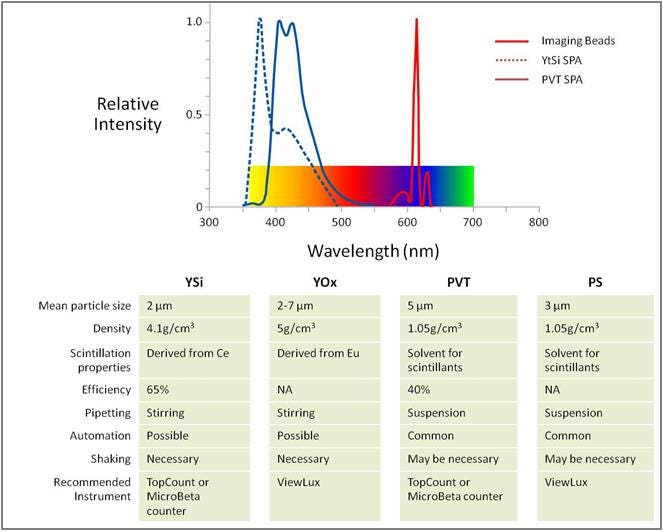
SPA bead options for capturing cell membranes
In addition to standard SPA scintillation beads (which can be measured on a Revvity MicroBeta Counter, we also offer SPA imaging beads. SPA imaging beads have a red-shifted signal output and can be measured on an appropriate instrument
- The most-commonly used SPA bead for this assay is the WGA-coated PVT scintillation SPA bead (#RPNQ0001)
- In addition to the beads below, we also carry kit #RPNQ0210 which contains WGA-coated PVT beads and buffer. This kit contains 750 mg of WGA PVT SPA beads and a 5X Assay Buffer concentrate (100 mM HEPES, 500 mM NaCl, 50 mM MgCl2, 5 mM EDTA, pH 7.4 prior to dilution).
| Bead coating | Bead type | Core bead type | Pack size | Catalog number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) | Scintillation | PVT | 100mg | RPNQ0252 |
| 500mg | RPNQ0001 | |||
| 25 x 500 mg | SPQ0031 | |||
| 2g | RPNQ0060 | |||
| YSI | 250 mg | RPNQ0011 | ||
| 1 g | RPNQ0023 | |||
| PS | 50 mg | RPNQ0262 | ||
| 500 mg | RPNQ0260 | |||
| VOX | 50 mg | RPNQ0272 | ||
| 500 mg | RPNQ0270 | |||
35S-gamma GTP radiochemicals
Two different 35S-gamma GTP products are available from Revvity, each in various sizes.
| Product number | Radioactive concentration | Specific activity | Buffer |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEG030H | 12.5 mCi/mL | 1250 Ci/mmol | 10 mM Tricine pH 7.6, 10 mM DTT |
| NEG030X | 1 mC/mL | 1250 Ci/mmol | 10 mM Tricine pH 7.6, 10 mM DTT |
Protocol-in-brief
This diagram shows how a SPA GTP binding assay works in general

Assay optimization
1. Concentration of GDP, MgCl in assay (cross-titration matrix):
Test 4 different concentrations:
- For MgCl2: 1 mM, 3 mM, 10 mM, and 30 mM
- For GDP: 1 µM, 3 µM, 10 µM and 30 µM
Work in triplicate:
- 3 basal wells (no agonist)
- 3 stimulated wells (with a high concentration of agonist)
As a general recommendation, you can run this experiment using 10 μg of membrane and 0.5 mg of beads per well (96-well format, 100 µL reaction volume).
2. Cell membrane and SPA bead titration (cross-titration matrix):
- Try three random membrane concentrations [for example: 5, 10 and 15 µg per well (100 µL reaction volume)] and three concentrations of beads [for example: 1, 0.5 and 0.25 mg beads per well (100 µL reaction volume)]. Set up both basal and stimulated samples.
3. Agonist dose-response under optimized conditions (antagonist dose response, Z' values if applicable).
- Perform a 10x serial dilution of your agonist (you want to cover a broad range of agonist concentrations). For antagonist dose-response, use agonist at concentration equivalent to the EC80.
Recommended assay conditions (SPA format) for 35S-gamma-GTP binding assays using Revvity cell membrane products validated for GTP binding
| Cat # | Assay buffer | Membranes (µg final) |
GDP (µM final) |
PVT-WGA SPA Beads (mg final) |
GTPg35S (dpm) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ES-010-M400UA | Adenosine, A1 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2 | 2.5 µg | 10 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-012-M400UA | Adenosine, A3 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2 | 4 µg | 1 µM | 0.25 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-030-M400UA | Adrenergic, alpha 2A | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2 | 5 µg | 10 µM | 0.25 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-031-M400UA | Adrenergic, alpha 2B | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2 | 10 µg | 15 µM | 0.5 mg | 25000 dpm |
| ES-110-M400UA | Cannabinoid, CB1 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.1% protease free BSA | 5 µg | 3 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-111-M400UA | Cannabinoid, CB2 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 200 mM NaCl, MgCl2, 0.1% protease free BSA. | 5 µg | 3 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-137-M400UA | Chemokine, CX3CR1 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2 | 5 µg | 1 µM | 0.25 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-142-M400UA | Chemokine, CXCR3 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2 | 5 µg | 3 µM | 0.25 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-145-M400UA | Chemokine, CXCR2 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.1% protease-free BSA. | 10 µg | 3 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-148-M400UA | Chemokine, CXCR1 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.1% protease free BSA. | 10 µg | 3 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-173-M400UA | Dopamine, D3 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 0.1% protease free BSA. | 10 µg | 1 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-340-M400UA | Leukotriene, BLT1 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 30 mM MgCl2 | 10 µg | 10 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-370-M400UA | MCH 1/ SCL1 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.1% protease free BSA. | 4 µg | 10 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-392-M400UA | Histamine, H3 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2 | 5 µg | 10 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-491-M400UA | Neuropeptide, NPFF1 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.1% protease free BSA. | 10 µg | 10 µM | 0.25 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-511-M400UA | Galanin, Gal 2 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2 | 5 µg | 1 µM | 5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-530-M400UA | Cholecystokinin, CCK1 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.1% protease free BSA | 5 µg | 1 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-521-M400UA | Somatostatin, sst2a | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2. | 5 µg | 3 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-522-M400UA | Somatostatin, sst5 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2 | 8 µg | 3 µM | 0.25 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-523-M400UA | Somatostatin, sst3 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2 | 10 µg | 3µM | 0.25 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-541-M400UA | Opioid, Kappa (OP2) | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl, 30 mM MgCl2, 0.1% protease free BSA. | 5 µg | 10 µM | 0.25 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-542-M400UA | Opioid, Mu (OP3) | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, | 5 µg | 1 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-561-M400UA | Prostanoid, CRTH2 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 30 mM MgCl2, 0.1% protease free BSA. | 10 µg | 10 µM | 0.5 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-610-M400UA | N-formyl Peptide, FPRL1 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.1% protease free BSA. | 10 µg | 30 µM | 0.25 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-620-M400UA | Melatonin, MT1 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2 | 10 µg | 10 µM | 0.25 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-621-M400UA | Melatonin, MT2 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2 | 10 µg | 50 µM | 0.25 mg | 25.000 dpm |
| ES-720-M400UA | Chemokine, CXCR6 | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2 | 10 µg | 3 µM | 0.5 mg | 25000 dpm |
| ES-730-M400UA | Chemotactic Peptide, C3a | 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4; 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 0.1% protease free BSA. | 5 µg | 30 µM | 0.25 mg | 25.000 dpm |
Application note, posters, guides and other resources
- NIH Assay Guidance website for GTP binding assays
- SPA bead technology knowledge base page
Tips and FAQs
- Cell membrane concentration and bead concentration are critical in SPA assays - these parameters need to be optimized carefully for each assay
- For GTP binding assays, we do not recommend using PEI-coated (polyethyleneimine-coated) SPA beads.
- The GTPγS assay works best with Gi-coupled GPCRs. Very low assay windows are usually obtained for Gs- and Gq-coupled receptors, due to both (1) levels of expression of Gi relative to Gs or Gq proteins and (2) the exchange rate of these G proteins for GTP.
- The GTPγS assay is sensitive to GDP concentration, concentration of 35S GTPγS, Mg2+ in the assay buffer.
- Controls: we recommend that when you develop your assay, you include a no-agonist control (substituting with buffer) to determine your basal GTP binding level, and a non-specific binding (NSB) control where you use unlabeled non-hydrolyzable GTP with 35S-gamma-GTP and cell membrane
Data analysis
Visit our GTP binding data analysis page.
Citations
- Wan, Y. et al. Identification of full, partial, and inverse CC chemokine receptor 3 agonists using 35S GTPgammaS binding. Eur. J. Pharmacol 456, 1-10 (2002). Link
- Rodgers, G. et al. Development of displacement binding and GTPgammaS scintillation proximity assays for the identification of antagonists of the micro-opioid receptor. Assay Drug Dev Technol 1, 627-636 (2003). Link
- Johnson, E.N. et al. A 1,536-well 35S GTPgammaS scintillation proximity binding assay for ultra-high-throughput screening of an orphan galphai-coupled GPCR. Assay Drug Dev Technol 6, 327-337 (2008). Link
- Ferrer, M. et al. A fully automated 35S GTPgammaS scintillation proximity assay for the high-throughput screening of Gi-linked G protein-coupled receptors. Assay Drug Dev Technol 1, 261-273 (2003). Link
Custom cell lines, membranes, frozen cells, and receptors
Revvity offers custom radiosynthesis, labeling, cell lines and membranes as well as custom assay development. If you are interested in our custom services, please contact us.
Radiosynthesis and Labeling Custom Assay Services
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
The information provided above is solely for informational and research purposes only. Revvity assumes no liability or responsibility for any injuries, losses, or damages resulting from the use or misuse of the provided information, and Revvity assumes no liability for any outcomes resulting from the use or misuse of any recommendations. The information is provided on an "as is" basis without warranties of any kind. Users are responsible for determining the suitability of any recommendations for the user’s particular research. Any recommendations provided by Revvity should not be considered a substitute for a user’s own professional judgment.