Overview
In vitro kinase assays are often performed using 32P- labeled ATP. In this assay, you will measure transfer of the gamma phosphate from ATP (or sometimes GTP) to a substrate. Radioactive assays can be used for kinetics or screening. The assay can be compatible with essentially any kind of substrate, including peptides, proteins, lipids, and small molecules. Radioactive biochemical kinase assays can be performed in several different formats. For low-throughput assays, the assay is traditionally performed in tubes or vials, then unreacted radioactive ATP is separated from substrate by gel electrophoresis, filtration, density gradient centrifugation, or chromatography. For higher-throughput assays, SPA homogeneous (non-separation) assays are typically used.
For cell-based assays, one typically uses 32P- orthophosphate or other phosphate salts rather than labeled ATP. In general, ATP does not permeate cells well.
Assays
DNA and RNA labeling
View detailed information on DNA and RNA labeling sing 32P- gamma-ATP. DNA and RNA can be end-labeled at the 5' position using 32P- gamma-ATP with T4 PNK (T4 polynucleotide kinase). This technique is often used to generate probes, or for DNA sequencing.
Standard low-throughput biochemical kinase assays
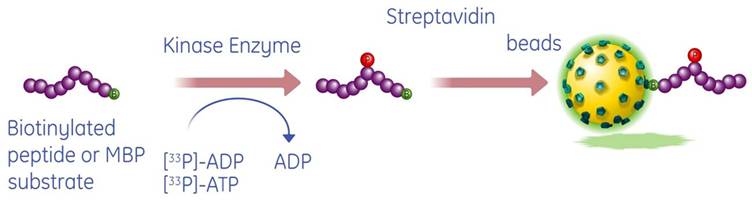
View more information on standard biochemical kinase assays using 32P-gamma-ATP. Radioactive in vitro kinase assays using purified substrates and kinase utilize 32P-labeled ATP or 35S-thio-labeled ATP to transfer a radioactive phosphate group from ATP to a substrate. A variety of substrates can be used in these assays (protein, peptide, lipid, etc.), as long as a method for separation of radiolabeled ATP and substrate is available. Standard low-throughput formats for radioactive in vitro kinase assays typically use gel electrophoresis, chromatography, or filtration techniques to separate radiolabeled ATP from radiolabeled substrate. The amount of phosphorylated substrate is then quantified using standard autoradiography, phosphorimaging, or liquid scintillation counting techniques as appropriate.
Cell labeling assay
View more information on cell labeling assays using 32Pi phosphate salts/orthophosphate. Cell-based radioactive phosphorylation assays/metabolic assays rely on the use of phosphate-free culture media supplemented with a radiolabeled source of phosphate to "feed" the cells, such as 32P. Identification of phosphorylation of a specific target substrate is typically carried out by immunoprecipitating the target-of-interest, then running on an SDS-PAGE gel and exposing to film (autoradiography) or phosphorimaging (though other methods of substrate extraction and detection are also possible).
SPA kinase assays
View more information on what materials you need, what optimizations you may need to perform, and references for SPA kinase assays. In the SPA format, kinase substrate is captured onto a SPA bead. If the substrate has been phosphorylated by kinase, the beta energy from the 32P will be in close enough proximity to the scintillant within the SPA bead, generating signal. This assay format is amenable to high-throughput screening and other medium- and high-throughput assays.

SPA kinase assay
Other Revvity kinase technologies
Protein Kinase Research Reagents
Custom services
Revvity offers custom radiochemical and other services.
Radiosynthesis and Labeling Custom Services
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures




























