Overview
LANCE™ Ultra epigenetics toolbox reagents were designed for the detection of specific methylation and acetylation marks on histone H3 peptide substrates in a TR-FRET assay. Reagents that detect other post-translational modifications (such as acetylation of p53) are also available. In LANCE Ultra assays, a biotinylated histone peptide is used as substrate in a biochemical enzymatic reaction employing either histone methyltransferase (HMT) or acetyltransferase (HAT) enzymes. When the enzymatic reaction is sped, the level of methylation or acetylation is determined using a Europium-labeled antibody and ULight™-streptavidin. The ULight-streptavidin captures the biotin moiety on the peptide substrate, whereas the Europium-labeled antibody recognizes the specific epigenetic mark (acetylation or methylation). Upon excitation of the Europium chelate fluorophore at 320 to 340 nm, energy can be transferred to the ULight acceptor fluorophore in proximity, resulting in the emission of light at 665 nm. The intensity of light emission is proportional to the level of substrate modification.

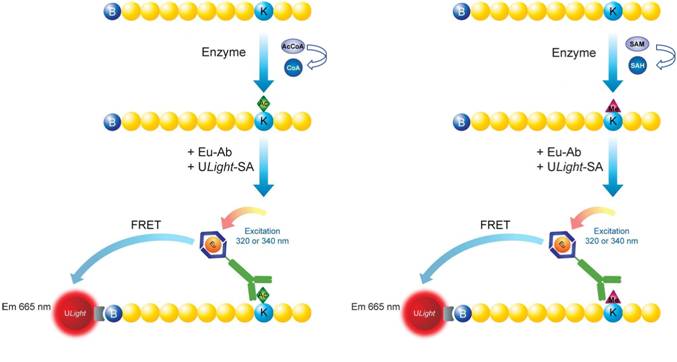
Figure 1. Assay principle for LANCE Ultra epigenetics toolbox reagents. On the left, schematic representation of a LANCE Ultra lysine acetyl-transferase (HAT) assay. On the right, schematic representation of a LANCE Ultra lysine methyl-transferase (HMT) assay. In both cases, a biotinylated histone H3 peptide substrate is used in conjunction with ULight-streptavidin and a Europium-labeled antibody specific to the particular modification (acetylated or methylated residue).
Specificity
HATs and HMTs modify their target substrates at specific residues. Acetylation typically occurs on lysine residues while methylation can occur on lysine or arginine residues. Lysine residues can be mono-, di-, or tri-methylated, while arginines can be mono-, or symmetrically or asymmetrically di-methylated.
Currently, LANCE Europium antibodies are offered for these epigenetic and other post-translationally modified targets:
| Detected modification | Description of modification | Catalog number |
|---|---|---|
| H3K9ac | Histone H3 acetylated lysine 9 | TRF0400 |
| H3K27ac | Histone H3, acetylated on lysine 27 | TRF0405 |
| H3K4 | Histone H3, unmodified on lysine 4 | TRF0404 |
| H3K4me1-2 | Histone H3, mono- or di-methylated on lysine 4 | TRF0402 |
| H3K9me2 | Histone H3, di-methylated on lysine 9 | TRF0403 |
| H3K27me2-1 | Histone H3, mono- or di-methylated on lysine 27 | TRF0406 |
| H3K27me3 | Histone H3, tri-methylated on lysine 27 | TRF0407 |
| H3K36me2 | Histone H3, di-methylated on lysine 36 | TRF0408 |
| p53K382ac | p53, acetylated on lysine 382 | TRF0409 |
| H3K9/K27 | Histone H3, unmodified on lysine 9 and lysine 27 | TRF0411 |
| H4Kac pan | Acetylated human Histone H4 |
TRF0412 |
| O-linked GlcNAc | O-linked n-acetylglucosamine | TRF0413 |
| H4R3me | Histone H4 methylated at arginine 3 | TRF0414 |
| H3/H4Rme pan | Histone H3 and H4 methylated arginine residues | TRF0415 |
Specificity of Europium-labeled antibodies has been assessed in a detection assay using biotinylated peptides with different epigenetic marks. Additional information can be obtained by contacting technical support (contact information is indicated in the upper right-hand corner of this page).
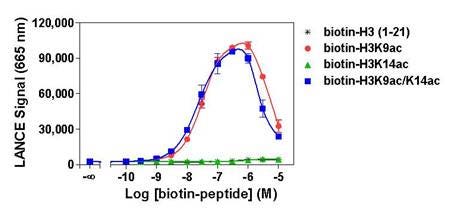
Figure 2. Specificity of TRF0400, which detects H3K9ac (Histone H3 peptide acetylated on lysine 9). Histone H3-derived peptides with different epigenetic marks were titrated. Signal was detected with an EnVision 2103 set in TR-FRET reading mode. The hook effect observed at higher peptide concentrations is typical of multi-component assays. In this particular application, a hooking type of curve is generated when peptide concentrations exceed the binding capacity of the ULight-streptavidin and/or Europium-labeled antibody.
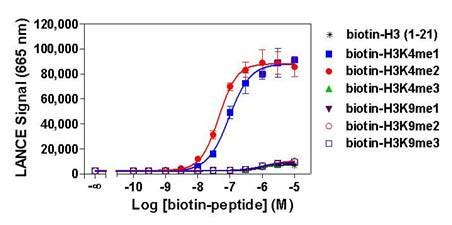
Figure 3. Specificity of TRF0402, which detects mono- or di-methylated states of lysine 4 on histone H3. Histone H3-derived peptides containing different epigenetic marks were titrated. Signal was detected with an EnVision 2103 set in TR-FRET reading mode.
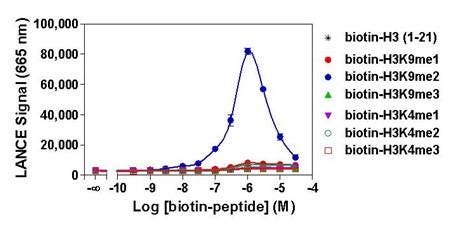
Figure 4. Specificity of TRF0403, which detects H3K9me2 (Histone H3 peptide di-methylated on lysine 9). Histone H3-derived peptides with different epigenetic marks were titrated. Signal was detected with an EnVision 2103 set in TR-FRET reading mode. The hook effect observed at higher peptide concentrations is typical of multi-component assays. Here, it occurs when peptide concentrations exceed the binding capacity of the ULight-streptavidin and/or Europium-labeled antibody.
Custom-labeled Europium antibodies may also be available upon request, and custom assay development services are offered through our custom teams (contact information is at the bottom of this page). It is also possible to use our LANCE Europium labeling reagents and other LANCE toolbox reagents to develop your own assay.
What do I need to run this assay?
Reagents available from Revvity:
- LANCE Ultra Europium-labeled antibody, specific to an acetylation or methylation site (refer to table in above section)
- LANCE ULight-streptavidin (Cat. No. TRF0102)
- 10X LANCE Detection Buffer (Cat. No. CR97-100)
- Seal-A™ adhesive plate seal (Cat. No. 6050185
- Microplates (We recommend white OptiPlate™ microplates, Cat. No. 6007299.)
- TRF-capable plate reader (We recommend our EnVision™ Multilabel Plate Reader, our VICTOR™ plate reader, or our ViewLux™ high-throughput CCD detector.)
Reagents available from AnaSpec and other suppliers:
- Biotinylated Histone H3 or p53 peptide substrates.
Depending on the enzyme under study, you may need to use a non-modified substrate, or you may need to start with a peptide substrate bearing a specific modification (for example a peptide containing a specific mono-methylated residue). In general, we recommend using a non-modified peptide if you are performing acetylation or methylation assays, while a pre-modified substrate will be required for deacetylation and demethylation assays (for example, tri-methylated lysine 9, acetylated lysine 9, etc). Of high interest is the recent availability of anti-non-modified residue antibodies, like the Eu-labeled anti-H3K4-non-modified antibody (TRF0404). The latter allows the development of assays for HDACs acting on H3 lysine 4 or HDMs able to fully demethylate this residue, in a very convenient signal increase mode. Before, these types of assays could only be performed in a signal decrease setup. In any case, make sure your assay is designed so that the Europium-labeled antibody could differentiate between substrate and product.
-
Additionally, you may wish to purchase a second peptide to be used as a positive detection control for your assay. For example, if you are measuring acetylation of lysine 9 on a Histone H3 peptide, you may wish to test the biotinylated acetyl-Lys9 Histone H3 peptide.
Product Sequence AnaSpec catalog number Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide (residues 1-21), non-modified (bare) ARTKQTARKSTGGKAPRKQLA-GGK(biotin)-Nh3 #61702 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide (residues 21-44), non-modified (bare) ATKAARKSAPATGGVKKPHRYRPG-GK(biotin) #64440 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, acetylated on Lysine 9 ARTKQTAR-K(Ac)-STGGKAPRKQLA-GGK(biotin)-Nh3 #64361 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, acetylated on Lysine 14 ARTKQTARKSTGG-K(Ac)-APRKQLA-GGK(biotin)-Nh3 #64362 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, acetylated on Lysine 9 and Lysine 14 ARTKQTAR-K(Ac)-STGG-K(Ac)-APRKQLA-GGK-biotin-Nh3 #64363 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, acetylated on Lysine 27 ATKAAR-K(Ac)-SAPATGGVKKPHRYRPGG-K(biotin) #64846 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, mono-methylated on Lysine 4 ART-K(Me1)-QTARKSTGGKAPRKQLA-GGK-biotin-Nh3 #64355 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, di-methylated on Lysine 4 ART-K(Me2)-QTARKSTGGKAPRKQLA-GGK(biotin)-Nh3 #64356 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, tri-methylated on Lysine 4 ART-K(Me2)-QTARKSTGGKAPRKQLA-GGK(biotin)-Nh3 #64356 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, tri-methylated on Lysine 4 ART-K(Me3)-QTARKSTGGKAPRKQLA-GGK(biotin)-Nh3 #64357 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, mono-methylated on Lysine 9 ARTKQTAR-K(Me1)-STGGKAPRKQLA-GGK(biotin)-Nh3 #64358 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, di-methylated on Lysine 9 ARTKQTAR-K(Me2)-STGGKAPRKQLA-GGK(biotin)-Nh3 #64359 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, tri-methylated on Lysine 9 ARTKQTAR-K(Me3)-STGGKAPRKQLA-GGK(biotin)-Nh3 #64360 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, mono-methylated on Lysine 27 ATKAAR-K(Me1)-SAPATGGVKKPHRYRPG-GK(biotin) #64365 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, di-methylated on Lysine 27 ATKAAR-K(Me2)-SAPATGGVKKPHRYRPG-GK(biotin) #64366 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, tri-methylated on Lysine 27 ATKAAR-K(Me3)-SAPATGGVKKPHRYRPG-GK(biotin) #64367 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, di-methylated on Lysine 36 ATKAARKSAPATGGV-K(Me2)-KPHRYRPG-GK(biotin) #64442 Biotinylated Histone H3 peptide, tri-methylated on Lysine 36 ATKAARKSAPATGGV-K(Me3)-KPHRYRPG-GK(biotin) #64441 Biotinylated p53 peptide (residues 361-393), non-modified (bare) Biotin-LC-GSRAHSSHLKSKKGQSTSRHKKLMFKTEGPDSD-Nh3 #62530 Biotinylated p53 peptide, acetylated on Lysine 382 Biotin-KGGHLKSKKGQSTSRHK-K(Ac)-LMFKTEGPDSD-Nh3 #64869 Reagents available from various suppliers:
- Cofactor (acetyl CoA for acetylation assays, or S-adenosylmethionine for methylation assays; refer to Tips and FAQs below to see where Revvity R&D gets these reagents.)
- Enzyme
- Reaction buffer
-
Test compounds as desired
Products and catalog numbers
View a listing of relevant products and catalog numbers for LANCE assays.
Protocol-in-brief
The assay is performed in two steps: first, the enzymatic assay is performed in an appropriate reaction buffer. Then, the reaction is sped and LANCE Eu-antibody and ULight-streptavidin are added in 1X LANCE Detection buffer for the detection step.
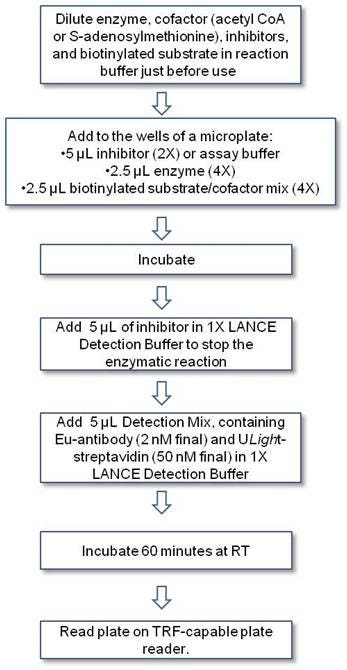
Workflow for LANCE epigenetics assay
Assay development
Assays have to be optimized using your particular enzyme/substrate pair. Examples of assay development for a number of enzymes can be found in the format of Technical Notes. The example below describes the optimization of a p300 acetyltransferase assay using the Eu-labeled anti-H3K9ac antibody (as found in the technical note).
1. Enzyme titration and time-course.
This experiment is set up using increasing concentrations of enzyme where multiple wells are filled for each enzyme concentration allowing sping the reaction at different time points. For subsequent assay optimization, you will want to choose a time and enzyme concentration providing for a linear increase of reaction product over time.
Keep in mind that if you are performing a methylation assay, sping the reaction at the appropriate time could be critical as several of our LANCE Europium antibodies detect specific methylation states. For example, if a methylation reaction were to proceed for a too long time period, substrate tri-methylation could occur (provided the enzyme is used at that capacity), with an eventual loss of signal if the antibody is specific for the di-methylated residue.
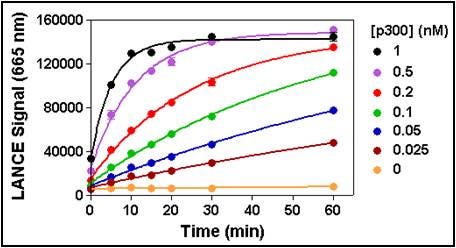
Figure 5. Enzymatic progress curves were performed by incubating p300 at concentrations ranging from 0.025 to 1 nM with 200 nM biotinylated H3 (1-21) peptide substrate and at a non-limiting concentration of acetyl CoA (25 µM). Reactions were sped by the addition of anacardic acid at the indicated times, followed by the Detection Mix. Signal was read after 60 min. A 30 min reaction time using 0.1 nM enzyme was selected for all subsequent experiments.
2. Cofactor titration.
This assay is performed to determine the apparent Km for the cofactor (either acetyl CoA for acetylation assays, or S-adenosylmethionine for methylation assays). Increasing concentrations of cofactor are tested at the optimal enzyme concentration and time point selected in the previous experiment. For most applications, you will want to select a final concentration of cofactor that is close to the apparent Km.
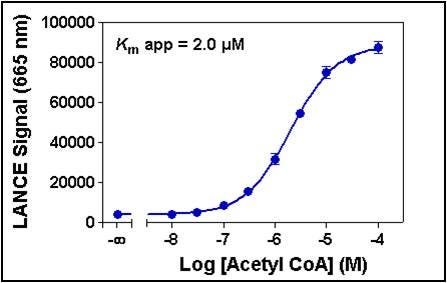
Figure 6. Serial dilutions of acetyl CoA ranging from 10 nM to 100 µM were added to 0.1 nM p300 and 200 nM biotinylated H3 (1-21) peptide substrate. A 5 µM acetyl CoA concentration was selected for subsequent experiments.
Before moving into the testing of the effect of compounds on the studied enzyme, it is important to perform an intermediate experiment to confirm that the selected conditions (in terms of reaction time, enzyme and cofactor concentrations) still allow for a linear increase of product over time (not shown). This can be easily accomplished by performing a time-course (enzymatic) assay using the conditions selected from Figures 5 and 6.
3. Enzyme inhibition.
This assay can be used to characterize inhibitors of your enzyme, or as part of assay validation using a reference inhibitor if you are screening. Increasing concentrations of inhibitor are tested at the enzyme concentration, time point, and cofactor concentration determined from the previous two experiments. An IC50 for the inhibitor can be derived from this data. It is important to note that if the compounds to be tested are dissolved in a solvent that is different than water (typically DMSO), its effect on the enzymatic reaction must be evaluated beforehand.
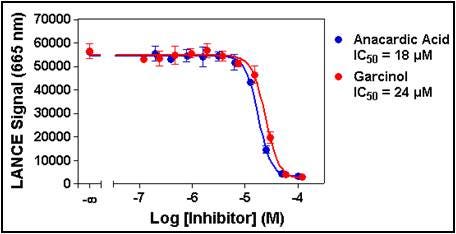
Figure 7. Serial dilutions of anacardic acid ranging from 200 nM to 100 µM and garcinol ranging from 120 nM to 120 µM were pre-incubated for 10 min with 0.1 nM p300. Enzymatic reactions were initiated by the addition of 200 nM biotinylated H3 (1-21) peptide substrate plus 5 µM acetyl CoA. Enzymatic reactions contained 1% DMSO.
4. Z'-factor determination.
If screening, you may wish to perform a Z'-factor determination experiment as part of your assay validation. Two conditions are chosen that will generate a high and low signal (for example, with and without a particular concentration of inhibitor, or with and without a particular concentration of cofactor). In general, a Z'-factor above 0.5 is highly desirable for screening campaigns.
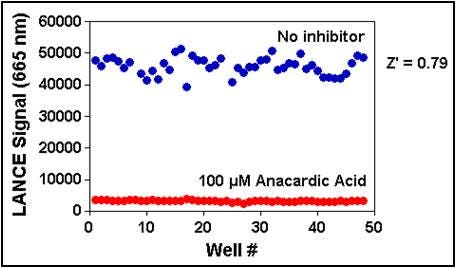
Figure 8. p300 (0.1 nM) was pre-incubated with or without 100 µM anacardic acid for 10 min. Enzymatic reactions were initiated by the addition of 200 nM biotinylated H3 (1-21) peptide substrate plus 5 µM acetyl CoA and sped after 30 minutes. Enzymatic reactions contained 1% DMSO.
Tips and FAQs
- Acetyltransferase and methyltransferase recombinant enzymes can exhibit low activity in biochemical assays, compared to other types of enzymes such as kinases. Reaction buffer optimization (including pH, salt surfactant concentration, etc.), enzyme titration, and time-course experiments are critical in achieving a good signal window.
- In order to avoid stability issues and minimize assay variability, enzyme, cofactor/s, substrate/s, and test compounds should be diluted in assay buffer just before use.
- Acetyl CoA cofactor is prepared at 50 mg/mL (56.9 mM) in h3O, aliquoted and stored at -80 °C. Revvity R&D obtains acetyl CoA from Sigma (#A2056).
- S-adenosylmethionine is prepared at 30 mM in 5 mM h3SO4/10% ethanol (v/v) in h3O, aliquoted, and stored at -80 °C. Revvity R&D obtains S-adenosylmethionine from Sigma (#A7007).
- The concentrations of biotin-peptide substrate indicated in the Tech Notes are the best concentrations to work with for the model enzymes indicated. For other enzymes, or if you would like to use a different peptide (longer, shorter, bearing other modifications already, etc.), it is possible that you will need to adjust the substrate concentration. Nevertheless, we suggest that you initially use the substrate concentration indicated on the technical notes (for a given anti-mark antibody) to generate your enzyme progression curves. You should only start adjusting the biotin-peptide substrate concentration if the enzymatic assay does not work well and other components in the assay have been optimized already. If possible, we strongly advise that you try changing the concentration of the co-factor or enzyme, or the reaction time rather than changing the concentration of biotin-peptide substrate. An important thing to keep in mind is that, generally, the concentration of biotin-peptide substrate cannot be increased too much because this could cause the detection assay to “hook” on the biotin-streptavidin interaction site.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
The information provided above is solely for informational and research purposes only. Revvity assumes no liability or responsibility for any injuries, losses, or damages resulting from the use or misuse of the provided information, and Revvity assumes no liability for any outcomes resulting from the use or misuse of any recommendations. The information is provided on an "as is" basis without warranties of any kind. Users are responsible for determining the suitability of any recommendations for the user’s particular research. Any recommendations provided by Revvity should not be considered a substitute for a user’s own professional judgment.
Tech notes
- LANCE Ultra SET7/9 Histone H3-Lysine N-methyltranferase Assay. Assay optimization to measure mono-methylation of a biotinylated Histone H3 peptide at lysine 4 by SET7/9 enzyme.
- LANCE Ultra p300 Histone H3-Lysine Acetyltransferase Assay. Assay optimization to measure acetylation of a biotinylated Histone H3 peptide at lysine 9 by p300 enzyme.
- LANCE Ultra G9a Histone H3-Lysine N-methyltransferase Assay. Assay optimization to measure di-methylation of a biotinylated Histone H3 peptide at lysine 9 by G9a enzyme.
- LANCE Ultra SIRT1 Histone H3-Lysine 4 Deacetylase Assay. Assay optimization to measure deacetylation of a biotinylated Histone H3 peptide at lysine 4 by SIRT1 enzyme.
- LANCE Ultra HDAC1 Histone H3-Lysine 27 Deacetylase Assay. Assay optimization to measure deacetylation of biotinylated Histone H3 peptide at lysine 27 by HDAC1 enzyme.
- LANCE Ultra SIRT1 p53 Lysine 382 Deacetylase Assay. Assay optimization to measure deacetylation of biotinylated p53 peptide at lysine 382 by SIRT1 enzyme.
- LANCE Ultra JMJD2C Histone H3-Lysine 9 Demethylase Assay. Assay optimization to measure demethylation of biotinylated Histone H3 peptide at lysine 9 by JMJD2C enzyme.
- LANCE Ultra JMJD3 Histone H3-Lysine 27 Demethylase Assay. Assay optimization to measure demethylation of biotinylated Histone H3 peptide at lysine 27 by JMJD3 enzyme.
- LANCE Ultra JMJD2A Histone H3-Lysine 36 Demethylase Assay. Assay optimization to measure demethylation of biotinylated Histone H3 peptide at lysine 36 by JMJD2A enzyme.
- LANCE Ultra EZh3 Histone H3-Lysine 27 N-methyltransferase Assay. Assay optimization to measure methylation of biotinylated Histone H3 peptide at lysine 27 by EZh3 enzyme.
- Poster: LANCE Ultra and AlphaLISA™ p300, G9a, and SET7/9 Assays. Assay optimization to measure Histone H3K4 Methyltransferases & H3K9 Methyl- and Acetyltransferases
- Poster: Development of Homogeneous Proximity Assays for JMJD2A/2C Histone Demethylases.
Custom reagents and custom assay development at Revvity
Revvity offers custom Europium labeling and ULight dye labeling services as well as custom assay development. If you are interested in custom services, please contact our custom teams:
Custom Labeling and Conjugation Services
Custom Assay Development Services




























