

HTRF Human & Mouse Phospho-YAP (Ser127) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points


HTRF Human & Mouse Phospho-YAP (Ser127) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points






The phospho-YAP (Ser127) assay enables the cell-based quantitative detection of phosphorylated YAP on Ser 127 as a readout of the Hippo-YAP pathway.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Cell Signaling |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |
The phospho-YAP (Ser127) assay enables the cell-based quantitative detection of phosphorylated YAP on Ser 127 as a readout of the Hippo-YAP pathway.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).



HTRF Human & Mouse Phospho-YAP (Ser127) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points



HTRF Human & Mouse Phospho-YAP (Ser127) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points



Product information
Overview
The Phospho-YAP (Ser127) cellular assay is ideal for detecting and quantifying YAP phosphorylated on Serine 127 as a readout of the Hippo-YAP pathway. With its central mediator role in the Hippo Pathway, YAP is an important target for oncological disease studies.
Specifications
| Application |
Cell Signaling
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Lysis Buffer Compatibility |
Lysis Buffer 1
Lysis Buffer 4
Lysis Buffer 5
|
| Molecular Modification |
Phosphorylation
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Phosphoproteins
|
| Target Species |
Human
Mouse
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
NASH/Fibrosis
|
| Unit Size |
500 Assay Points
|
Video gallery

HTRF Human & Mouse Phospho-YAP (Ser127) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points

HTRF Human & Mouse Phospho-YAP (Ser127) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points

Citations
How it works
Phospho-YAP (Ser127) assay principle
The Phospho-YAP (Ser127) assay measures YAP when phosphorylated at Ser127. Contrary to Western Blot, the assay is entirely plate-based and does not require gels, electrophoresis or transfer. The Phospho-YAP (Ser127) assay uses 2 labeled antibodies: one with a donor fluorophore, the other one with an acceptor. The first antibody is selected for its specific binding to the phosphorylated motif on the protein, the second for its ability to recognize the protein independent of its phosphorylation state. Protein phosphorylation enables an immune-complex formation involving both labeled antibodies and which brings the donor fluorophore into close proximity to the acceptor, thereby generating a FRET signal. Its intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of phosphorylated protein present in the sample, and provides a means of assessing the protein's phosphorylation state under a no-wash assay format.

Phospho-YAP (Ser127) 2-plate assay protocol
The 2 plate protocol involves culturing cells in a 96-well plate before lysis then transferring lysates to a 384-well low volume detection plate before adding phospho-YAP (Ser127) HTRF detection reagents. This protocol enables the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored.

Phospho-YAP (Ser127) 1-plate assay protocol
Detection of Phosphorylated YAP (Ser127) with HTRF reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, stimulation and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS designed protocol enables miniaturization while maintaining robust HTRF quality.

Assay validation
Compatibility of the HTRF phospho-YAP(Ser127) assay with various cell lines
Human (HEK293, HEK293 A, U-2 OS, HeLA, breast cancer cells, MCF 10A) and murine (NIH 3T3) cells were plated at 100,000 cells/ well in a 96 well plate in serum-deprived cell culture medium, and incubated for 24h at 37°C, 5% CO2. Medium was then removed and cells were lysed with 50 µL of lysis buffer for 30min at RT under gentle shaking. 16 µL of lysate was transferred into a 384-well sv white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF phospho-YAP Ser127 detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation

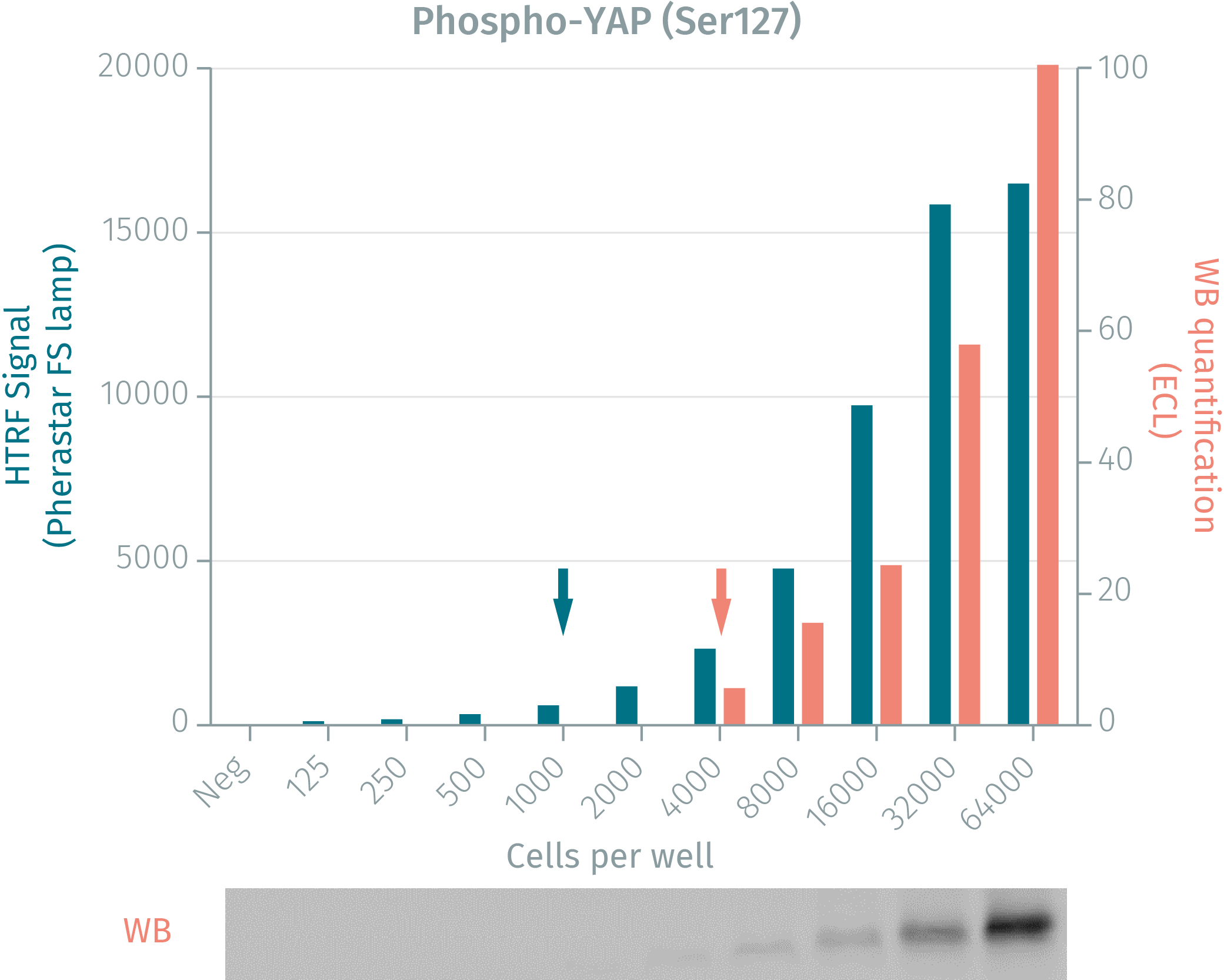
HTRF assay vs Western Blot using phospho-YAP cellular assay
Human breast cancer cells were grown in a T175 flask at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 48 h. After medium removal, the cells were lysed with 3 mL of supplemented lysis buffer for 30 min at room temperature. Soluble fractions were then collected after a 10 min centrifugation. Serial dilutions of the cell lysate were performed in the supplemented lysis buffer, then 16 µL of each dilution were dispensed and analyzed side-by-side by Western Blot and by HTRF. The HTRF phospho YAP assay is at least 4-fold more sensitive than the Western Blot. Using HTRF, 1,000 cells are sufficient for minimal signal detection while 4,000 cells are needed for a Western Blot signal.
Serum dose-response measured by the HTRF phospho-YAP cellular assay
100,000 HEK 293A cells were plated in 96-well plate in serum-deprived cell culture medium, and incubated for 24h, at 37°C, 5% CO2. Increasing concentrations of serum were added for 1h. After cell culture medium removal, cells were lysed with 50 µL of lysis buffer for 30min at RT under gentle shaking. 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well sv white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF phospho-YAP detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation. Stimulation with increasing concentrations of serum induces a decrease in YAP phosphorylation.

Kinetic of serum stimulation on phospho YAP
100,000 of the HEK293A were plated in 96 well plate in serum-deprived cell culture medium, and incubated for 24h, at 37°C - 5% CO2. Serum was added for different times. After cell culture medium removal, cells were lysed with 50 µL of lysis buffer for 30 min at RT under gentle shaking. 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well sv white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF phospho-YAP detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation. Maximum phosphorylation is obtained after a 1 hour stimulation with serum.

Simplified pathway
Hippo-YAP cell signaling active pathway
The Hippo/YAP pathway regulates organ size by playing a role in the balance between proliferation & apoptosis. This pathway is involved in mechanical and cytoskeletal signal transduction. The Hippo/YAP pathway is activated by numerous stimuli, such as cell attachment, high cell density, mechanical tension, or in the absence of growth factors. The activation of this pathway first activates MTS kinase, which in turn phosphorylates Lats kinases. YAP is then phosphorylated on Serine 127, leading to its cytoplasmic retention and eventually to its degradation by the proteasome machinery. Thus phosphorylated YAP represents the inactivated form of the protein. YAP/TAZ mutations have been reported in certain types of cancer (e.g. breast, lung, ovary, and colon).

Hippo-YAP cell signaling inactive pathway
The Hippo/YAP pathway regulates organ size by playing a role in the balance between proliferation & apoptosis. In addition this pathway is involved in mechanical and cytoskeletal signal transduction. When the Hippo/YAP pathway is inactivated, YAP/TAZ accumulates in the nucleus and induces the transcription of genes involved in cell proliferation. In addition to its properties and oncogene potential, some mutations in the Hippo/Yap pathway confer an overgrowth phenotype, visible on organ size. Finally, the dysregulation of the Hippo/yap pathway confers self-regenerative properties on cancer cells. (Cordenonsi. et al Cell 2011, Pan D. et al Genes & Dev. 2007, Pan D. et al Developmental Cell 2010)

Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
Discover the versatility and precision of Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) technology. Our HTRF portfolio offers a...


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























