

HTRF Streptavidin Tb-Conjugate, 5,000 Assay Points

HTRF Streptavidin Tb-Conjugate, 5,000 Assay Points




Tb cryptate-labeled Streptavidin for capturing biotinylated proteins, peptides, antibodies, small molecules, nucleic acids....
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Protein-Protein Interaction |
Tb cryptate-labeled Streptavidin for capturing biotinylated proteins, peptides, antibodies, small molecules, nucleic acids....
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.



HTRF Streptavidin Tb-Conjugate, 5,000 Assay Points



HTRF Streptavidin Tb-Conjugate, 5,000 Assay Points



Product information
Overview
Streptavidin has been labeled with Tb crypate. Biotin binds to Streptavidin with high affinity (Ka=1015M-1). The binding is rapid and stable, making it an ideal choice for use in a variety of assays such as enzyme assays, protein-protein binding assays and molecular biology assays.
Specifications
| Application |
Protein-Protein Interaction
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Product Group |
Fluorescent Reagent
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped Ambient
|
| Target Class |
Binding Assay
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Cardiovascular
Infectious Diseases
Inflammation
Metabolism/Diabetes
NASH/Fibrosis
Neuroscience
Oncology & Inflammation
Rare Diseases
|
| Unit Size |
5,000 Assay Points
|
Video gallery

HTRF Streptavidin Tb-Conjugate, 5,000 Assay Points

HTRF Streptavidin Tb-Conjugate, 5,000 Assay Points

How it works
Assay principle
In an HTRF interaction assay, one partner is labeled (directly or indirectly) with the donor, and the other with the acceptor (again, directly or indirectly). The intensity of the signal is proportional to the binding of the 2 partners. In the example shown here: Streptavidin-Tb cryptate binds to the biotinylated tagged partner A while partner B* binds to a specific Ab labeled with an HTRF acceptor. *partner B can also be biotinylated, tagged, Fc fused. In these cases, use the corresponding HTRF reagent (anti-Tag, anti-species, protA, Streptavidin) labeled with acceptor for the detection.

Assay protocol
The example on the right describes the protocol using a 20 µL final assay volume for detecting an interaction between a biotinylated-tagged partner A and a non-tagged partner B*. Dispense the 2 partners (10 µL), incubate, add Streptavidin-Tb cryptate (5 µL) and anti-partner B labeled with acceptor (5 µL), incubate and read. *partner B can also be tagged, Fc fused or directly labeled. In these cases use for the detection, the corresponding HTRF reagent (anti-Tag, anti species, protA, Streptavidin), labeled with donor.

Assay details
How do the number of tests relate to active moiety?
The average conjugate quantity per well reflects overall biological material content. Using the active moiety amount is generally preferred to the quantity of total conjugate. For Cryptate and d2 conjugates, the total conjugate amount equals that of the active moiety, since the molecular weight of the label is negligible. This is not the case for XL665 labeled entities for which the quantity of total conjugate will vary depending on the final molar ratio of the XL665 conjugate, however, the amount of active moiety, provided by Revvity, is constant and based on the number of tests ordered.
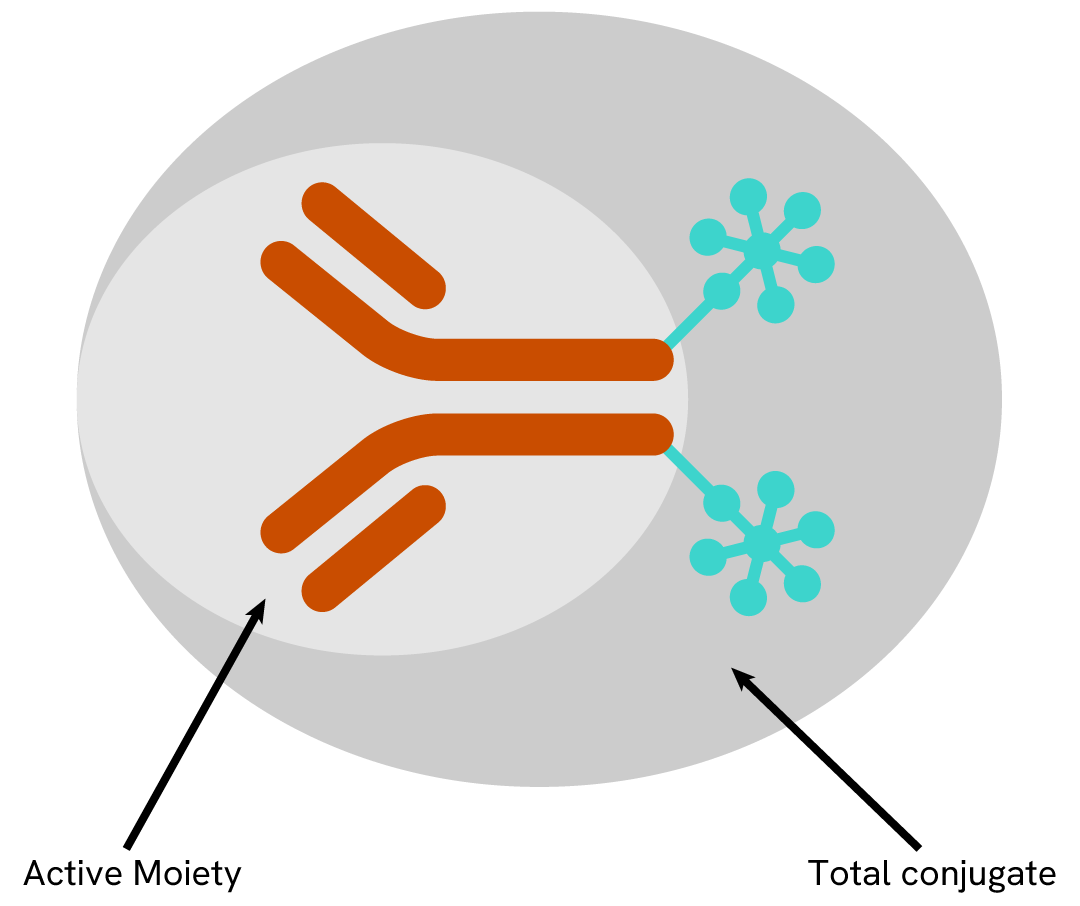
| Description | Active Moiety/5,000 tests |
|---|---|
| Streptavidin Tb | 4 µg |
Recommended quantities of Cryptate and XL665 conjugates
Cryptate conjugates must not be excessive in order to prevent reader saturation and an unacceptable level of background. In most cases, a cryptate concentration of 1 to 5nM is appropriate, and will generate 20,000 to 80,000 cps at 620 nm depending on the HTRF compatible reader used. The XL665 conjugate must match its assay counterpart as closely as possible in order for the maximum number of biomolecules to be tagged with the XL665 acceptor. Thus, to detect a tagged molecule at an assay concentration of 20nM, the concentration of anti-Tag-XL665 should be equimolar or higher.
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has transformed the field of immuno-oncology providing a novel approach to treating...


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























