

HTRF Human & Mouse Phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points


HTRF Human & Mouse Phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points






The phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) kit enables the cell-based quantitative detection of JNK protein phosphorylated at Thr183/Tyr185.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Cell Signaling |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |
The phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) kit enables the cell-based quantitative detection of JNK protein phosphorylated at Thr183/Tyr185.



HTRF Human & Mouse Phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points



HTRF Human & Mouse Phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points



Product information
Overview
Based on our homogeneous and robust HTRF technology, the Phospho-JNK assay kit is designed for detecting and studying activated JNK when phosphorylated at Thr183 and Tyr185 directly in whole cells. Using a streamlined mix and read, no wash protocol, this kit can be used from basic research to High Throughput drug screening.
Specifications
| Application |
Cell Signaling
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Lysis Buffer Compatibility |
Lysis Buffer 3
|
| Molecular Modification |
Phosphorylation
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Phosphoproteins
|
| Target Species |
Human
Mouse
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Cardiovascular
Infectious Diseases
Metabolism/Diabetes
NASH/Fibrosis
Neuroscience
Oncology & Inflammation
|
| Unit Size |
500 assay points
|
Video gallery

HTRF Human & Mouse Phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points

HTRF Human & Mouse Phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points

How it works
Phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) assay principle
The phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) assay measures JNK when phosphorylated at Thr183/Tyr185. Contrary to Western Blot, the assay is entirely plate-based and does not require gels, electrophoresis or transfer. The phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) assay uses 2 labeled antibodies: one with a donor fluorophore, the other one with an acceptor. The first antibody is selected for its specific binding to the phosphorylated motif on the protein, the second for its ability to recognize the protein independent of its phosphorylation state. Protein phosphorylation enables an immune-complex formation involving both labeled antibodies and which brings the donor fluorophore into close proximity to the acceptor, thereby generating a FRET signal. Its intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of phosphorylated protein present in the sample, and provides a means of assessing the proteins phosphorylation state under a no-wash assay format.

Phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) 2-plate assay protocol
The 2 plate protocol involves culturing cells in a 96-well plate before lysis then transferring lysates to a 384-well low volume detection plate before adding phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) HTRF detection reagents. This protocol enables the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored.

Phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) 1-plate assay protocol
Detection of Phosphorylated JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) with HTRF reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, stimulation and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS designed protocol enables miniaturization while maintaining robust HTRF quality.

Assay validation
HTRF phospho-JNK assay compared to Western Blot
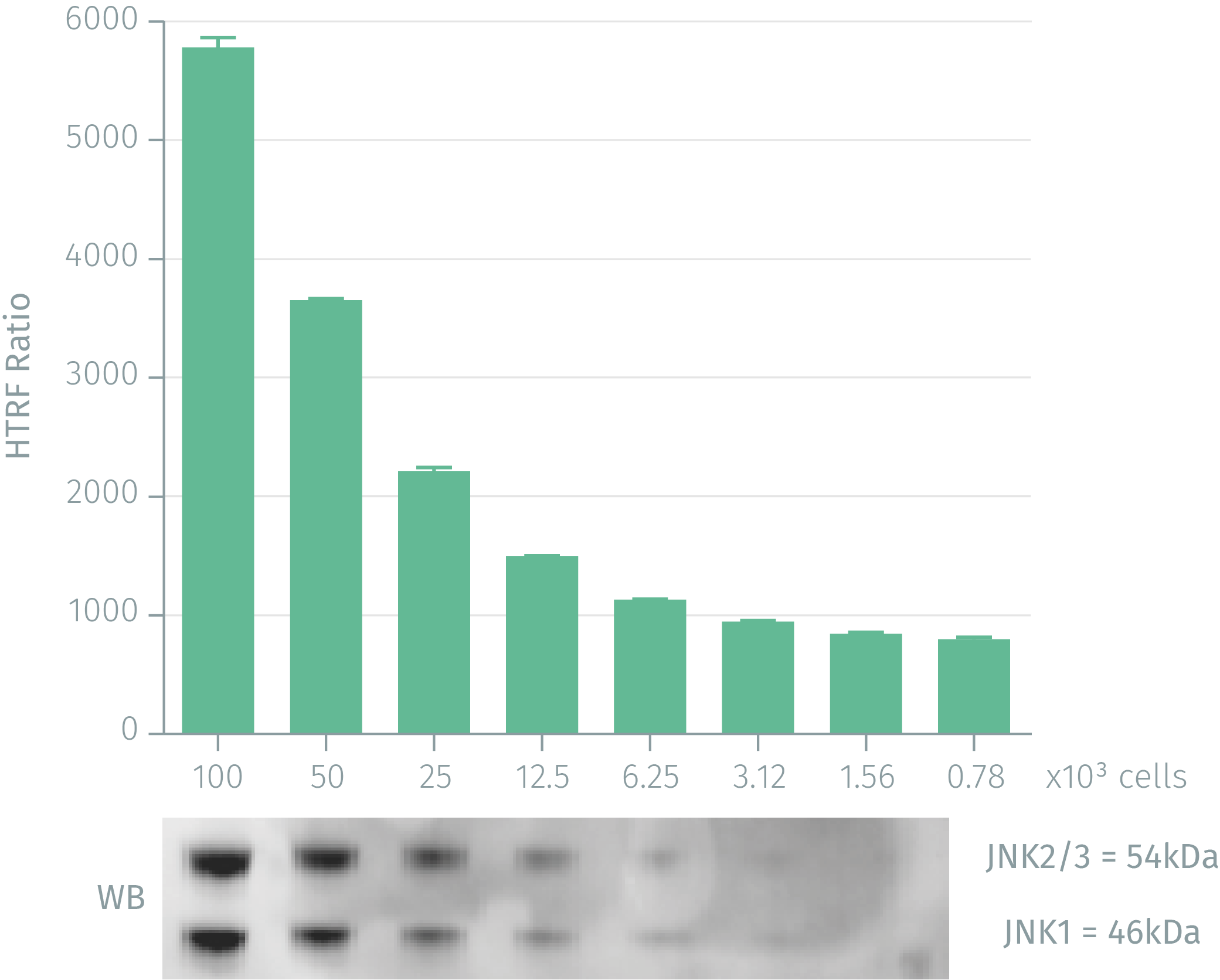
HEK293 cells were cultured for 2 days. Stimulation was done with 500nM anisomycin for 30 min. Following cell lysis, soluble supernatants were collected by centrifuging for 10 minutes. Equal amounts of lysates were used for a side by side comparison of WB and HTRF. 100,000 cells corresponds to 16 µg of total protein. HTRF phospho-JNK assay shows the same level of sensitivity as Western Blot: 3,125 cells were needed for the two technologies.
Anysomycin dose-response on NIH-3T3 cells
Murine NIH-3T3 cells (100,000 cells/well) were stimulated for 30 minutess at 37°C with various concentrations of anisomycin. After a 30 minutes lysis incubation time, phosphorylated JNK was measured using the two-plate assay protocol of the Phospho-JNK assay.

Inhibition effect of IL-1Ra on Jurkat cells stimulated with IL-1ß
Suspended Jurkat cells (80,000 cells/well) were incubated for 10 min at 37°C with various concentrations of IL-1Ra (IL-1 receptor antagonist). 10nM IL-1ß (agonist) were then added and incubated for 10 minutes. After a 30 minutes lysis incubation time, inhibition of JNK phosphorylation was measured using the Phospho-JNK assay. The asssay was done using the one-plate assay protocol.

Simplified pathway
Simplified Pathway for Phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) assay kit
C-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs), also called Stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs) are members of the MAPK family. JNKs are activated by a variety of environmental stresses, inflammatory cytokines and, in some instances, by growth factors and GPCR agonists. Activated JNK translocates to the nucleus where it can phosphorylate multiple transcription factors, such as c-Jun, ATF-2 and p53. The JNK pathway regulates numerous cellular responses including proliferation, survival & apoptosis, neural development, inflammation, metabolism and DNA repair.

Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
Obesity is a complex condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation, posing significant health and socioeconomic challenges...
Loading...


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























