
HTRF Phospho-VAV1 (Tyr174) Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points
HTRF Phospho-VAV1 (Tyr174) Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points


This HTRF kit enables the cell-based quantitative detection of human phosphorylated VAV1 (Vav proto-oncogene 1) at Tyr174, as a readout of the signaling activity of adaptive immunity receptors, specifically T-cell receptor (TCR) and B-cell receptor (BCR).
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Cell Signaling |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |
This HTRF kit enables the cell-based quantitative detection of human phosphorylated VAV1 (Vav proto-oncogene 1) at Tyr174, as a readout of the signaling activity of adaptive immunity receptors, specifically T-cell receptor (TCR) and B-cell receptor (BCR).
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).


HTRF Phospho-VAV1 (Tyr174) Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points


HTRF Phospho-VAV1 (Tyr174) Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points


Product information
Overview
VAV1, also known as Vav proto-oncogene 1, is a protein that plays a crucial role in cellular signaling and immune responses. It is primarily expressed in cells of hematopoietic origin, including T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells.
VAV1 acts as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for the Rho family GTPases, including Rac1, Rac2, and RhoA. VAV1 activates these GTPases by promoting the exchange of GDP (guanosine diphosphate) for GTP (guanosine triphosphate) on these enzymes. Through this mechanism, VAV1 is an important regulator of essential cellular processes such as cytoskeletal rearrangement, cell adhesion, proliferation, and migration.
In immune cells, VAV1 is an important intermediary in the downstream signaling of specialized antigen receptors, including T cell receptors (TCRs) and B cell receptors (BCRs). As such, VAV1 has been implicated in several diseases, including the autoimmune disorders systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In these conditions, abnormal VAV1 signaling can contribute to immune dysregulation and inflammation. Additionally, VAV1 is involved in certain types of cancer, where aberrant activation can promote cellular transformation and metastasis.
Specifications
| Application |
Cell Signaling
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Molecular Modification |
Phosphorylation
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Phosphoproteins
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Unit Size |
10,000 Assay Points
|
How it works
HTRF Human Phospho-Y174 VAV1 assay principle
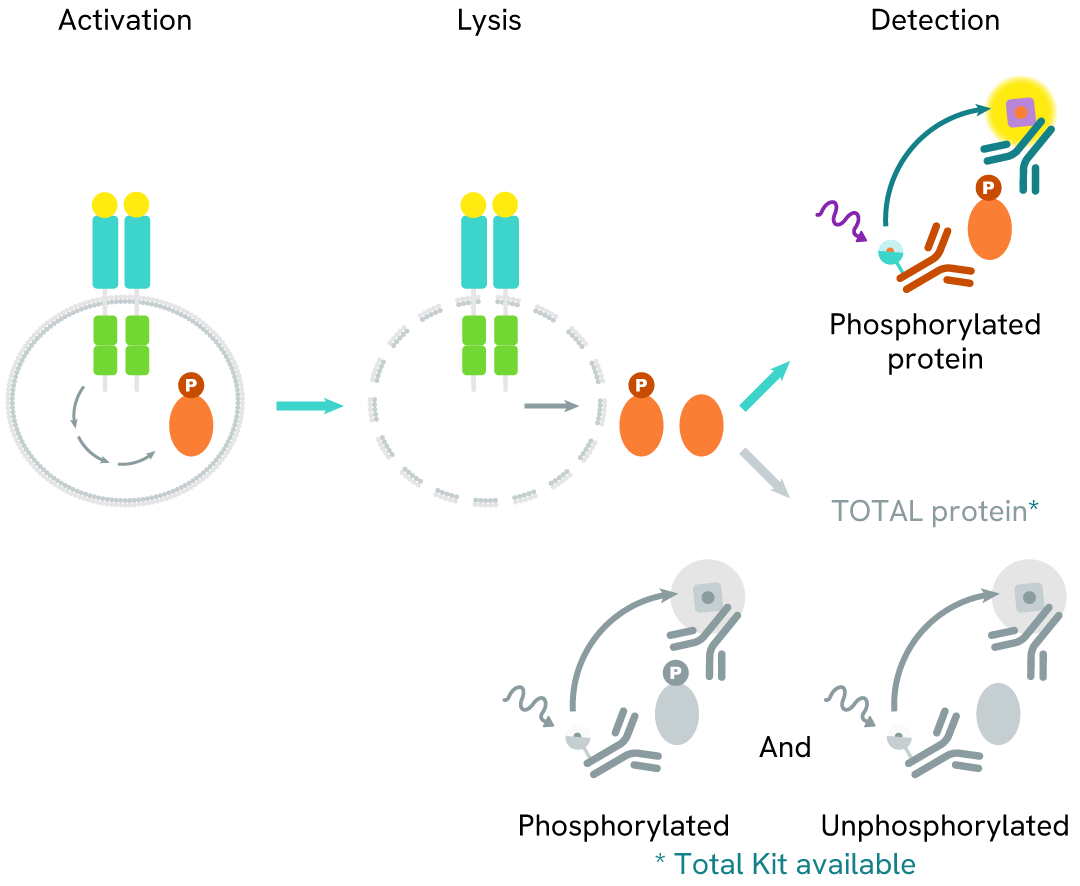
The Phospho-Y174 VAV1 assay measures VAV1 when phosphorylated at Tyr174. Unlike Western Blot, the assay is entirely plate-based and does not require gels, electrophoresis, or transfer. The assay uses 2 antibodies, one labeled with a donor fluorophore and the other with an acceptor. The first antibody was selected for its specific binding to the phosphorylated motif on the protein, the second for its ability to recognize the protein independently of its phosphorylation state. Protein phosphorylation enables an immune-complex formation involving both labeled antibodies, and which brings the donor fluorophore into close proximity to the acceptor, thereby generating a FRET signal. Its intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of phosphorylated protein present in the sample, and provides a means of assessing the protein's phosphorylation state under a no-wash assay format.

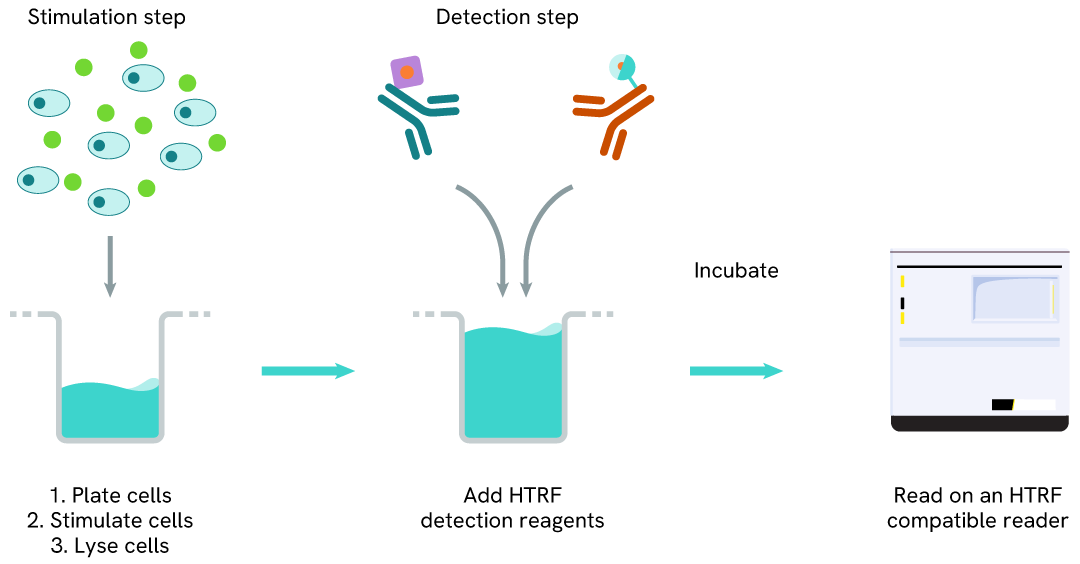
HTRF Human Phospho-Y174 VAV1 one-plate assay protocol
Detection of Phospho-Y174 VAV1 with HTRF reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, stimulation, and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS designed protocol enables miniaturization while maintaining robust HTRF quality.
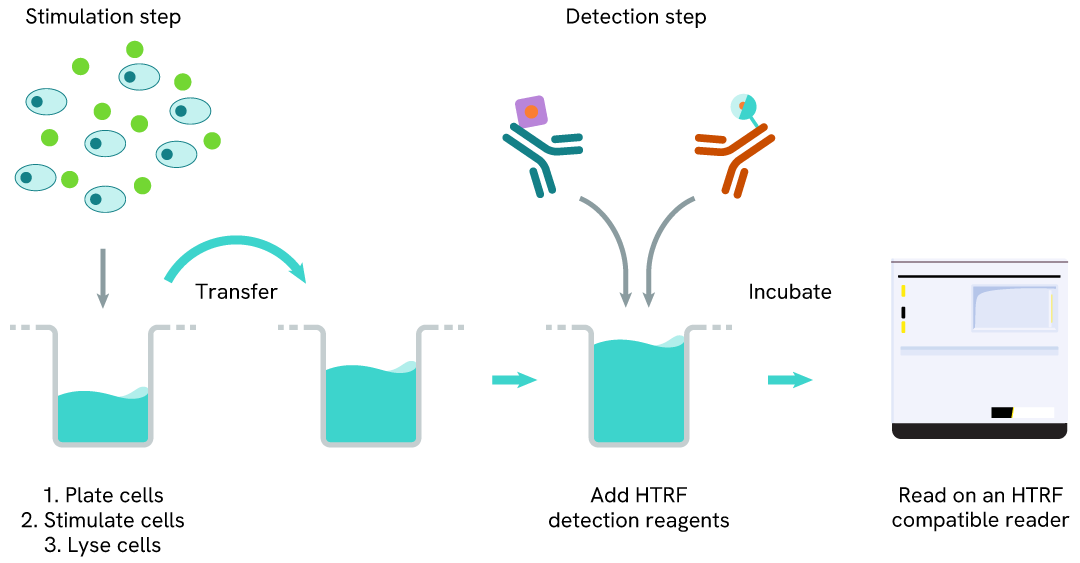
HTRF Human Phospho-Y174 VAV1 two-plate assay protocol
The two-plate protocol involves culturing cells in a 96-well plate before lysis, then transferring lysates into a low volume detection plate (either HTRF 384-lv or 96-lv plate) before the addition of HTRF Phospho-Y174 VAV1 detection reagents. This protocol enables the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored.
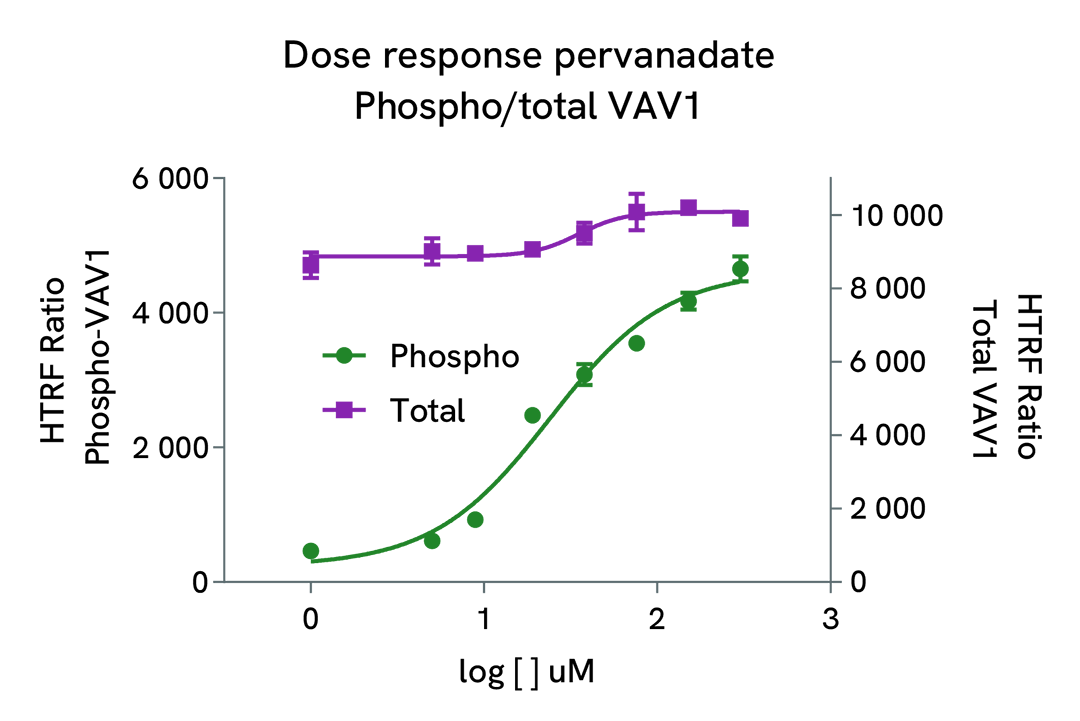
Assay validation
Dose-response of the HTRF Phospho/Total VAV1 assay on cells treated with pervanadate
Jurkat cells (100,00 cells/well) were plated at 25 µL in a 96-well plate in complete culture medium and treated with 5 µL of increasing concentrations of pervanadate diluted in media, and incubated for 30 min at 37ºC, 5% CO2.
The cells were lysed with 10 µL of 4x lysis buffer #1 for 45 minutes at RT. After lysis, 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a low volume white microplate before the addition of 2 µL each of the donor and acceptor HTRF PVAV1 or Total VAV1 detection reagents. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation.
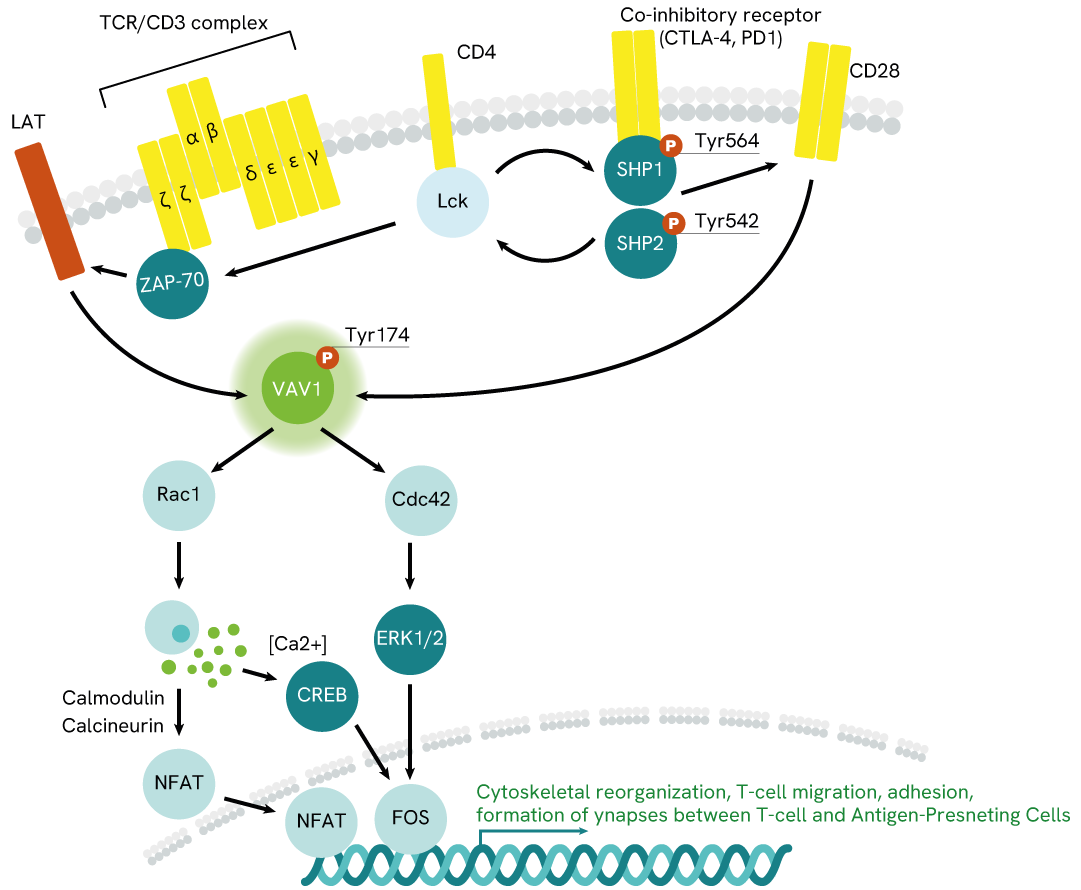
Simplified pathway
VAV1 signaling pathway
Conformational changes on the intracellular portion of the receptor promotes the recruitment of tyrosine kinases Lck and ZAP-70, which phosphorylate its tyrosine domains as well as other neighboring signaling proteins, like LAT (Linker for Activation of T cells).
Phosphorylated LAT then recruits VAV1 and promotes its phosphorylation and activation. Phospho-VAV1 goes on to catalyze GDP/GTP exchanges on proteins of the Rho family, especially Rac1 and Cdc42. These Rho proteins then trigger a cascade of downstream signaling events which include sending transcription factors to the nucleus to promote cytoskeletal reorganization, cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation, as well as other immune-cell mechanisms promoting the elimination of pathogens or compromised cells.
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
HTRF: unfamiliar territory?
This technical brochure reviews the general principles of HTRF™ and the associated Tag-lite™ technology...
Your guide for improving cell signaling assay performance
This complete Revvity guide provides you with all the tools you need to...


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























