
HTRF dsRNA (IVT) Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points

HTRF dsRNA (IVT) Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points




The HTRF dsRNA (IVT) kit is intended for the simple and rapid quantification of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) particles in samples resulting from In Vitro Transcription (IVT) of mRNA. It offers a fast and homogeneous alternative to ELISA or immunoblot.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Protein Quantification |
| Sample Volume | 10 µL |
The HTRF dsRNA (IVT) kit is intended for the simple and rapid quantification of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) particles in samples resulting from In Vitro Transcription (IVT) of mRNA. It offers a fast and homogeneous alternative to ELISA or immunoblot.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).


HTRF dsRNA (IVT) Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points


HTRF dsRNA (IVT) Detection Kit, 10,000 Assay Points


Product information
Overview
In Vitro Transcription or IVT is molecular biology technique used to synthesize RNA sequence from a DNA template. During that process, a DNA template is incubated with RNA polymerase and ribonucleotides, resulting in RNA copies of the template.
While this process aims at producing single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) sequences, it is also prone to generating double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) contaminants. These can arise for different reasons (polymerase pausing, secondary structure formation, template contamination, etc) and are undesirable in the final product.
The end-goal therapeutic applications of IVT are mostly related to gene therapy and mRNA vaccine development or production, and in many cases IVT applications are parts of production processes for patient-intended products. One of the main concerns when running such processes is the QA/QC aspect of it as well as guaranteeing patient safety with the end results. For that reason, dsRNA is a contaminant to monitor with great attention and robust tools, as it is usually a strongly immunogenic molecule that can be picked up by multiple nucleic acid receptors of our innate immunity and trigger violent immune and inflammatory responses in patients. Rapid, convenient, and robust quantification of dsRNA is therefore required at multiple purification steps of the IVT process to ensure maximum elimination of that contaminant.
This HTRF dsRNA (IVT) Kit is intended for the robust detection of dsRNA in such IVT samples. It was developed with IVT applications specifically in mind offers a ready-to-use homogeneous alternative to traditional ELISA and Dot-blot approaches.
Specifications
| Application |
Protein Quantification
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
10 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target |
dsRNA
|
| Target Class |
Nucleic Acid
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Unit Size |
10,000 Assay Points
|
How it works
Principle of the HTRF dsRNA (IVT) assay
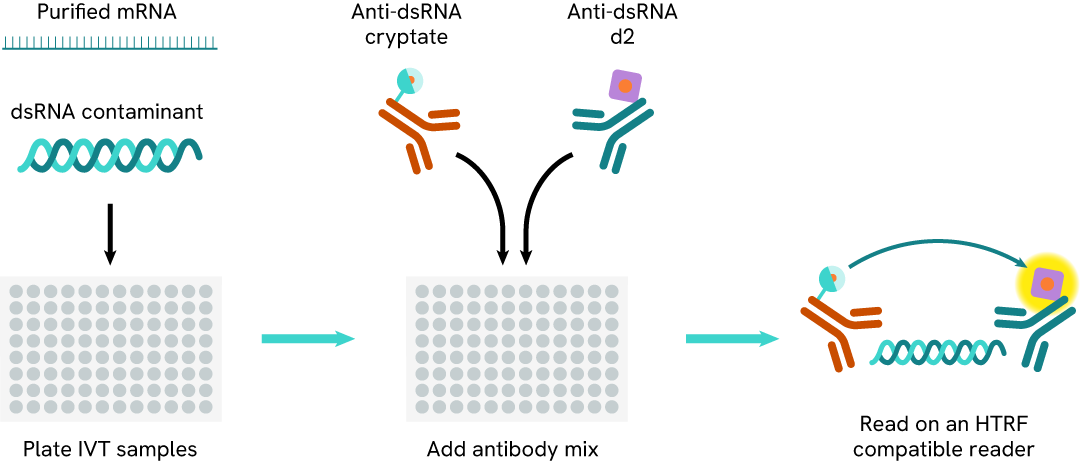
The dsRNA (IVT) assay measures dsRNA in samples. The assay uses two labeled antibodies: one coupled to a donor fluorophore, the other to an acceptor. In presence of dsRNA in a sample, the addition of these conjugates brings the donor fluorophore into close proximity with the acceptor, and thereby generates a FRET signal. Its intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of the dsRNA present in the sample in a no-wash assay format.

Protocol of the HTRF dsRNA (IVT) assay
The dsRNA (IVT) assay protocol, using a 384-well small volume white plate, is described on the right. 10 µL of sample or standard are dispensed directly into the detection plate for detection by HTRFTM reagents. The antibodies labeled with HTRF fluorophores were added before an overnight incubation. The assay can be run in up to a 1536-well format by simply resizing each addition volume proportionally.
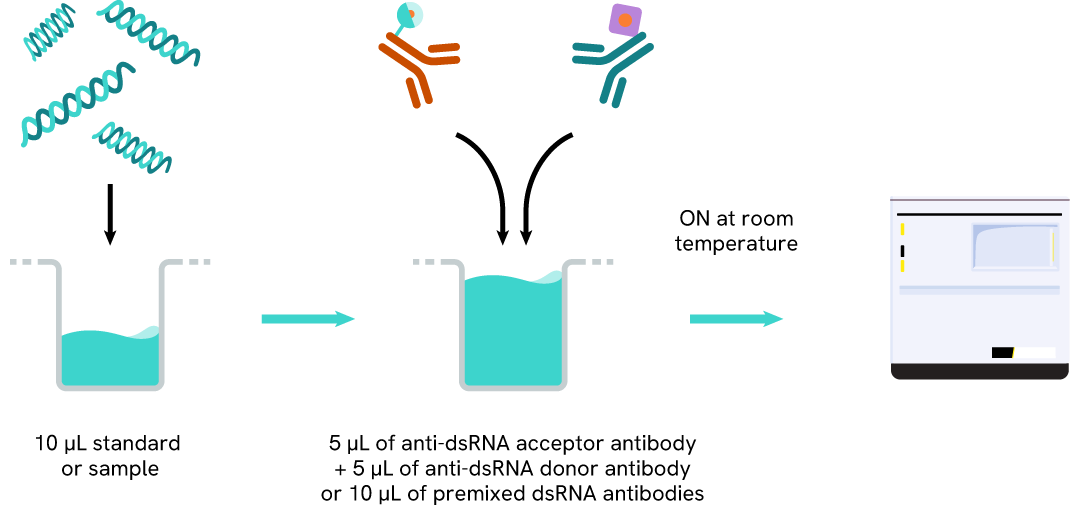
Assay details
dsRNA (IVT) assay details
| Sample size | 10 µL |
|---|---|
| Final assay volume | 20 µL |
| Kit components | frozen standard, frozen detection antibodies, buffers & Manual |
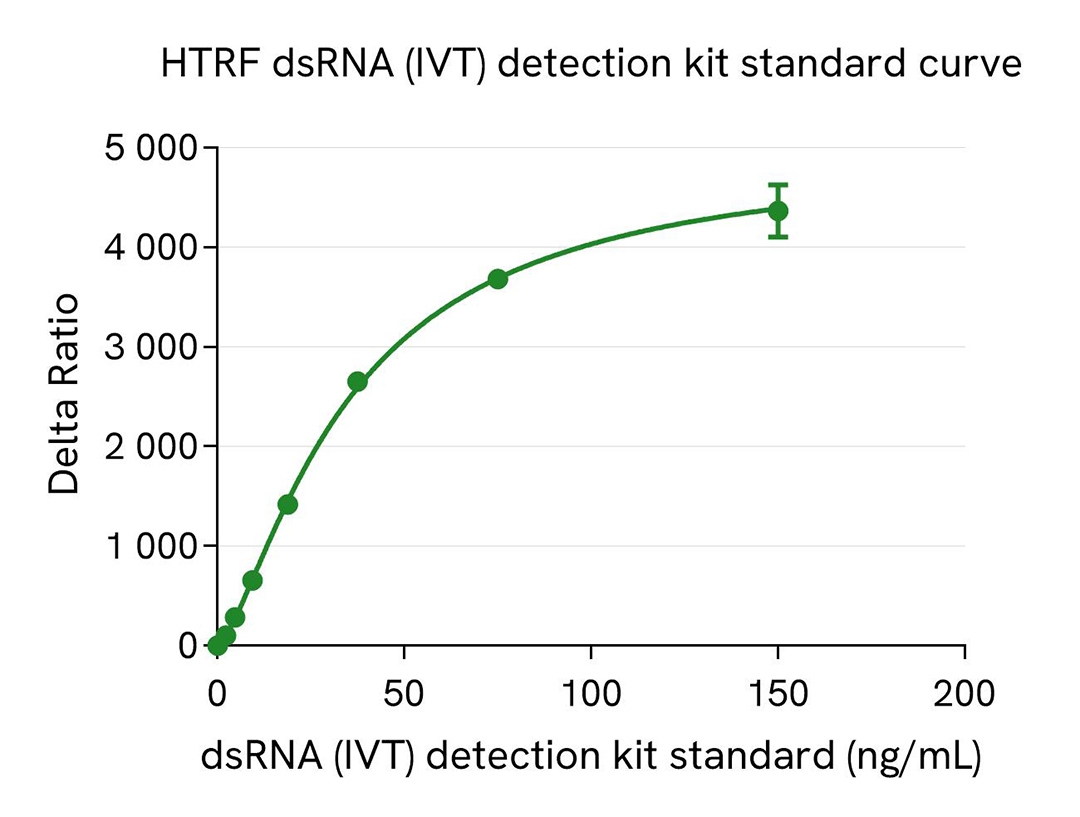
| LOD & LOQ (in Diluent) | 0,3 ng/mL & 0,5 ng/mL |
| Range | 0,5 – 150 ng/mL |
| Time to result | Overnight at RT |
| Nature of dsRNA detected | Natural dsRNA, Synthetic Poly I:C, N1-methyl pseudo-uridine incorporated-dsRNA |
| Length detectable | 35 to at least 1000 bp |
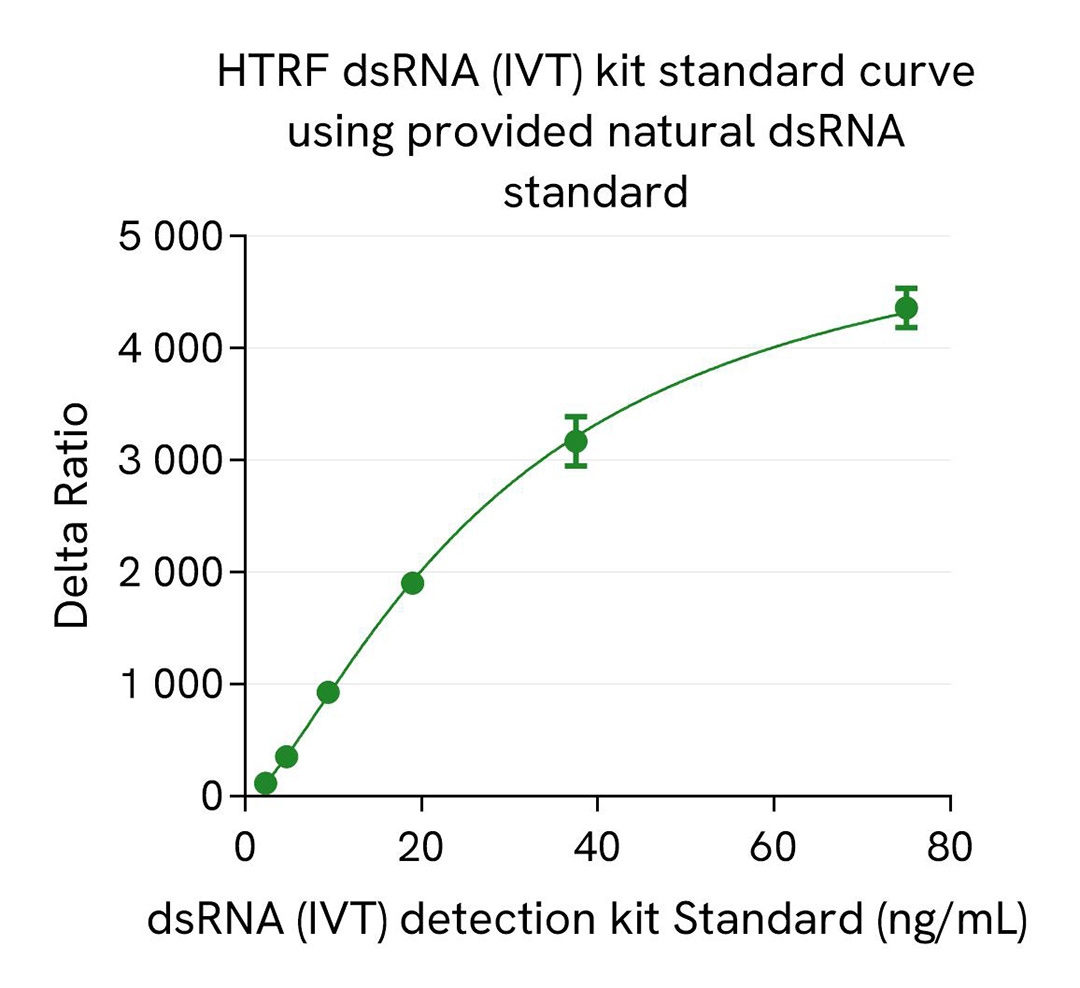
dsRNA (IVT) kit standard curve
Analytical performance
Intra-assay precision table
Each of the 3 samples was measured 24 times, and the % CV was calculated for each sample.
| Sample | Mean [dsRNA] (ng/mL) | CV |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 122 | 9% |
| 2 | 29 | 4% |
| 3 | 7,9 | 5% |
| Mean CV | 6% |
Inter-assay precision table
Each of the samples was measured in 3 independent experiments performed by different operators. The % CV was calculated for each sample.
| Sample | Mean [dsRNA] (ng/mL) | CV |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 141,1 | 11% |
| 2 | 37,8 | 4% |
| 3 | 9,5 | 3% |
| Mean CV | 6% |
Dilutional linearity table
Samples were generated from serial dilution of dsRNA in diluent#14. The excellent % of recovery obtained from these experiments shows the good dilution linearity of the assay (Dilution test acceptance criteria: 85-115%).
| Dilution Factor |
[dsRNA] Expected (ng/mL) |
[dsRNA] Measured (ng/mL) |
Dilution Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neat | - | 93,7 | 100% |
| 2 | 45 | 45,1 | 100% |
| 4 | 22,5 | 23,3 | 96% |
| 8 | 11,3 | 12,4 | 91% |
| 16 | 5,6 | 6,3 | 89% |
| 32 | 2,8 | 2,7 | 104% |
| Mean CV | 96% |
dsRNA (IVT) Kit cross-reactivity table
Cross reactivities were assessed using other reagents commonly present in mRNA samples during IVT production process, such as single strand RNA (ssRNA), DNA template (circular and fragments) or T7 polymerase. Titration of each reagent diluted in the kit diluent was performed using concentrations in line with what if found in IVT production processes.
For each reagent and concentration tested, 10 µL of each sample was transferred into a white detection plate (384 low volume), and 5 µL of each HTRF dsRNA (IVT) detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal (Delta Ratio) was recorded after overnight incubation at room temperature (22°C).
No detection signal was recorded using for any of the ssRNA, DNA Template and T7 polymerase samples in comparison with positive controls of dsRNA. In these assay conditions, the kit shows detection specificity for dsRNA over other tested IVT reagents.
| Sample | Reagents | Titration | Delta Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Positive controls |
Natural dsRNA kit Standard |
2,3 to 150 ng/mL |
132 to 4561 |
|
Natural dsRNA Sample of 142 bp (GFP N-term sequence) |
0,5 to 37,5 ng/ mL |
116 to 3423 | |
|
Samples tested for cross-reactivity |
ssRNA of 142 bp (same sequence than dsRNA sample) |
100 to 100 000 ng/mL |
No detection |
|
Circular DNA template |
40 to 2500 ng/mL |
No detection | |
|
Digested DNA template by DNase I (Fragments) |
40 to 2500 ng/mL | No detection | |
|
T7 polymerase (for enzymatic IVT reaction) |
0,5 to 500 U/mL | No detection |
dsRNA (IVT) Kit interference using other commonly used IVT reagents
To test for the absence of interference of this dsRNA (IVT) kit with other reagents commonly used in mRNA IVT process, a fixed concentration of a 142 bp natural dsRNA sample (50 ng/mL) was mixed with a 2000-folds more concentrated 142 bp ssRNA sample (10 µg/mL), digested DNA template (10 µg/mL) and 500 U/mL of T7 polymerase. A dsRNA sample at 50 ng/mL was used as reference control.
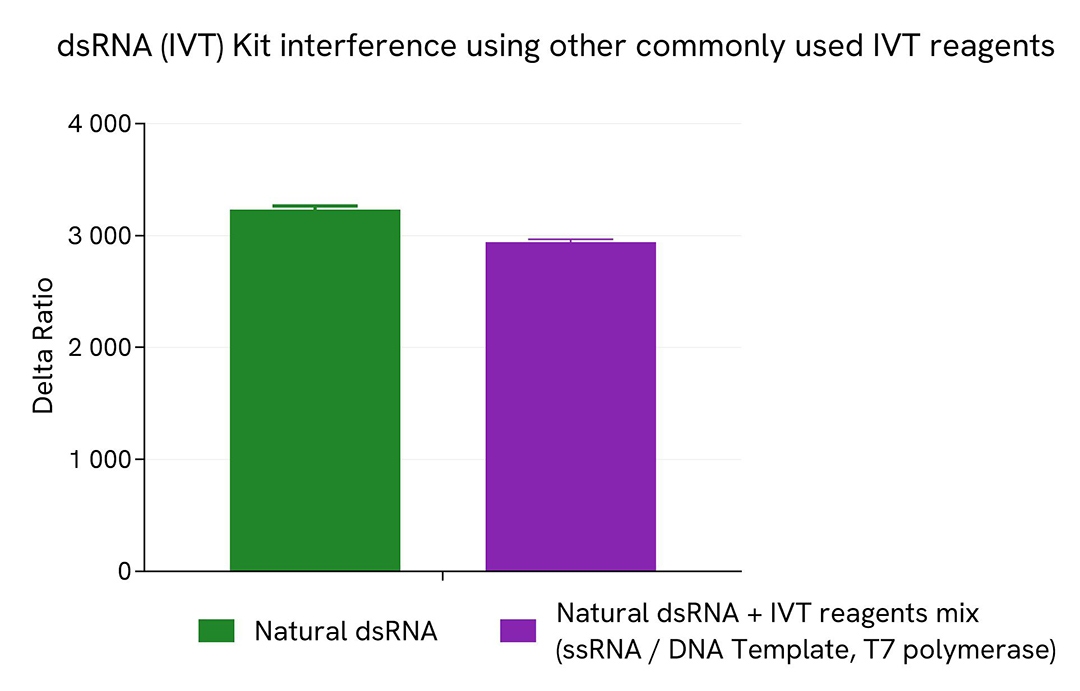
10 µL of each sample were plated in a 384sv white plate and 10 µL of HTRF (IVT) kit detection reagents mix were added. The HTRF signal (Delta Ratio) was recorded after overnight incubation at room temperature (22°C).
No significant change of HTRF signal was recorded between the natural dsRNA control and the dsRNA + IVT reagent mix, demonstrating the absence of interference from common reagents present in IVT samples.
Assay validation
Role of standard type in dsRNA sample measurement
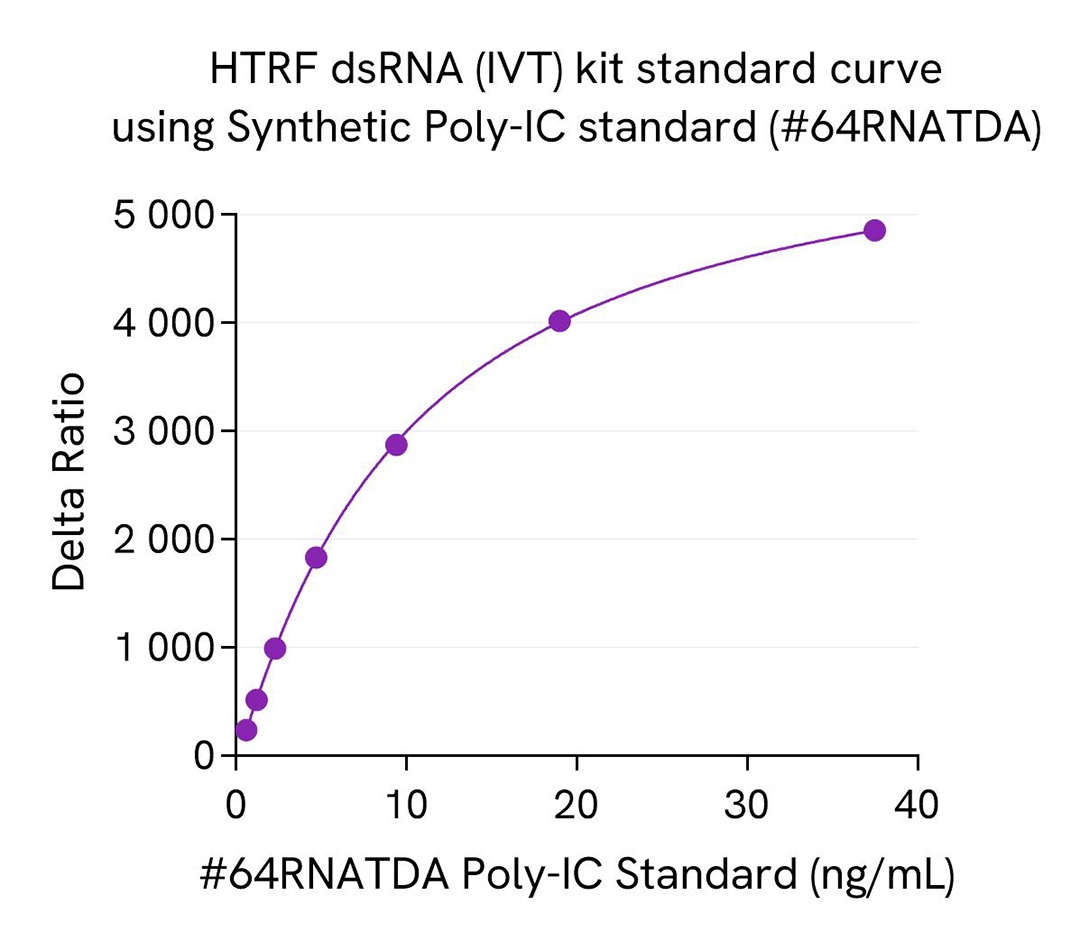
The HTRF dsRNA (IVT) kit includes a natural dsRNA standard for more relevant quantification of dsRNA in real IVT samples compared to synthetic Poly-IC standards, which are commonly used in Dot blot or ELISA dsRNA assays. A synthetic Poly IC standard, part of HTRF viral dsRNA kit (64RNAPEG), is also available as spare reagent (#64RNATDA) and is compatible with this HTRF dsRNA (IVT) kit.
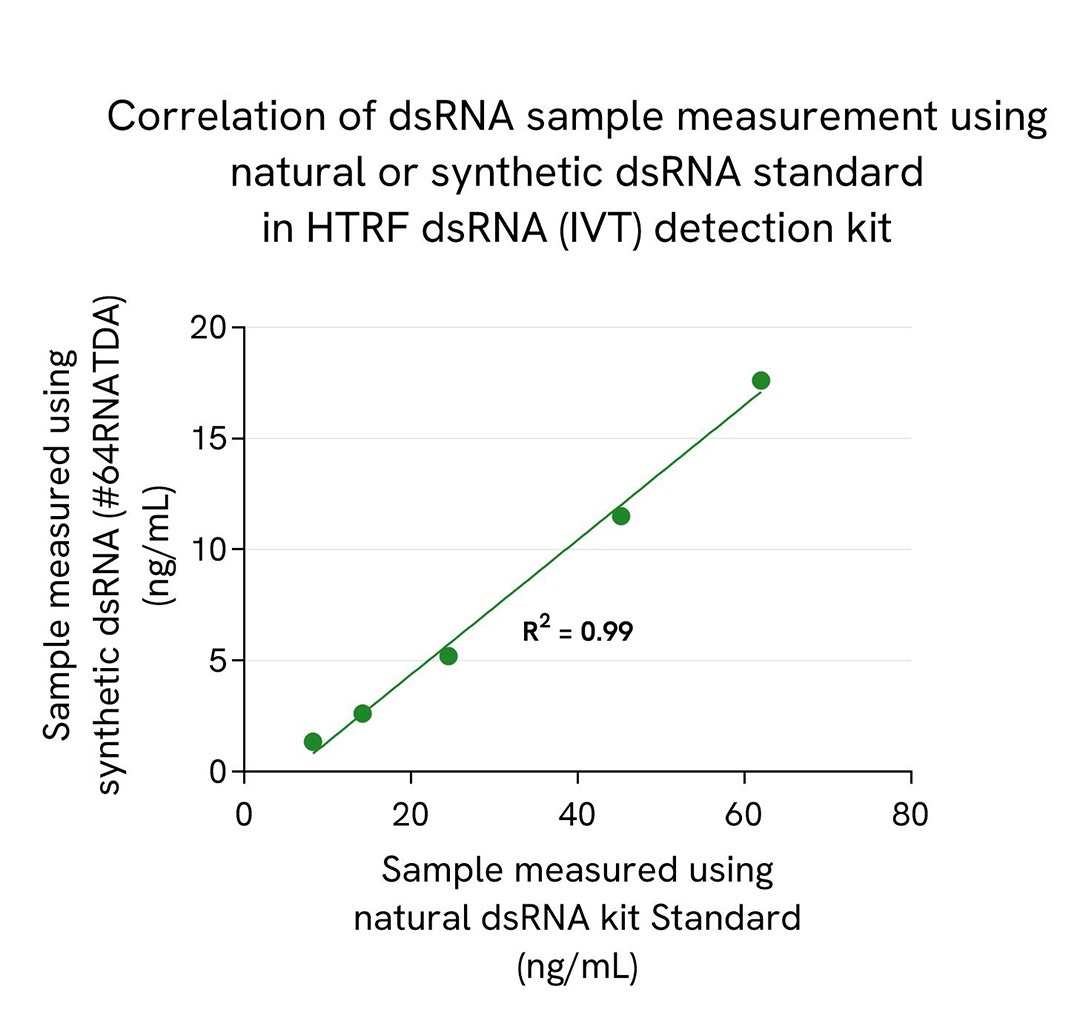
We present here standard curves using the natural dsRNA standard from the HTRF dsRNA (IVT) Kit and the synthetic Poly-IC standard (#64RNATDA) from the HTRF dsRNA (virology) Kit. The main result is a 4X higher sensitivity for Poly-IC synthetic standard compared to the dsRNA natural standard. This result is expected and reported in the literature as a consequence of different antibody affinities for natural and synthetic dsRNAs, which is especially true and published for anti-dsRNA gold standard antibodies. This difference of sensitivity between standards is key as it drastically affects the reading of samples when related to the resulting standard curves. The most accurate measurement of dsRNA in a sample is obtained when the standard used is in line with the sample, meaning that synthetic dsRNA standard generally introduce a bias when working with IVT samples that are based on natural nucleic acid.
To demonstrate dsRNA sample quantification correlation using both standards, a natural 100 bp dsRNA (Nterm of GFP protein sequence) was serially diluted in the kit diluent. 10 µL of each sample were added in a 384sv white plate, and 10 µL of HTRF dsRNA (IVT) detection reagents mix was added. The HTRF signal (Delta Ratio) was recorded after an overnight incubation at room temperature (22°C). dsRNA quantification was obtained by interpolating samples signals on each standard curves. Obtained concentrations using each natural and synthetic standard are plotted and presented in the correlation graph.
Results show perfect correlation of natural dsRNA sample quantification using natural dsRNA kit standard and synthetic poly-IC standard.
While the correlation between natural and synthetic dsRNA standard is assured, we still report a difference of 3,5-fold in dsRNA sample quantification between both standards. Due to that bias coming from the synthetic Poly-IC standard, dsRNA sample concentration is underestimated in that case.
different length of dsRNA detectable table
In IVT processes, dsRNA contaminants present themselves as an arrays of fragments of different length in bp. To assess the HTRF dsRNA (IVT) kit’s ability to detect these dsRNA fragment of various length, serial dilutions of different lengths of dsRNA were made in diluent 14. All fragments were generated from the N-term portion of GFP protein sequence.
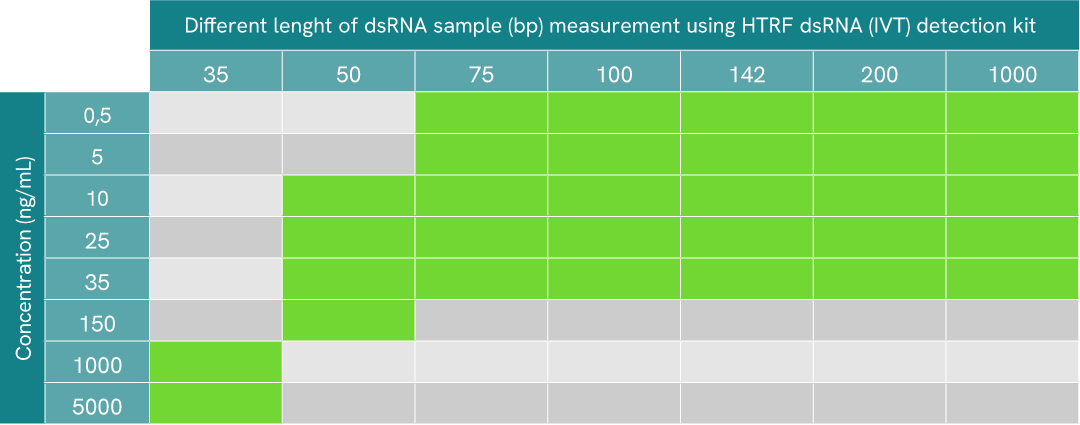
10 µL of each sample were plated in a 384sv white plate, and 10 µL of HTRF dsRNA (IVT) detection reagents mix were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after overnight incubation at room temperature (22°C).
For this specific sequence, results show that the detectable range of dsRNA fragment length goes from 35 to at least 1000 bp, where green boxes represent range of detection for each dsRNA length. As expected, detection and sensitivity are enhanced when dsRNA length increases, due to the repeat epitope-based detection of the assay.
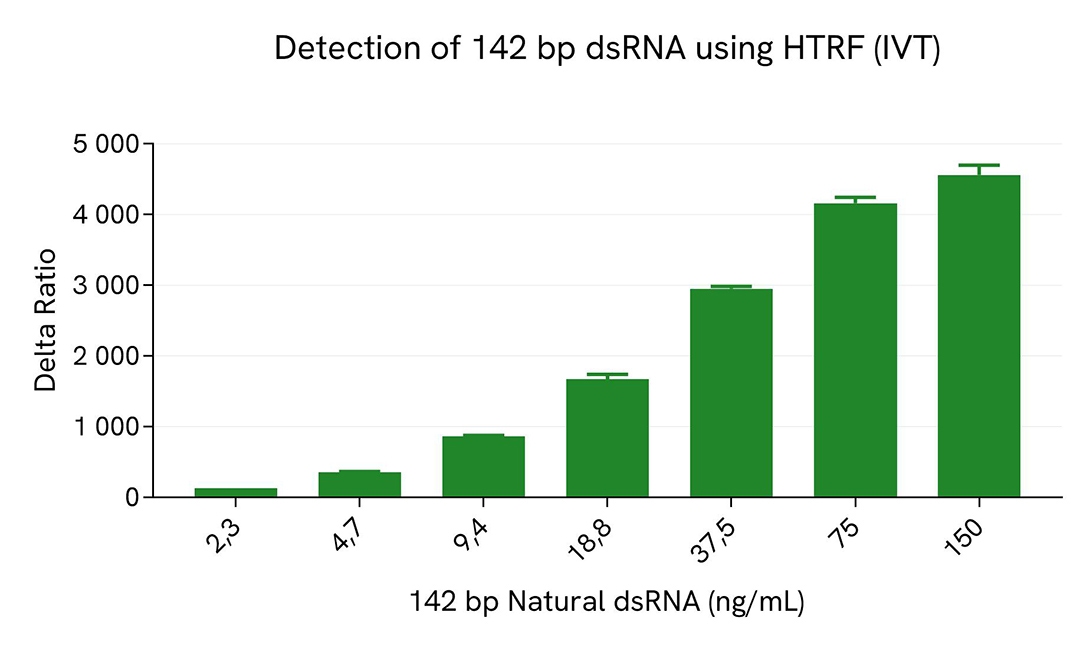
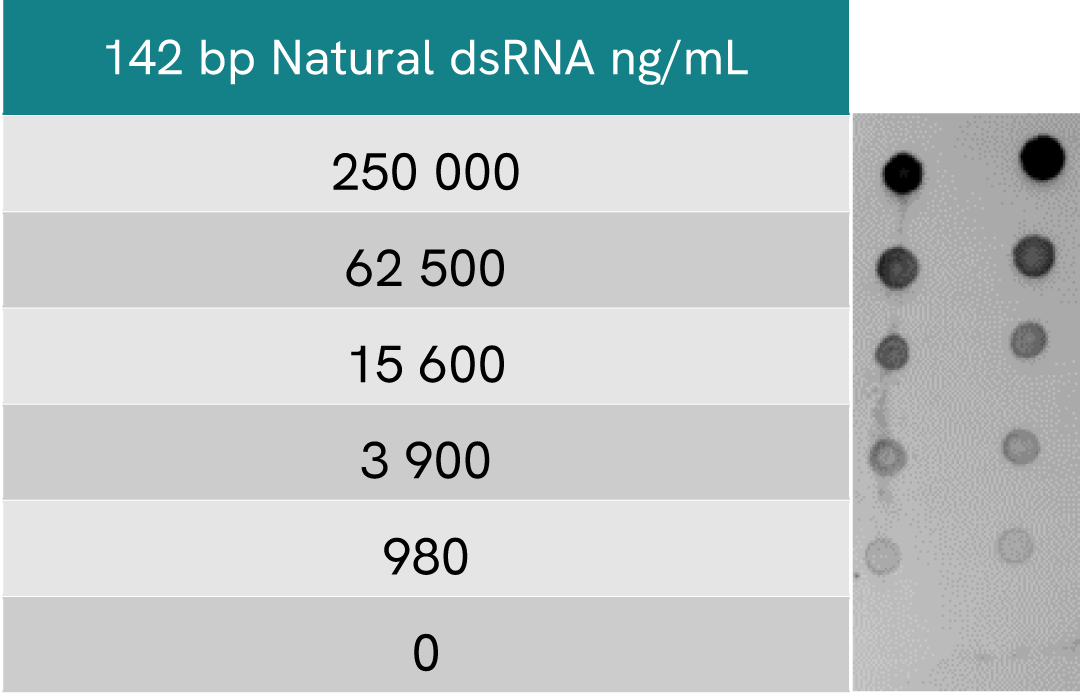
HTRF dsRNA (IVT) assay compared to Dot Blot
Dot blot assays are commonly used to detect dsRNA particles in samples resulting from In Vitro Transcription (IVT) of mRNA. A comparison between HTRF and Dot Blot was performed to assess the limit of sensitivity of each method.
For HTRF, serial dilutions of dsRNA were made using diluent 14, and 10 µL of each dilution were transferred into a low volume white microplate before the addition of 10 µL of Anti dsRNA detection reagents.
For Dot Blot assays, serial dilutions of the same dsRNA were blotted at 5 µl per drop.
After incubating with primary dsRNA-specific monoclonal J2 antibody and secondary HRP antibody, the membrane was treated with ECL reagent and revealed at 1 sec exposure.
A side-by-side comparison of Dot Blot and HTRF demonstrates that the HTRF assay is 400-fold more sensitive than the Dot Blot, at least under these experimental conditions.
Beyond this difference in sensitivity, it is worth noting than a Dot blot approach to dsRNA detection is generally more qualitative than quantitative.
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























