
Functional genomic screening with the Pin-point base editing platform
Base editing with the Pin-point platform provides precise, controlled changes in target sequences with lower potential for on- or off-target DNA damage and healthier cell outcomes, even in sensitive cell types.
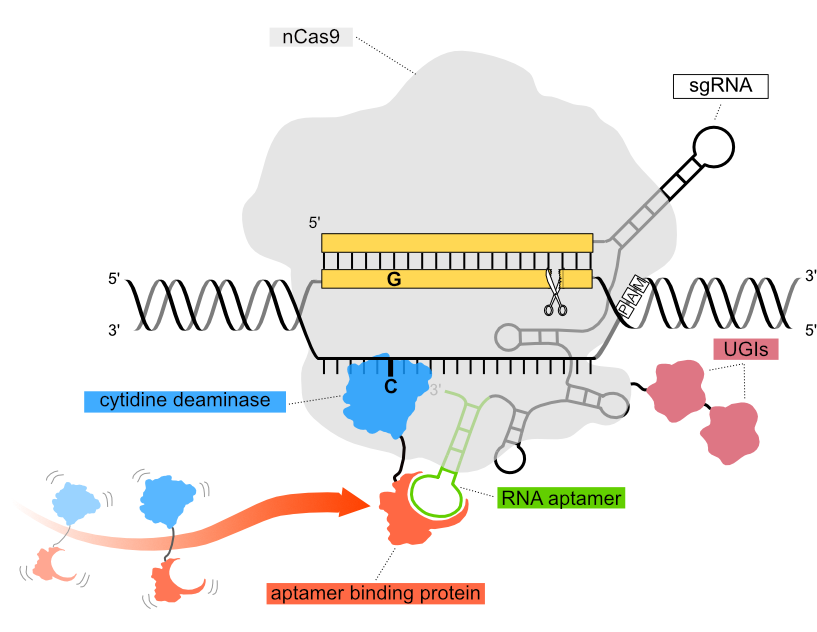
In the Pin-point base editing platform configuration used in our functional genomics screens, a nickase Cas9 (nCas9) component is recruited to the DNA target sequence via a single guide RNA (sgRNA) encoding an aptamer in the scaffold region. The aptamer recruits a DNA-modifying deaminase to the DNA target sequence via an aptamer binding protein. The three independent components of the system can be configured according to editing requirements and delivered to cells either as mRNA, or packaged in viral vectors.
Modify up to every PAM-accessible cytidine in the gene of interest to gain unparalleled understanding of the genotype-phenotype relationship
As part of our functional genomic screening services, we can partner with you on tiled base editing screens with the Pin-point platform. These tiled base editing screens can be used to interrogate every accessible cytosine in a DNA sequence by generating precise C-to-T mutations. This information can then be used to select the best guide RNA(s) for potential therapeutic applications, identify critical amino acids in structure-function analysis, or to test ligand binding relationships in drug candidate screening and confirm target identity.
With FGS and Pin-point base editing, you can:
- Target splice sites and introduce premature stop codons to recapitulate CRISPRko and CRISPRi screens.
- Identify novel hits by the introduction of missense mutations that may not be possible to reveal with parallel methods.
- Include loss of function and gain of function mutations in a single screen to elucidate possible mechanisms of drug sensitivity and resistance or protein function.
- Utilize different deaminases to maximize the editing window and evaluate more of the genetic sequence.
- Leverage our data analysis to generate hit lists and potentially identify putative causative mutations.
- Explore drug-gene interactions for sensitivity and resistance, and illuminate unique functional protein domains.
Our services team has broad expertise in CRISPR-based pooled screens and has directly been involved in the development of the Pin-point base editing platform, so are uniquely positioned to support you.
How do pooled tiled base editing screens work?
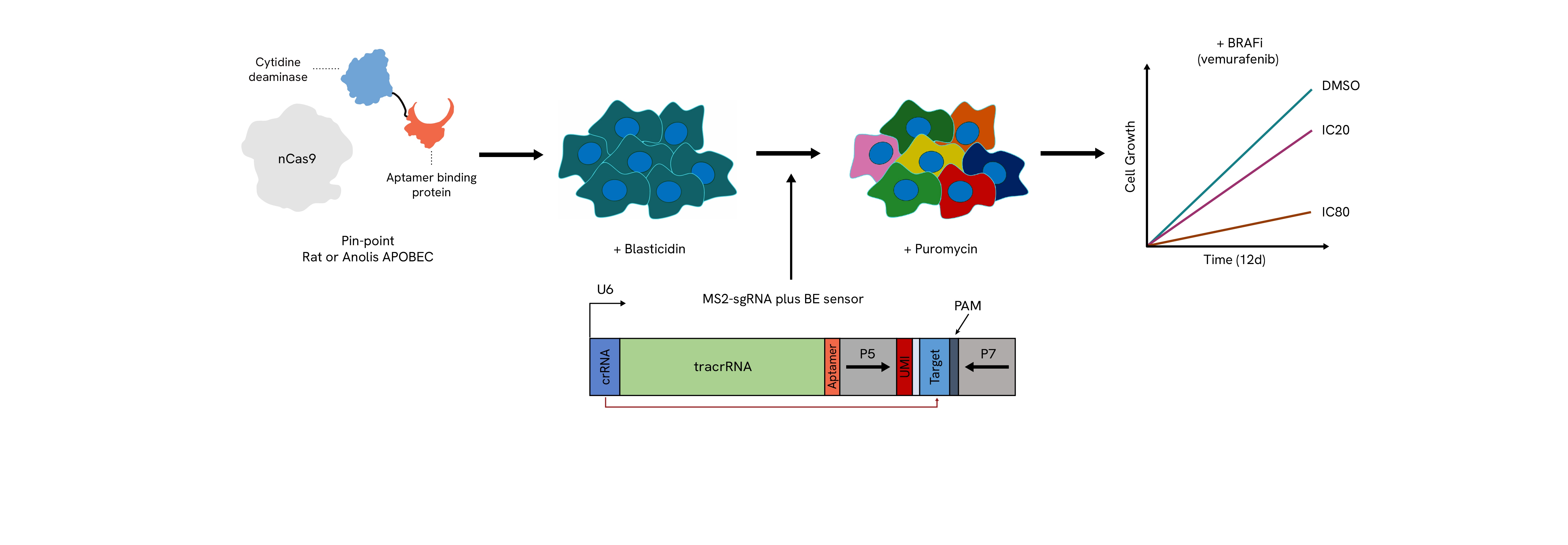
The Pin-point platform components are stably transduced into cells expressing either the rat or anolis APOBEC deaminase. A library of sgRNAs that include a sensor element with its corresponding target sequence are delivered into cells with lentivirus at high coverage. The presence of the sensor allows for the measurement of the editing that could be achieved at the endogenous locus by NGS in a pooled screen format. After selection for the sgRNAs, cells are challenged with the compound to be tested (e.g. vemurafenib) at an IC20 or IC80 dose to determine perturbations that confer sensitivity or resistance to the drug. Throughout the screen, samples are taken for subsequent NGS analysis to determine the levels of editing achieved and the loss or enrichment of the guide sequences.
See example screen data
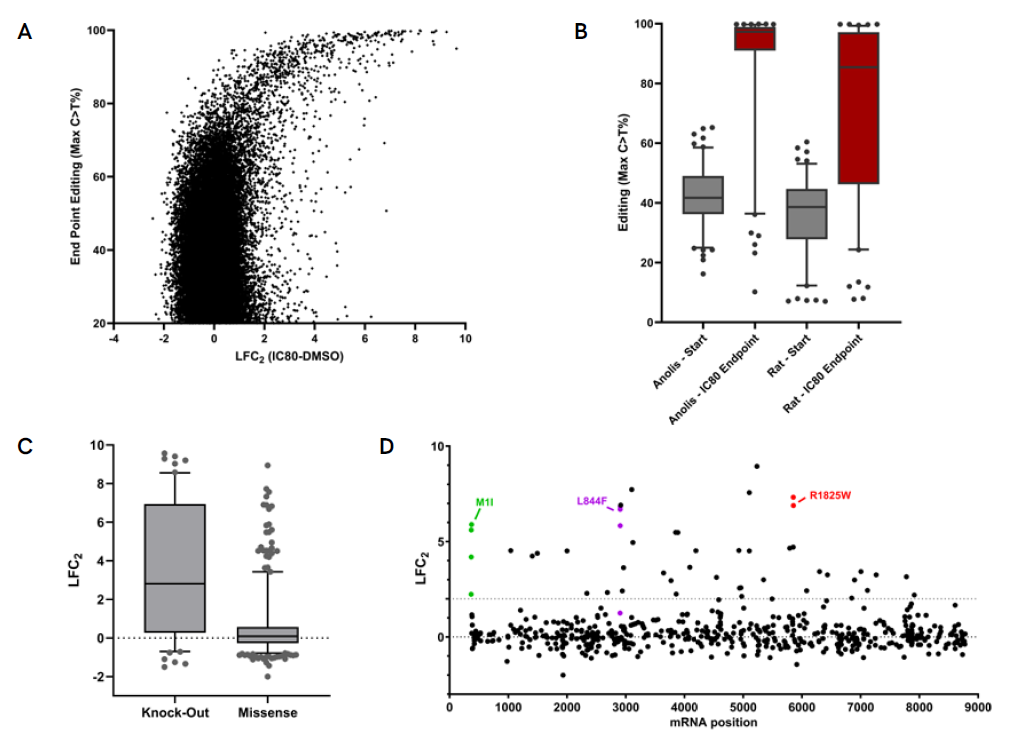
A. Endpoint data of the IC80 screen showing enrichment of guides that confer resistance to the drug correlating with increased levels of editing. B. Comparison of editing levels of guides shown to confer resistance between the start and end of the screen, shows strong enrichment for edited genomes. The enrichment is more pronounced in the presence of the Pin-point platform configured with anolis APOBEC, where initial editing levels are higher. Loss of expression of the Neurofibromin 1 (NF1) has previously been reported to confer BRAFi resistance. C. Data demonstrates that guides resulting in NF1 knockout by targeting either the mRNA slice sites or introducing nonsense mutations in the NF1 mRNA are more likely to confer drug resistance when compared to guides introducing missense mutations. D. Identified missense mutations that confer resistance show no hotspot regions in the NF1 gene, which is in agreement with clinical observations. Multiple guides introducing the same resistance conferring mutation are shown to demonstrate similar screen phenotypes.
What's included
- Tiled guide RNAs for C-to-T base changes across an entire gene, amplicon, or other custom target region of your choice.
- Tune the Pin-point base editing platform for focused or broad editing windows.
- Stable or transient expression of base editing components.
- Custom guide RNA libraries designed by our team of experts to your target region(s) of interest.
- Each custom pooled library is quality checked for representation, distribution, and particle titer to ensure consistent results.
- Readout of editing outcome for each gRNA via internal sensor sequence.
- Next-generation sequencing reporting with bioinformatic analysis and hit nominations.
- Increased cell health:
- Perturbations are introduced while avoiding dsDNA breaks, leading to less cytotoxicity, particularly in sensitive cell types.
- Edit cells that are typically sensitive to DNA damage in wild type CRISPR studies.





























