
Overview
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) play a central role in tumor growth, vascularization and metastasis. MMPs are a family of zinc containing endopeptidases known to degrade extracellular matrix proteins such as collagens, gelatins, fibronectin, and laminin. MMPs can be used as markers of cancer progression. MMP activity is involved in many disease-related processes including cancer progression, invasion and metastasis, rheumatoid arthritis, pulmonary diseases and areas of cardiovascular disease.
IVISense™ MMP and IVISense MMP FAST fluorescent probes (formerly MMPSense) are matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activatable probes that are optically silent upon injection and produce fluorescent signals after cleavage by disease related MMPs. They are members of a family of activatable fluorescent imaging probe comprising a novel architecture termed F.A.S.T. (Fluorescent Activatable Sensor Technology) which confers an improved pharmacokinetic profile with earlier imaging time points. They may be used in animal models to monitor the progression of disease or to evaluate the potential therapeutic efficacy of drugs targeting the underlying mechanisms involved in a particular disease. Activation can occur by a broad range of MMPs including MMP 2, 3, 7, 9, 12, and 13.

Figure 1: Schematic of IVISense MMP fluorescent probes. Two quenched fluorophores are separated by a cleavable linker in the native state. MMPs recognize the cleavable linker and once the probe is cleaved, the fluorophores produce signal. The probes also contain a pharmacokinetic modifier (PKM) selected to provide optimal attributes for in vivo imaging.
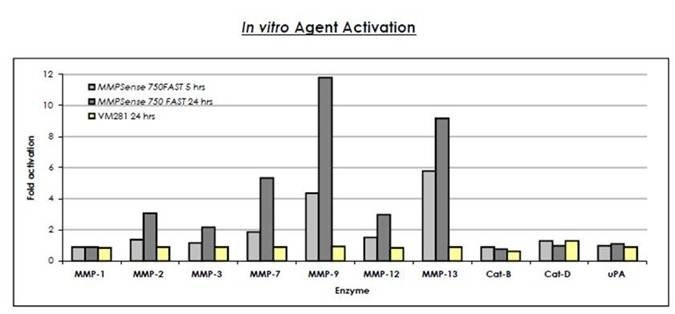
Figure 2: IVISense MMP 750 FAST (formerly MMPSense) (0.5 μM final concentration) was cleaved in the presence of 0.05-0.1 μM activated MMPs, Cathepsins B, D or urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA). These reactions were carried out in optimal buffers, pH and temperature. The fluorescence was read using a fluorescence microplate reader at 5 and 24 hours. The fold activation was measured by dividing the fluorescence released after cleavage with the enzyme by the fluorescence of the probe only. The control (VM281) is not significantly cleaved by any enzyme.
Products and catalog numbers
| Product | Catalog Number | Ex/Em wavelength (nm) | Molecular weight (g/mol) | Validated Experiments | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVISense MMP 645 FAST | NEV10100 | 649/666 | 43,000 | In vivo/Ex vivo | Oncology |
| Pulmonary | |||||
| Cardiovascular | |||||
| IVISense MMP 680 | NEV10126 | 680/700 | 450,000 | In vivo/Ex vivo | Oncology |
| Pulmonary | |||||
| Cardiovascular | |||||
| IVISense MMP 750 FAST | NEV10168 | 749/775 | 43,000 | In vivo/Ex vivo | Oncology |
| Pulmonary | |||||
| Cardiovascular |
Using IVISense MMP fluorescent probes for in vivo/ex vivo studies
- IVISense MMP 645 FAST is administration via intravenous injection and imaging 6-72 hours post injection. IVISense MMP 645 FAST will clear from tissues after approximately 96 hours. Repeat injection and imaging may be performed every four days for longitudinal studies. It is recommended that a pre-injection baseline image be taken prior to reinjection and imaging. IVISense MMP 645 FAST enables imaging of tumors and inflammation in a broad range of oncology, pulmonary and cardiovascular applications.
- IVISense MMP 680 is administration via tail vein injection and imaging 24 hours post tailvein injection. IVISense MMP 680 can be used as a marker for disease progression in animal tumor models.
- IVISense MMP 750 FAST is administration via intravenous injection and imaging 6 hours post injection. IVISense MMP 750 FAST will clear from tissues after approximately 96 hours. Repeat injection and imaging may be performed every four days for longitudinal studies. It is recommended that a pre-injection baseline image be taken prior to reinjection and imaging. IVISense MMP 750 FAST enables imaging of tumors and inflammation in a broad range of oncology, pulmonary and cardiovascular applications
- Instructions on setting up an in vivo mouse experiment with IVISense MMP 680 fluorescent probe
- Instructions on setting up an in vivo mouse experiment with IVISense MMP 750 FAST fluorescent probe
| Product | Route of Injection | Mouse Dose (25 g) | Rat Dose (250 g) | Blood t 1/2 | Tissue t 1/2 | Optimal imaging time | Optimal Re-injection Time (complete clearance) | Route of Metabolism/ background tissue | FMT and IVIS settings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVISense MMP 645 FAST | IV | 4 nmol | 12-40 nmol | 5 h | 72 h | 24 h (6-24) | 6-7 d | Liver > kidneys | FMT 635/655 |
| IVIS 640/660 with spectral unmixing | |||||||||
| IVISense MMP 680 | IV | 2 nmol | 6-20 nmol | 5 h | 72 h | 24 h (24-36) | 6-7 d | Liver | FMT 680/700 |
| IVIS 675/720 | |||||||||
| IVISense MMP 750 FAST | IV | 2 nmol | 6-20 nmol | 5 h | 72 h | 24 h (12-24) | 6-7 d | Liver > kidneys | FMT 750/770 |
| IVIS 745/800 |
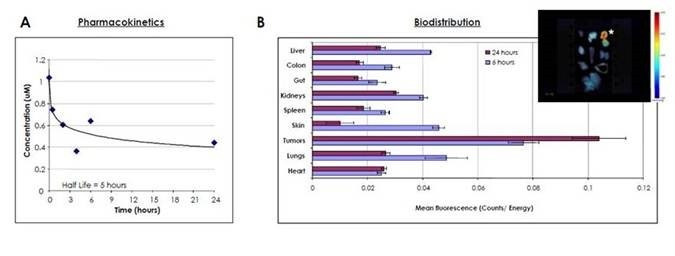
Figure 3: A) The pharmacokinetics is shown for IVISense MMP 750 FAST. BALB/c mice were injected intravenously with 2 nmoles of IVISense MMP 750 FAST and blood was drawn at various times. The plasma was obtained by centrifugation and the concentration of the probe was assessed using a competitive ELISA. As shown, IVISense MMP 750 FAST exhibits a plasma half-life of approximately 5 hours. B) The biodistribution of IVISense MMP 750 FAST is shown. Nu/Nu mice were injected subcutaneously in the mammary fat pads with human colorectal adenocarcinoma HT-29 tumor cells. Once tumors reached the desired volume, mice were injected intravenously with 3 nmoles of IVISense MMP 750 FAST and sacrificed at 6 and 24 hours later. The organs were excised and imaged on the FMT 2500 system using the reflectance mode. Regions of interest (ROI) were drawn around each organ using the FMT software, and the mean fluorescence (Counts/Energy) determined. This graph shows the mean fluorescence + SEM. The insert shows a representative image of the fluorescence detected in different organs at 6 hours after probe injection. The star (*) shows the tumor. As shown, the IVISense MMP 750 FAST preferentially localizes to tumors.
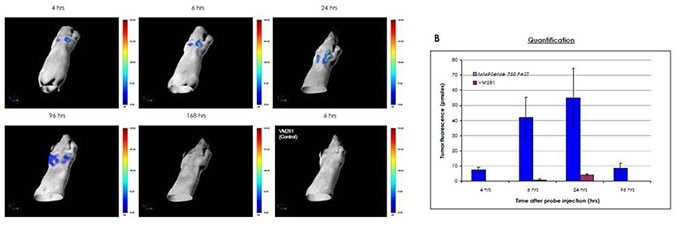
Figure 4: Monitoring tumor growth. Nu/Nu mice were injected subcutaneously bilaterally in the mammary fat pads with mouse breast carcinoma 4T-1 cells. One week later, mice were injected intravenously with 2 nmoles of IVISense MMP 750 FAST and imaged 4-168 hours later by FMT quantitative tomography. Control mice were injected with 2 nmoles of VM281 (the control). In vivo imaging was performed using FMT 2500 under gas anesthesia. A) Representative volume rendering projections taken at the same color gating from mice injected with IVISense MMP 750 FAST and imaged at different time points thereafter, or a mouse injected with VM281 (the control) and imaged 6 hours later. B) The total amount of fluorescence (pmol) was quantified in specific ROIs for each tumor. Maximum signal was detected between 6-24 hours post probe injection.
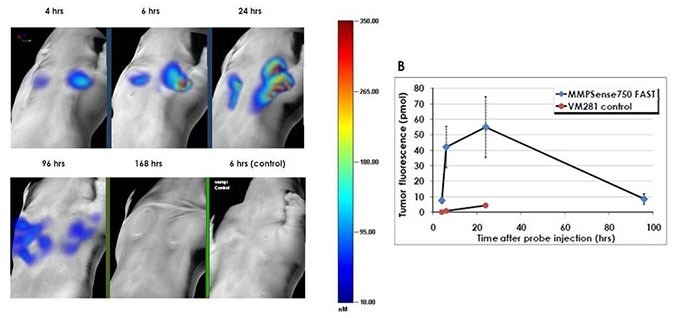
Figure 5: Mice were injected subcutaneously bilaterally on the chest with mouse breast carcinoma 4T-1 cells. One week later, mice were injected intravenously with 2 nmoles of IVISense MMP 750 FAST (formerly MMPSense) and imaged 4 -168 hours later by the FMT 2500. Control mice were injected with 2 nmoles of VM281 (as an inactivatable negative control using D-amino acids for the peptide sequence). In vivo imaging was performed using the FMT 2500 under gas anesthesia. A) Representative volume rendering projections taken at the same color gating. B) The total amount of fluorescence (pmol) was quantified in specific ROIs for each tumor. Maximum signal was detected between 6 - 24 hours post probe injection.
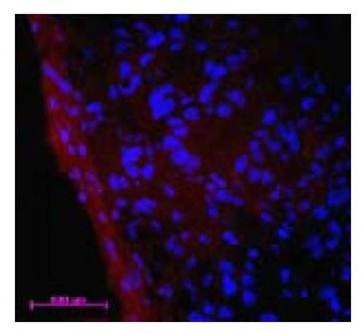
Figure 6: Ex Vivo Imaging. Immediately following the FMT quantitative tomography imaging session (Fig 5), mice were sacrificed, and tumors excised and snap-frozen in OCT for fluorescence microscopy. The distribution of NIR fluorescence was determined using a fluorescence microscope. Digital images were captured using appropriate filters for DAPI, and the near-infrared agent. The distribution of IVISense MMP 750 FAST is shown in red and the nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (shown in blue). Note that IVISense MMP 750 FAST localizes predominantly in the tumor margins.
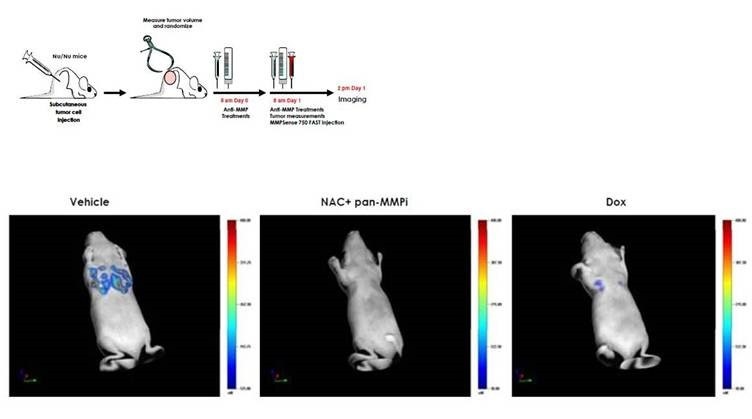
Figure 7: Anti-Matrix-Metalloproteinase Treatment: IVISense MMP 750 FAST can be used as an in vivo mechanistic biomarker of therapeutic efficacy in oncology. HT-29 tumor-bearing mice were randomized into 3 groups: 1) Doxycyline (Dox), 2) N-Acetyl-Cysteine (NAC) + pan-MMP Inhibitor (pan-MMPi) or 3) Vehicle. Mice in the Dox group received 1 mg Doxycyline/mouse subcutaneously, mice in NAC + pan-MMPi group received 3.2 g NAC/240 ml drinking water + 5 mg pan-MMPi/mouse intraperitoneally, and mice in the Vehicle group received only PBS. The following day, mice received the same treatment and were injected intravenously with 2 nmoles of IVISense MMP 750 FAST. The mice were imaged using FMT quantitative tomography 6 hours later. (Upper left panel) Schematic representation of the experimental protocol. (Upper right panel) Quantification of the tumor fluorescence in pmoles using FMT showing a significant decrease in IVISense MMP 750 FAST signal in the NAC+pan-MMPi and Dox groups (88% and 70%, respectively). (Lower panel) Representative volume rendering projections of a mouse having received Vehicle, a mouse treated with NAC + pan-MMPi and a mouse with Dox treatment.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
The information provided above is solely for informational and research purposes only. Revvity assumes no liability or responsibility for any injuries, losses, or damages resulting from the use or misuse of the provided information, and Revvity assumes no liability for any outcomes resulting from the use or misuse of any recommendations. The information is provided on an "as is" basis without warranties of any kind. Users are responsible for determining the suitability of any recommendations for the user’s particular research. Any recommendations provided by Revvity should not be considered a substitute for a user’s own professional judgment. Users are solely responsible for complying with all relevant laws, regulations, and institutional animal care and use committee (IACUC) guidelines in their use of the information provided.




























