
HTRF Androgen Receptor (Variant 7/AR-V7) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points
HTRF Androgen Receptor (Variant 7/AR-V7) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Cell Signaling |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |



Product information
Overview
The HTRF Androgen Receptor Variant 7 detection assay monitors the expression of the Androgen Receptor splice Variant 7 (AR-V7), providing insights into its presence, whether endogenous or overexpressed, within various cells.
The Androgen Receptor is a nuclear receptor that is activated by androgen hormones, including testosterone (T) and Dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Androgens bind to the ligand binding domain of the Androgen Receptor, resulting in receptor homodimerization and translocation to the nucleus. Downstream gene expression and signaling pathways are then activated, including the PI3K/AKT pathway. The gene expression induced by the Androgen Receptor promotes cell division, proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis. Dysregulation of the Androgen Receptor pathway can lead to oncogenic phenotypes, with Androgen Receptor activation or subexpression having been linked to conditions such as prostate cancer, breast cancer, glioblastoma, and other malignancies. Moreover, Androgen Receptor variants are expressed in various human cancer cell lines.
The Androgen Receptor Variant 7 (AR-V7) is a splice variant of the androgen receptor mRNA characterized by a truncated ligand-binding domain. It is constitutively active and widely expressed in human cancer cell lines. Among the AR-Vs described to date, AR-V7 is the most extensively evaluated and characterized, and several blood-based tests for AR-V7 have been developed.
Androgen Receptor and Variant 7 in particular has therefore become an important drug target for the pharmaceutical industry. The development of PROTAC compounds targeting the degradation of the Androgen Receptor is a popular therapeutic strategy to target Androgen Receptor-positive cancers.
How it works
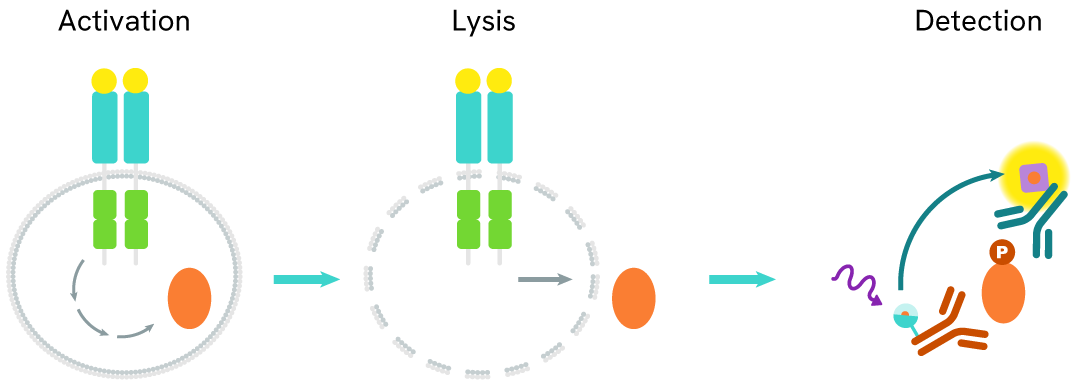
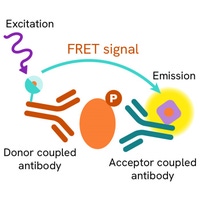
HTRF androgen receptor variant 7 assay principle
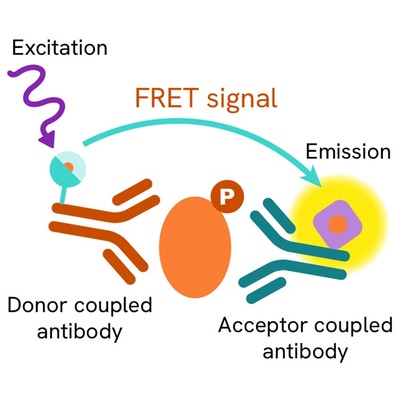
The HTRF Human Androgen Receptor Variant 7 assay quantifies the expression level of Androgen Receptor in a cell lysate. Unlike Western Blot, the assay is entirely plate-based and does not require gels, electrophoresis, or transfer. The Human Androgen Receptor Variant 7 assay uses two labeled antibodies, one coupled to a donor fluorophore and the other to an acceptor. Both antibodies are highly specific for a distinct epitope on the protein. In presence of Androgen Receptor in a cell extract, the addition of these conjugates brings the donor fluorophore into close proximity with the acceptor, and thereby generates a FRET signal. Its intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of the protein present in the sample, and provides a means of assessing the protein’s expression under a no-wash assay format.

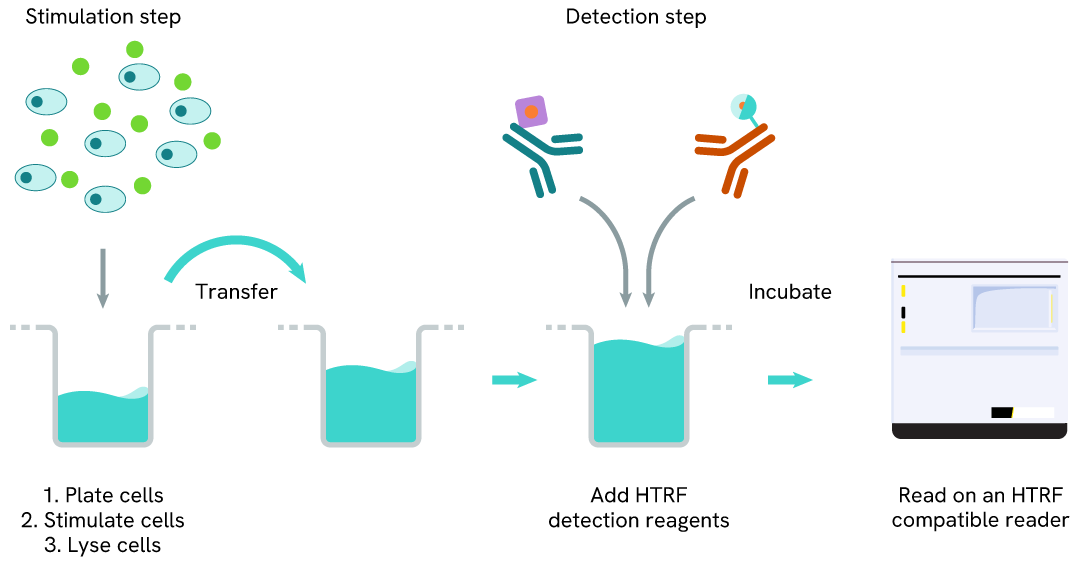
Human androgen receptor variant 7 two-plate assay protocol
The two-plate protocol involves culturing cells in a 96-well plate before lysis, then transferring lysates into a 384-well low volume detection plate before the addition of Human Androgen Receptor Variant 7 HTRF detection reagents. This protocol enables the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored.
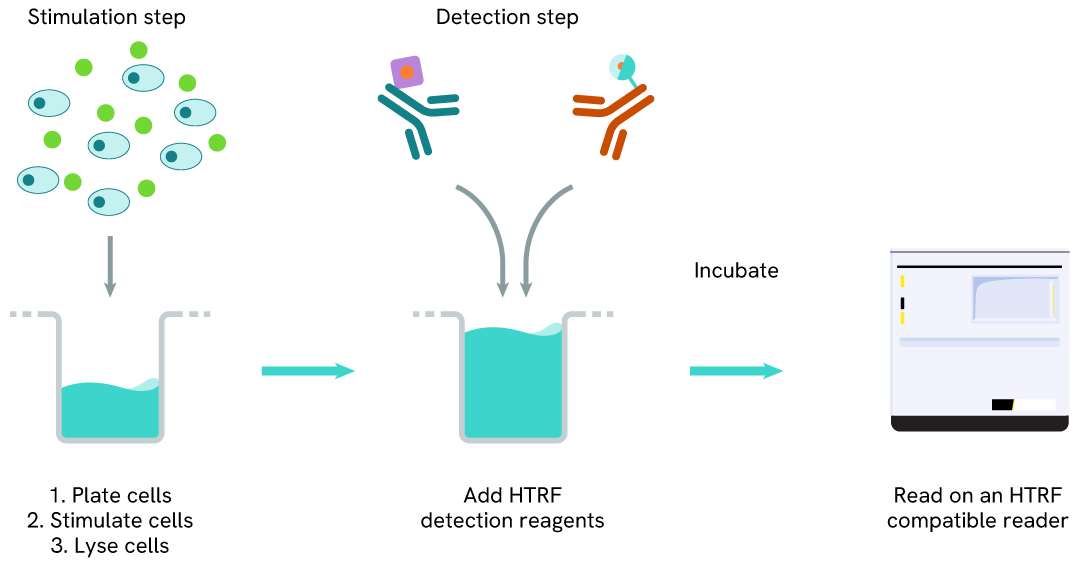
Human Androgen Receptor Variant 7 one-plate assay protocol
Detection of Human Androgen Receptor Variant 7 with HTRF reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, stimulation, and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS designed protocol enables miniaturization while maintaining robust HTRF quality.
Assay validation
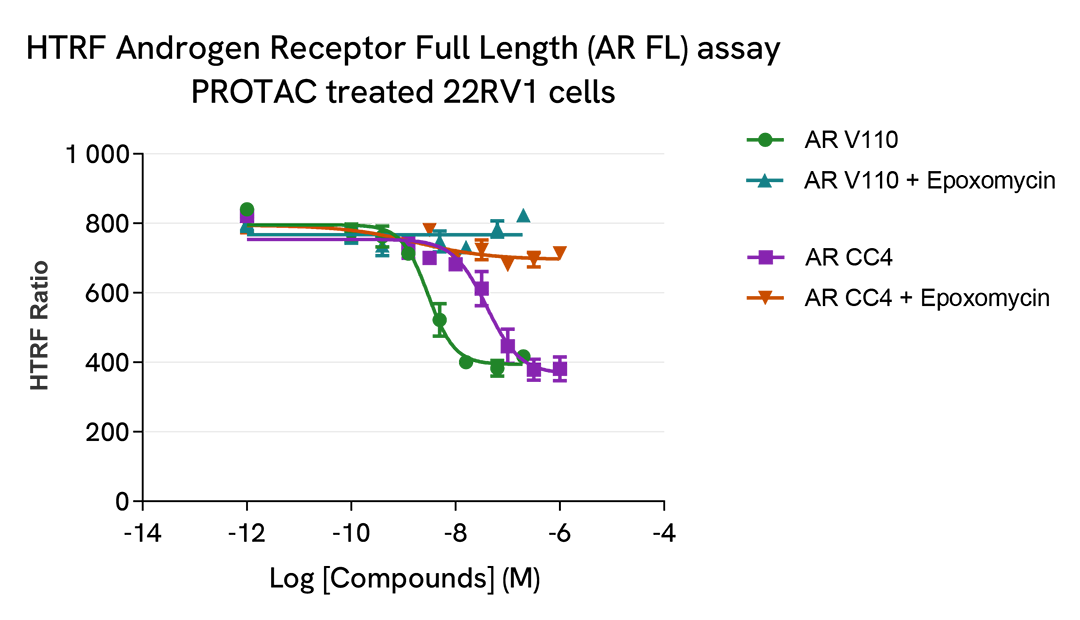
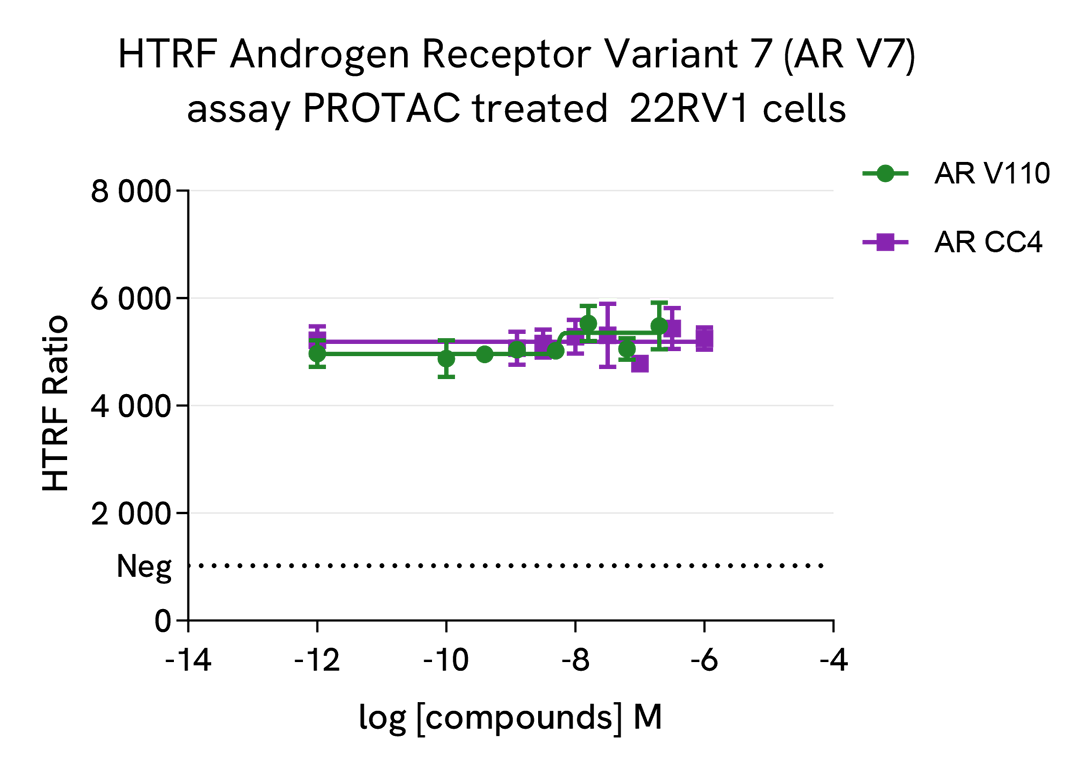
PROTAC® induced full length androgen receptor and androgen receptor variant 7 degradation
Prostate cancer cells 22RV1 were plated at 75,000 cells per well in a 96-well culture-treated plate in complete culture medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. Cells were treated with the 2 PROTAC compounds ARCC4 and ARV110 for 4h at 37°C, 5% CO2 in presence or not of 1 µM of epoxomicin, an inhibitor of proteasome. The medium was then removed, and the cells were lysed with 50 µl of supplemented lysis buffer #3 (1X) for 30 min at RT under gentle shaking.
After cell lysis, 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF Androgen Receptor Full Length (ARFL), or HTRF Androgen Receptor Variant 7 (ARV7) reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation at room temperature.
As expected, the 2 PROTAC compounds induced the degradation of Androgen Receptor Full Length, while epoxomicin co-treatment prevented its degradation. On the other hand, these two PROTACs were not efficient in degrading Androgen Receptor Variant 7.
The IC50 values of each compound (ARCC4 : 39 nM & ARV110 : 3 nM) are in agreement with the literature.
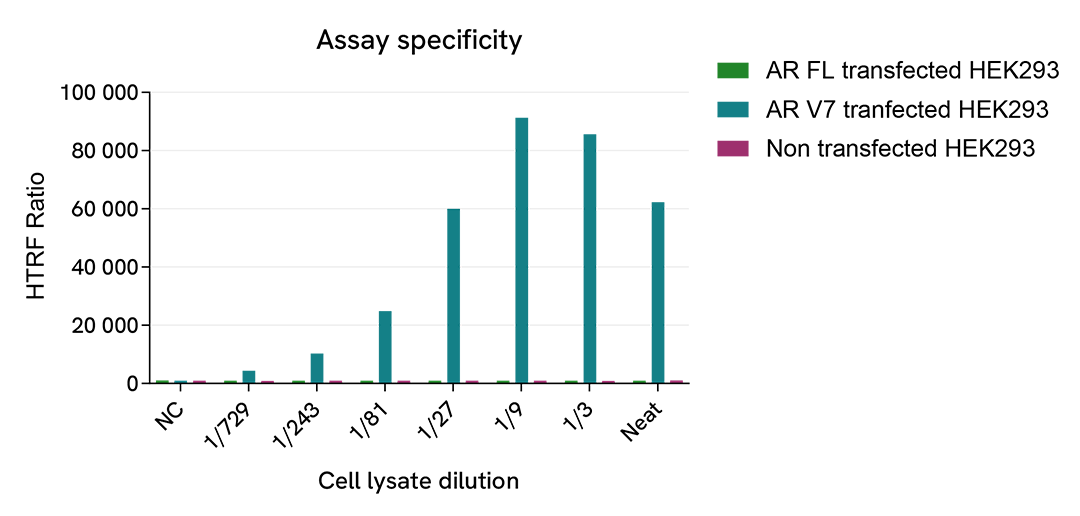
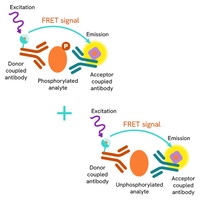
HTRF Androgen Receptor Variant 7 assay specificity
HEK293 cells were plated in a T175 flask in a complete culture medium for 24h at 37°C, 5% CO2, then were transfected with Androgen Receptor Full Length (AR FL) or Androgen Receptor Variant 7 (AR-V7) plasmids. After 24h, the cells were lysed with 3 mL of lysis buffer# 3 (1X) for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking.
Serial dilutions of the cell lysate were performed using lysis buffer# 3 (1X) , then 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF Androgen Receptor Variant 7 (AR-V7) reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after a 2h incubation at room temperature.
As the HEK293 cells did not express Androgen Receptor or Androgen Receptor Variant 7, the non transfected cells did not give any signal. Similarly, AR FL transfected cells were not detected with the AR-V7 assay. The AR-V7 transfected cells gave a very high HTRF signal, demonstrating the specificity of the assay.
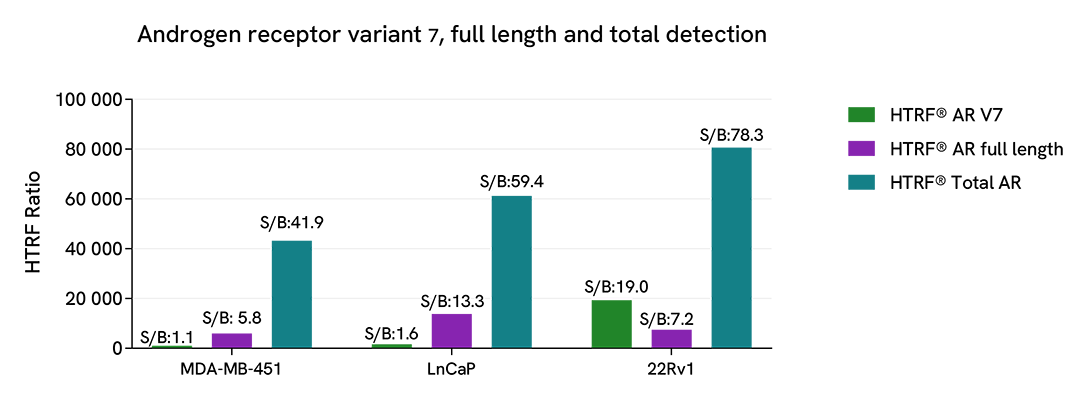
Androgen Receptor detections on various human cell lines
Human breast cancer cells MDA-MB-451 and prostate cancer cells LnCap and 22RV1 were seeded at 100,000 cells / well in a 96-well microplate. After a 24h incubation, the cells were lysed with supplemented lysis buffer #3 (1x).
16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate before the addition of 4 µL of the HTRF Androgen receptor Full Length (ARFL), HTRF Androgen Receptor Variant 7 (AR-V7), or HTRF Total Androgen Receptor reagents. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation.
As expected, little Variant 7 (AR-V7) was detected in the MDA-MB-451 and LnCap cell lines, while it was well detected in the 22RV1 cell line.
The Total Androgen Receptor assay able to detect Full Length, as well as all variants, giving a high signal in the 3 cell lines.
Full Length Androgen Receptor was well detected in the 3 cell lines.
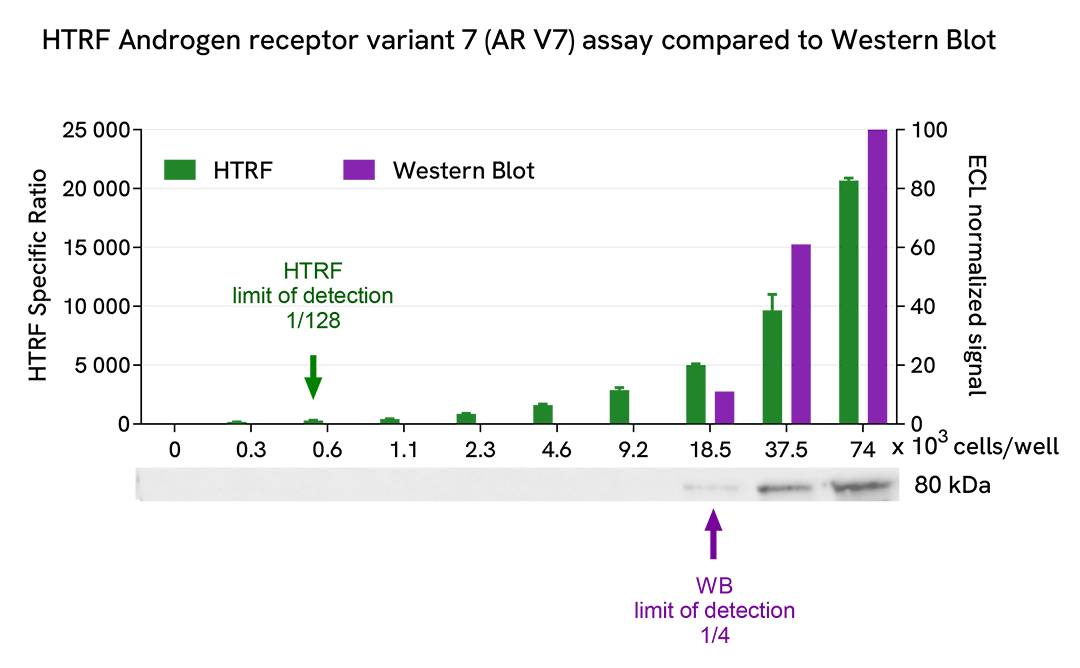
HTRF Androgen Receptor Variant 7 (AR-V7) assay compared to Western Blot
22RV1 prostate cancer cells were cultured in a T175 flask in a complete culture medium for 24h at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were then lysed with 3 mL of supplemented lysis buffer #3 (1x) for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking.
Serial dilutions of the cell lysate were performed using supplemented lysis buffer #3 (1x), and 16 µL of each dilution were transferred into a low volume white microplate before the addition of 4 µL of HTRF Androgen Receptor Variant 7 (AR-V7) detection reagents.
Equal amounts of lysates were used for a side-by-side comparison between HTRF and Western Blot.
In these conditions, the HTRF Androgen Receptor Variant 7 (AR-V7) assay was 32 times more sensitive than the Western Blot technique.
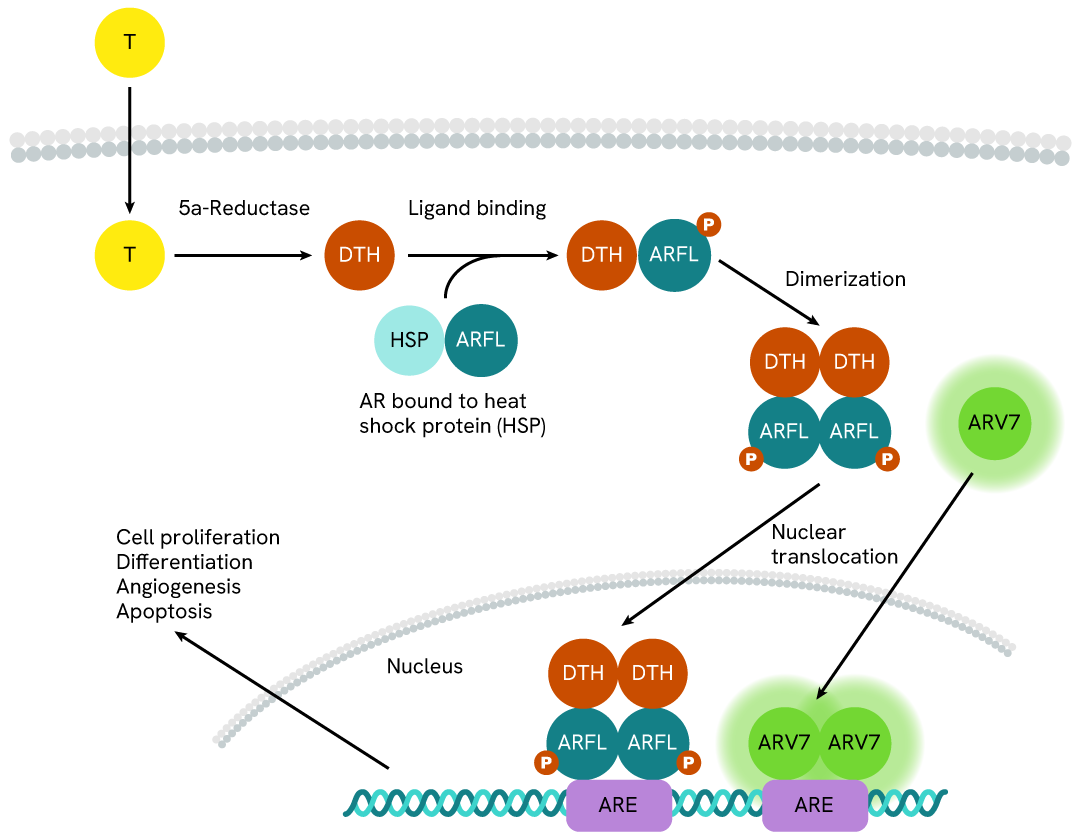
Simplified pathway
Androgen Receptor Variant 7 ARV7 signaling pathway
Androgen Receptor (AR) is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by androgen hormones, like testosterone (T) and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The androgen hormones cross the cell membrane to bind directly onto the Androgen Receptor, inducing homodimerization of the Androgen Receptor and permiting nucleus translocation. The Androgen Receptor dimers then bind to the Androgen Response Element (ARE) to lead gene expression, resulting in cell division, proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis.
The Androgen Receptor Variant 7 (AR-V7), a splice variant of the androgen receptor mRNA resulting in the truncation of the ligand-binding domain, is constitutively active and widely expressed in human cancer cell lines. In the same way as the Full Length, ARV7 dimerize to translocate into the nucleus to activate the same effectors.
To be added to total androgen receptor kit as well.
Specifications
| Application |
Cell Signaling
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Phosphoproteins
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Unit Size |
500 assay points
|
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
Discover the versatility and precision of Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) technology. Our HTRF portfolio offers a...
SDS, COAs, manuals and more
Are you looking for technical documents related to the product? We have categorized them in dedicated sections below. Explore now or request your COA/TDS, SDS, or IFU/manual.
- LanguageEnglishCountryUnited States
- LanguageFrenchCountryFrance
- LanguageGermanCountryGermany
- Lot Number04ALot DateNovember 7, 2027
- Lot Number02DLot DateSeptember 13, 2027
- Lot Number02BLot DateSeptember 13, 2027
- Resource TypeManualLanguageEnglishCountry-


Recently viewed
How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























