
HTRF Human Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points
HTRF Human Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points


This HTRF kit allows for the cell-based quantitative detection of MerTK when phosphorylated at Tyr749.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Cell Signaling |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |
This HTRF kit allows for the cell-based quantitative detection of MerTK when phosphorylated at Tyr749.


HTRF Human Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points


HTRF Human Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points


Product information
Overview
MerTK (Myeloid-Epithelial-Reproductive Tyrosine Kinase) is a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor predominantly expressed in dendritic cells, macrophages, epithelial cells, and cells of the reproductive tract. When stimulated by ligands such as Protein S or Gas6, activated MerTK confers a survival advantage to cancer cells by promoting their survival, enhancing migration, and inhibiting apoptosis. The overexpression of MerTK is implicated in a wide range of cancers, making it an intriguing target for cancer therapies.
Specifications
| Application |
Cell Signaling
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Buffer/Solvent |
Lysis Buffer 4
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Host Species |
Human
|
| Molecular Modification |
Phosphorylation
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target |
MerTK
|
| Target Class |
Phosphoproteins
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Inflammation
Oncology
|
| Unit Size |
500 assay points
|
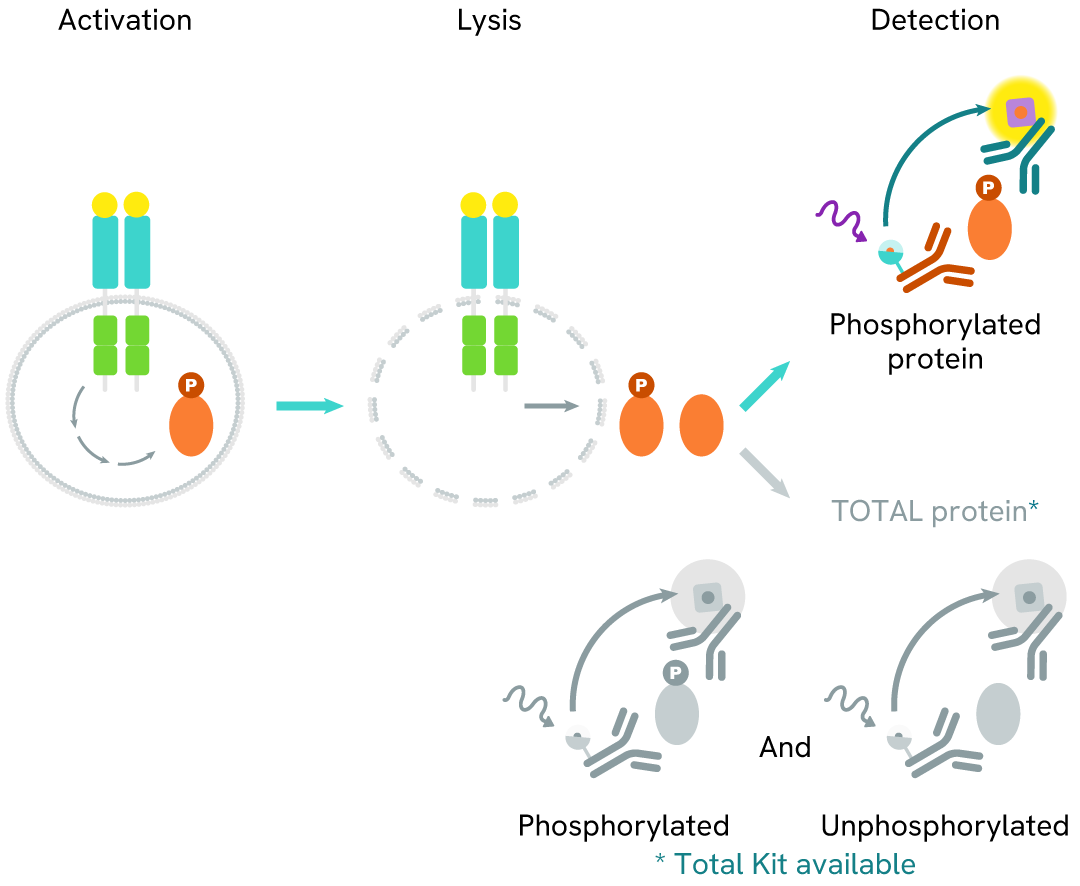
How it works
Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) assay principle
The Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) assay measures MerTK when phosphorylated at Tyr749. Unlike Western Blot, the assay is entirely plate-based and does not require gels, electrophoresis, or transfer. The assay uses 2 antibodies, one labeled with a donor fluorophore and the other with an acceptor. The first antibody was selected for its specific binding to the phosphorylated motif on the protein, and the second for its ability to recognize the protein independently of its phosphorylation state. Protein phosphorylation enables an immune-complex formation involving both labeled antibodies, and which brings the donor fluorophore into close proximity to the acceptor, thereby generating a FRET signal. Its intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of phosphorylated protein present in the sample and provides a means of assessing the protein's phosphorylation state under a no-wash assay format.

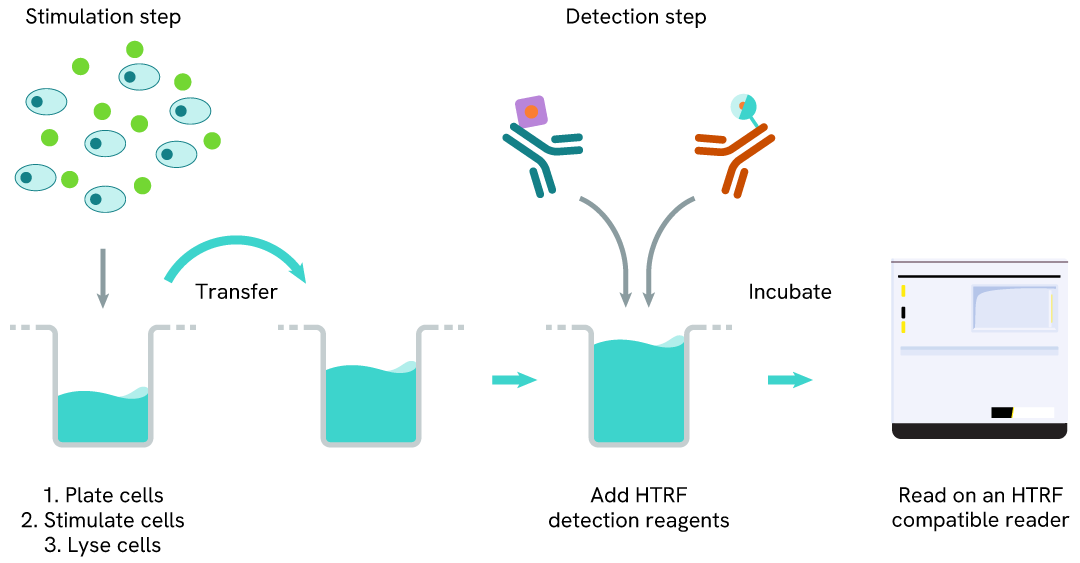
Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) two-plate assay protocol
The two-plate protocol involves culturing cells in a 96-well plate before lysis, then transferring lysates into a 384-well low volume detection plate before the addition of Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) HTRF detection reagents. This protocol allows for the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored.
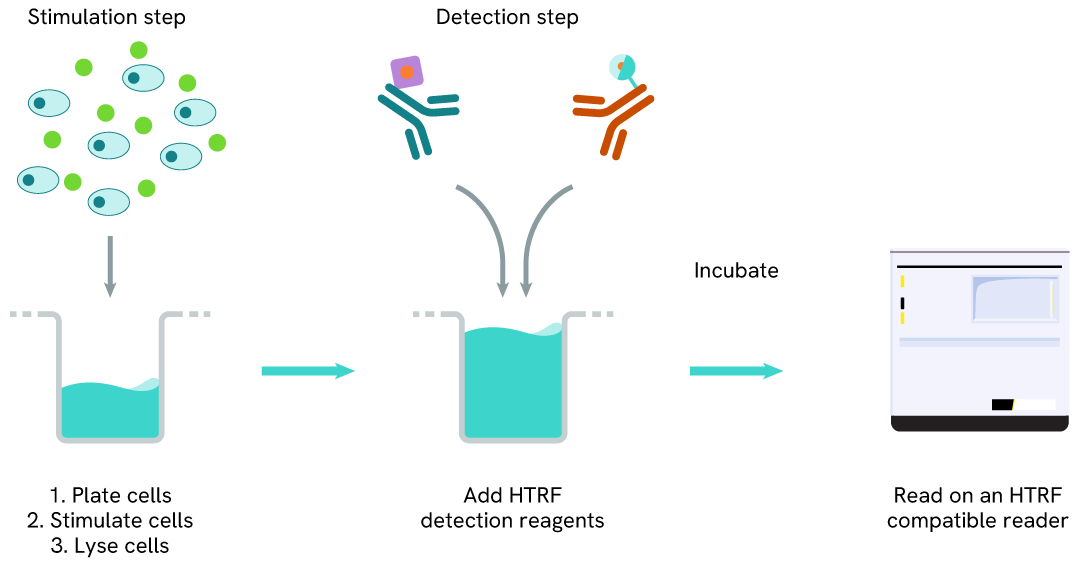
Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) one-plate assay protocol
Detection of Phosphorylated MerTK (Tyr749) with HTRF reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, stimulation, and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS designed protocol facilitates miniaturization while maintaining robust HTRF quality.
Assay validation
Induction of phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) in endogenous and overexpressed MerTK cellular models
HepG2 cells were seeded in a 96-well culture-treated plate (100,000 cells/well) in complete culture medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were treated for 30 minutes with 100 µM of Pervanadate.
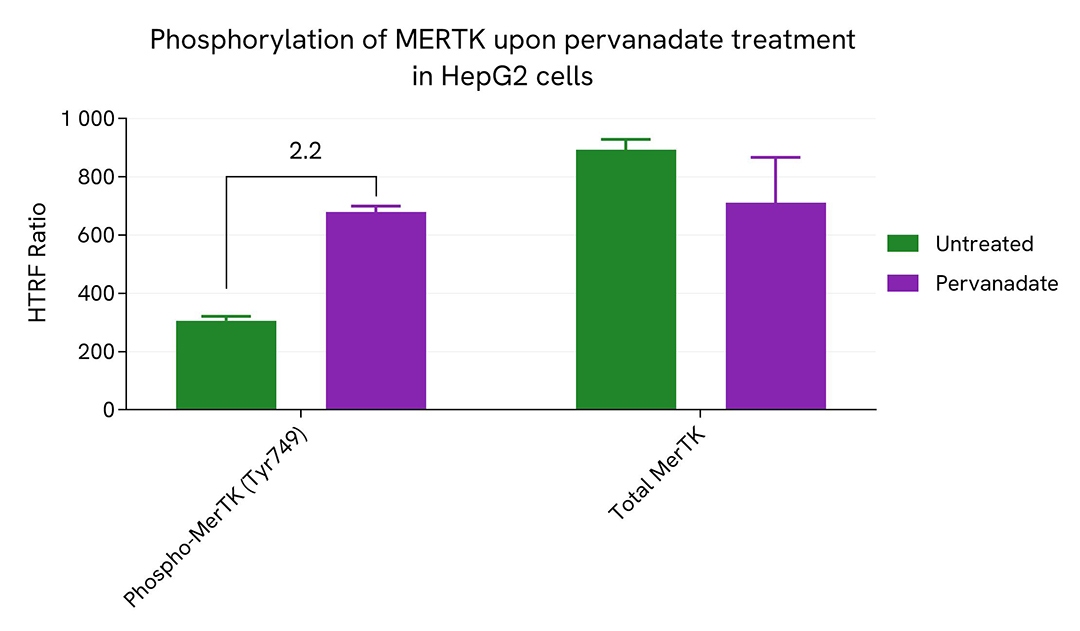
After treatment, the cells were lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking. For the detection step, 16 µL of cell lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) or Total MerTK detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation.
As expected, Pervanadate induced an increase in the level of Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749).
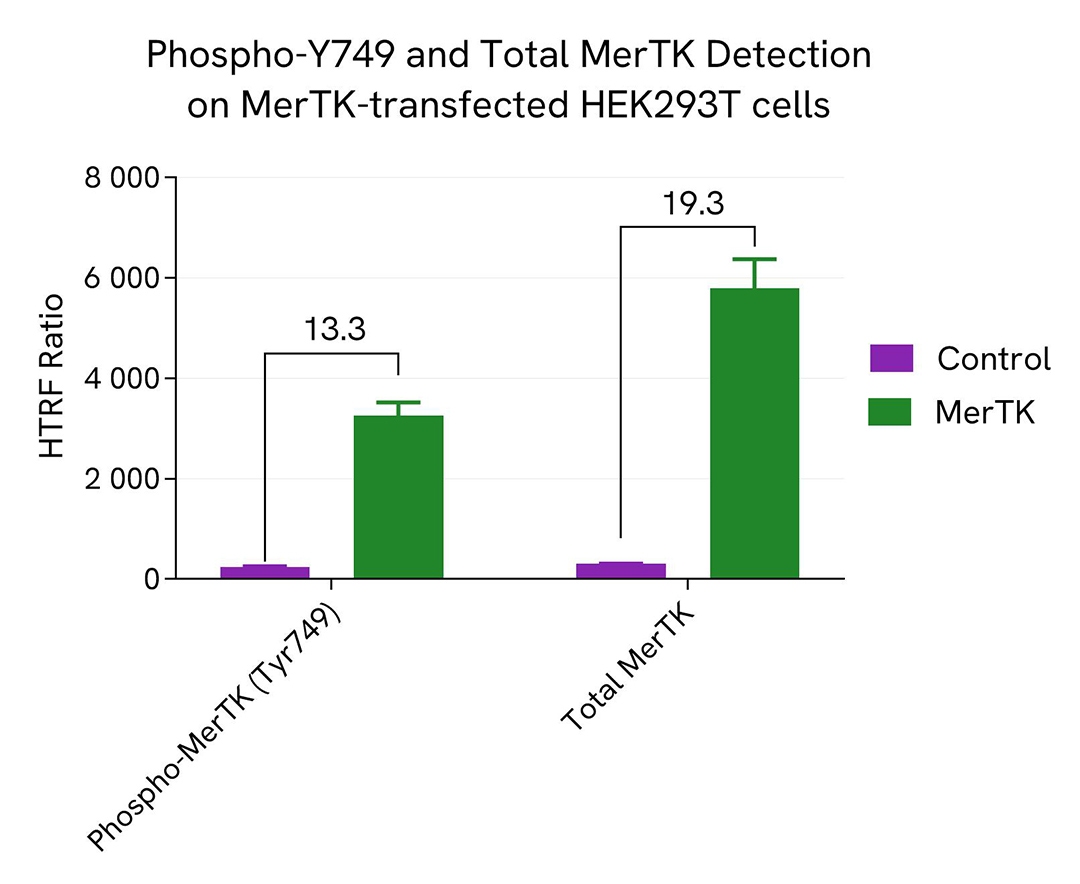
HEK293T cells were seeded in a 96-well culture-treated plate (12,500 cells/well) in complete culture medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were transfected with MerTK plasmid using DharmaFECT kb (Revvity's Dharmacon products) or with an empty plasmid as control.
After 24h of incubation, the cells were lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking. For the detection step, 16 µL of cell lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) or Total MerTK detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation. As anticipated, the increased levels of MerTK without treatment led to its autophosphorylation, allowing for the detection of Phospho and Total MerTK.
Inhibition of phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) in endogenous and overexpressed MerTK cellular models
HepG2 cells were seeded in a 96-well culture-treated plate (100,000 cells/well) in complete culture medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were treated for 1 hour with increasing concentrations of UNC1062 (a MerTK inhibitor), and 5 µM of Pervanadate were added 30 minutes before the end of the treatment. The cells were lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking.
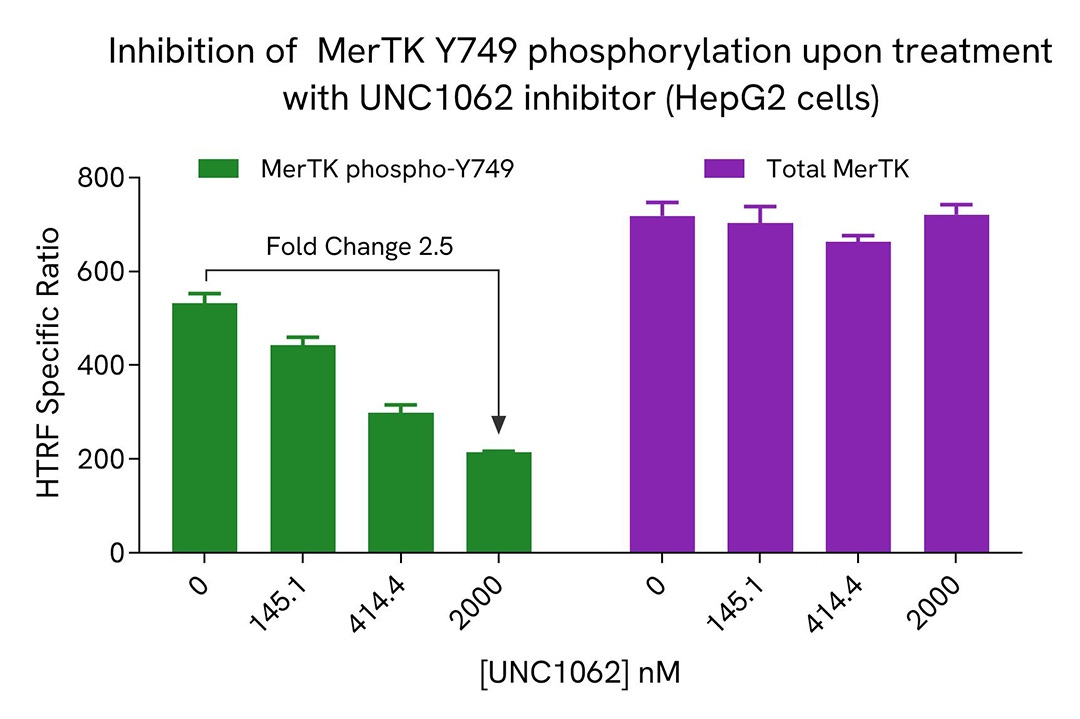
For the detection step, 16 µL of cell lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF Phospho-MerT (Tyr749) or Total MerTK detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation.
As anticipated, the MerTK inhibitor UNC1062 led to a dose-dependent reduction in MerTK phosphorylation, while not affecting the expression level of the receptor.
HEK293T cells were seeded in a 96-well culture-treated plate (12,500 cells/well) in complete culture medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were transfected with MerTK plasmid using DharmaFECT kb (Horizon Discovery). After 24h of incubation, the cells were treated for 1 hour with increasing concentrations of UNC1062 or UNC2025 (MerTK inhibitors).
The cells were lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking. For the detection step, 16 µL of cell lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) or Total MerTK detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation.
As expected, both MerTK inhibitors led to a dose-dependent reduction in MerTK phosphorylation, while not affecting the expression level of the receptor.
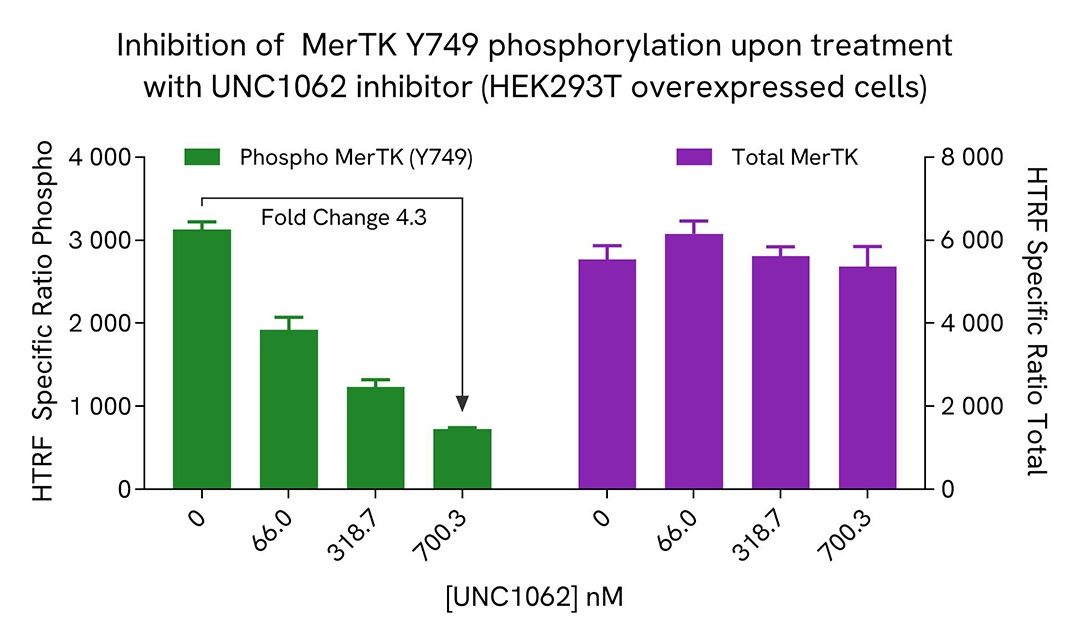
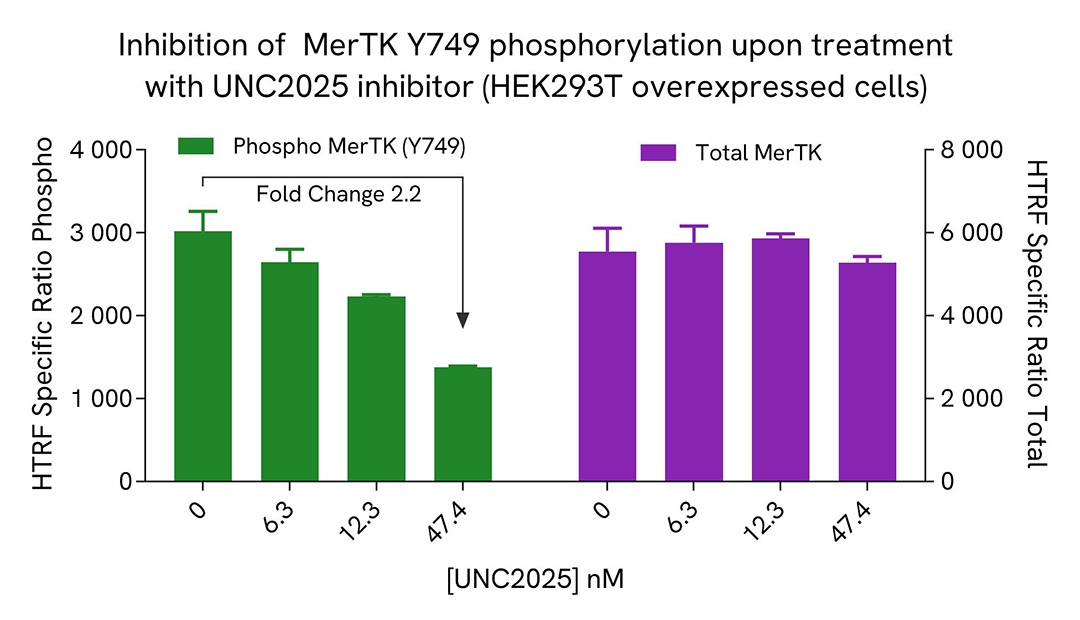
Selectivity of phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) assay using transfection of members of the TAM family
HEK293T cells were grown in a T175 flask in complete culture medium at 37°C - 5% CO2 until 80% confluence. Transfection of MerTK, Axl, or Tyro3, as well as a negative control, was carried out using DharmaFECT kb (Revvity’s product). After 24h of incubation, the cells were treated for 30 min with 100 µM of Pervanadate before being lysed with 3 mL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 (1X) for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking.
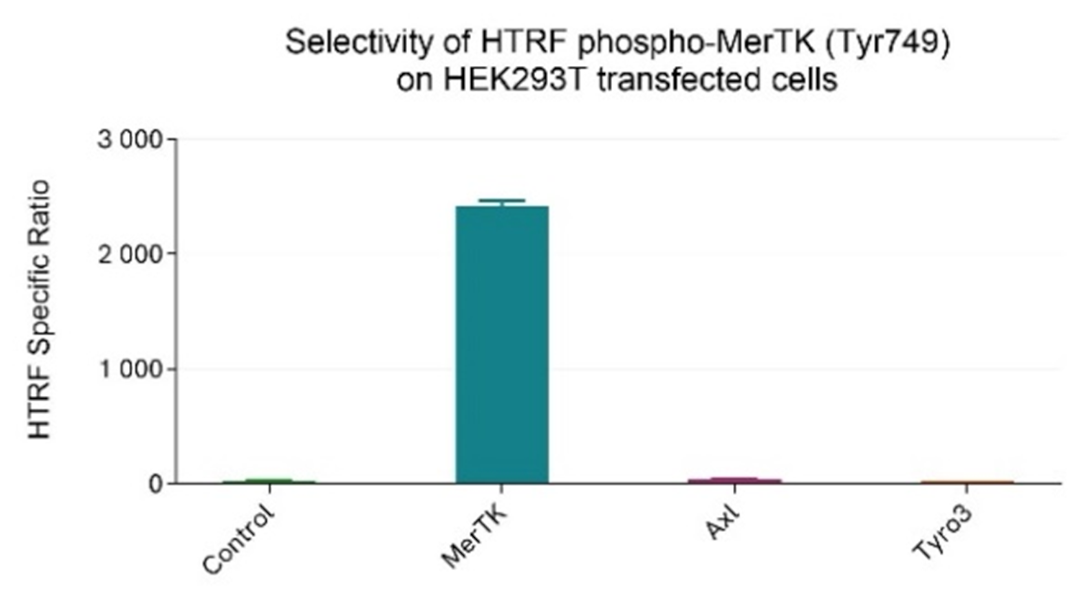
After cell lysis, 16 µL of lysates, diluted 1/16 in supplemented lysis buffer #4 (1X) to be in the linear range of the assay, were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate and 4 µL of the HTRF Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) detection reagents were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation.
Cell transfection with MerTK alone resulted in the detection of Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) compared to the negative control. In contrast, transfection of Axl or Tyro3 did not lead to any signal increase, demonstrating that the Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) assay is specific for MerTK and, as expected, does not cross-react with other members of the TAM family.
Assessment of Total phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) level in various cell lines
HepG2 cells with endogeneous expression of MerTK and Hek293T cells overexpressing MerTK were seeded at respectively 100,000 and 12,500 cells/well in a 96-well microplate. After 24h of incubation, the cells were treated for 30 min with 100 µM of Pervanadate before being lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking.
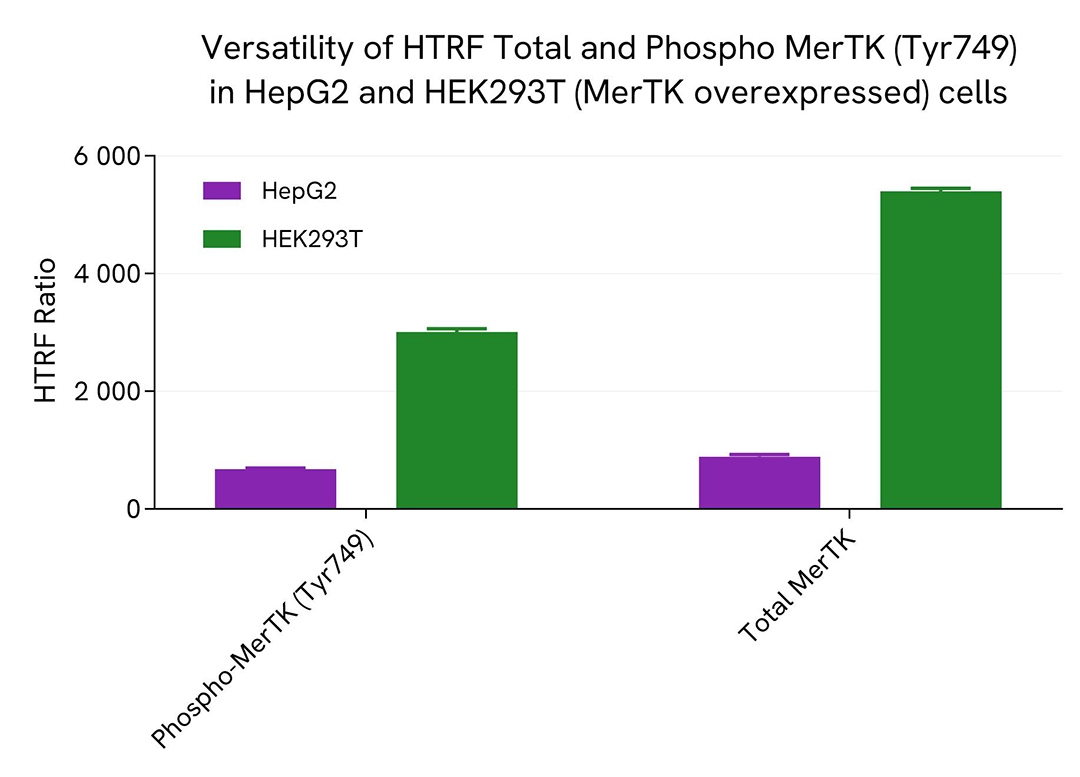
16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate before the addition of 4 µL of the HTRF Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) or HTRF Total MerTK detection reagents. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation.
The HTRF Total MerTK assay efficiently detected Total MerTK in various cellular models expressing dvarying levels of the protein.
HTRF MerTK phospho-Y749 assay compared to Western Blot
HEK293 cells were grown in a T175 flask in complete culture medium at 37°C - 5% CO2 until 80% confluence. Transfection of MerTK plasmid was performed with DharmaFECT kb (Horizon Discovery). After 24h of incubation, the cells were lysed with 3 mL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 (1X) for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking.
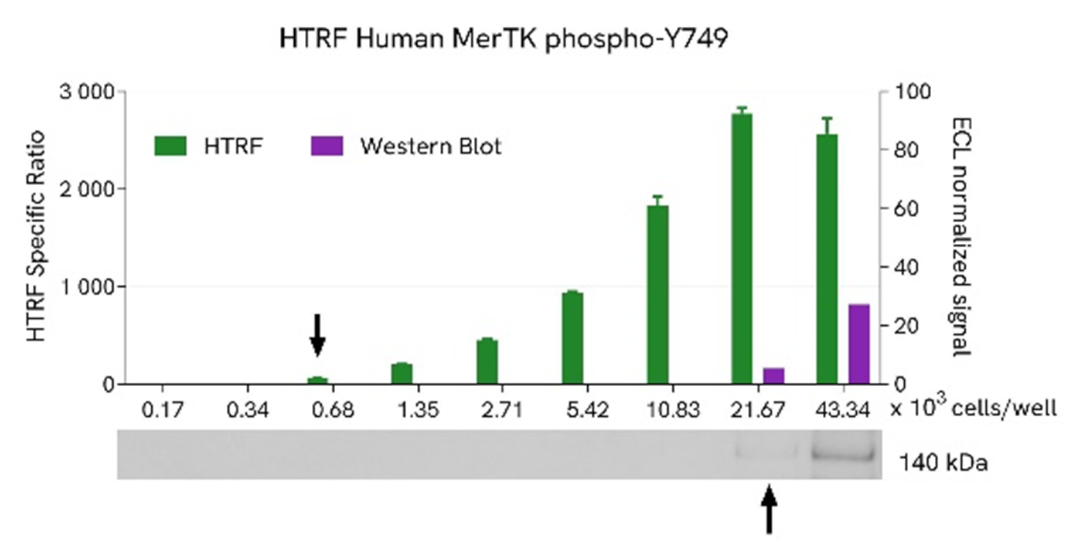
Serial dilutions of the cell lysate were performed using supplemented lysis buffer, and 16 µL of each dilution were transferred into a low volume white microplate before the addition of 4 µL of HTRF Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) detection reagents. Equal amounts of lysates were used for a side-by-side comparison between HTRF and Western Blot.
Using the HTRF Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) assay, 680 cells/well were enough to detect a significant signal, while 21670 cells were needed to obtain a minimal chemiluminescent signal using Western Blot. Therefore, in these conditions, the HTRF Phospho-MerTK (Tyr749) assay was 32 times more sensitive than the Western Blot technique.
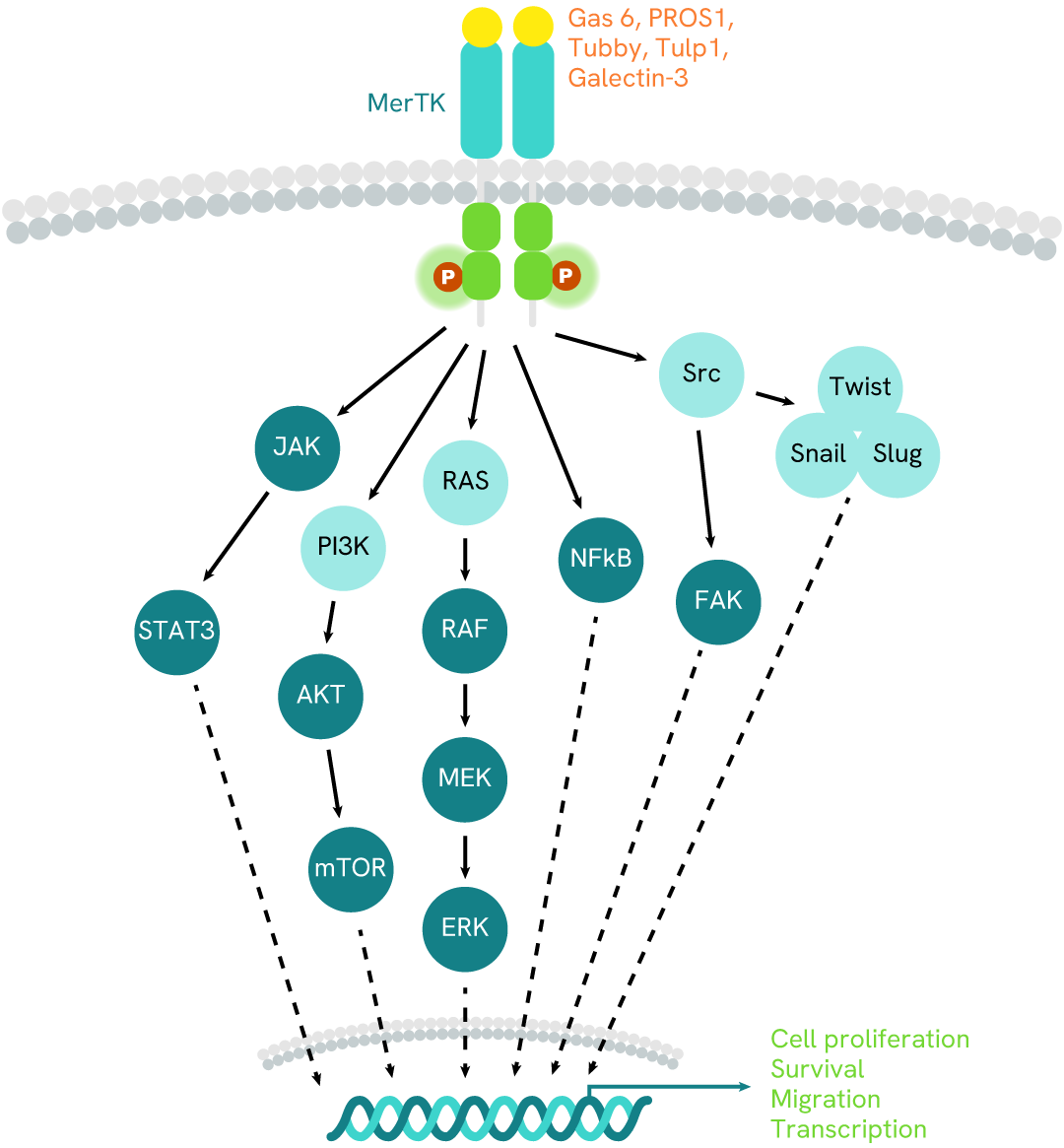
Simplified pathway
MerTK signaling pathway
MerTK, also known as Mer receptor tyrosine kinase, belongs to the TAM family of tyrosine kinase receptors. It plays crucial roles in various cellular mechanisms, including inflammatory responses, cell survival, phagocytosis, and the clearance of apoptotic cell debris. Activation of MerTK occurs when it interacts with specific ligands such as Gas6, protein S, and Galectins. These ligands act as bridges between the receptor and cellular debris generated by nearby apoptotic cells. Upon activation, MerTK undergoes dimerization and autophosphorylation at specific intracellular tyrosine residues. These phosphorylated sites serve as docking points for recruiting and activating downstream signaling proteins. The downstream pathways influenced by MerTK include the PI3K/AKT pathway (involving the mTOR transcription factor), the MAPK pathway (contributing to cell proliferation and differentiation), and the JAK/STAT pathway (relying on STAT transcription factors to induce inflammatory responses). In summary, MerTK orchestrates essential cellular processes by integrating signals from its ligands and initiating downstream pathways.
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
Discover the versatility and precision of Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) technology. Our HTRF portfolio offers a...
Loading...


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.