
HTRF Human & Mouse LC3B II Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points

HTRF Human & Mouse LC3B II Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points




This HTRF kit enables the cell-based quantitative detection of LC3B-II (LC3-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate).
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Protein Quantification |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |
This HTRF kit enables the cell-based quantitative detection of LC3B-II (LC3-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate).
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).


HTRF Human & Mouse LC3B II Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points


HTRF Human & Mouse LC3B II Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points


Product information
Overview
LC3 is a mammalian homolog of the yeast ATG8 protein and is distributed throughout mammalian tissues and cultured cells. LC3 is a key component of the autophagy process - a degradative program that maintains cellular homeostasis.
During autophagy, cytoplasmic components such as cytosolic proteins and organelles are engulfed by autophagosomes Concurrently, a cytosolic form of LC3 (LC3-I) is conjugated to phosphatidylethanolamine to form LC3-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate (LC3-II). This newly formed conjugate is recruited to autophagosomal membranes. The subsequent fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes results in the formation of autolysosomes, and intra-autophagosomal components are degraded by lysosomal hydrolases. At the same time, LC3-II within the autolysosomal lumen is degraded.
The LC3-II level has been found to be proportional to autophagosome abundance making LC3-II the most popular marker of autophagy.
Specifications
| Application |
Protein Quantification
|
|---|---|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target Class |
Biomarkers
|
| Target Species |
Human
Mouse
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Unit Size |
500 Assay Points
|
How it works
LC3B-II assay principle
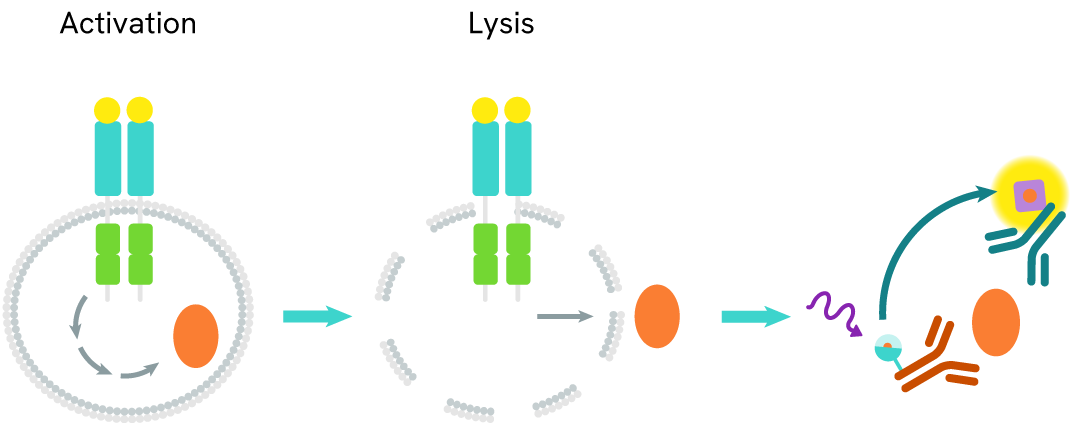
The HTRF LC3B-II assay quantifies the expression level of LC3B-II in a cell lysate. Unlike Western Blot, the assay is entirely plate-based, and does not require gels, electrophoresis, or transfer. The LC3B-II assay uses two labeled antibodies, one coupled to a donor fluorophore, the other to an acceptor. Both antibodies are highly specific for a distinct epitope on the protein. In presence of LC3B-II in a cell extract, the addition of these conjugates brings the donor fluorophore into close proximity with the acceptor, and thereby generates a FRET signal. Its intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of the protein present in the sample, and provides a means of assessing the protein’s expression under a no-wash assay format.

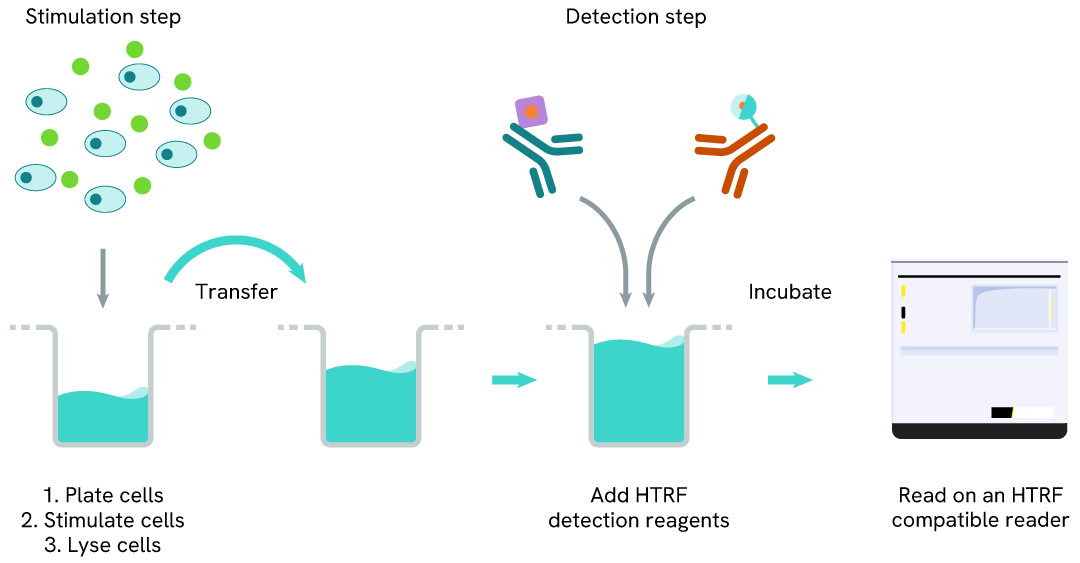
LC3B-II two-plate assay protocol
The 2-plate protocol involves culturing cells in a 96-well plate before lysis, then transferring lysates into a 384-well low volume detection plate before the addition of the LC3B-II HTRF detection reagents. This protocol enables the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored.
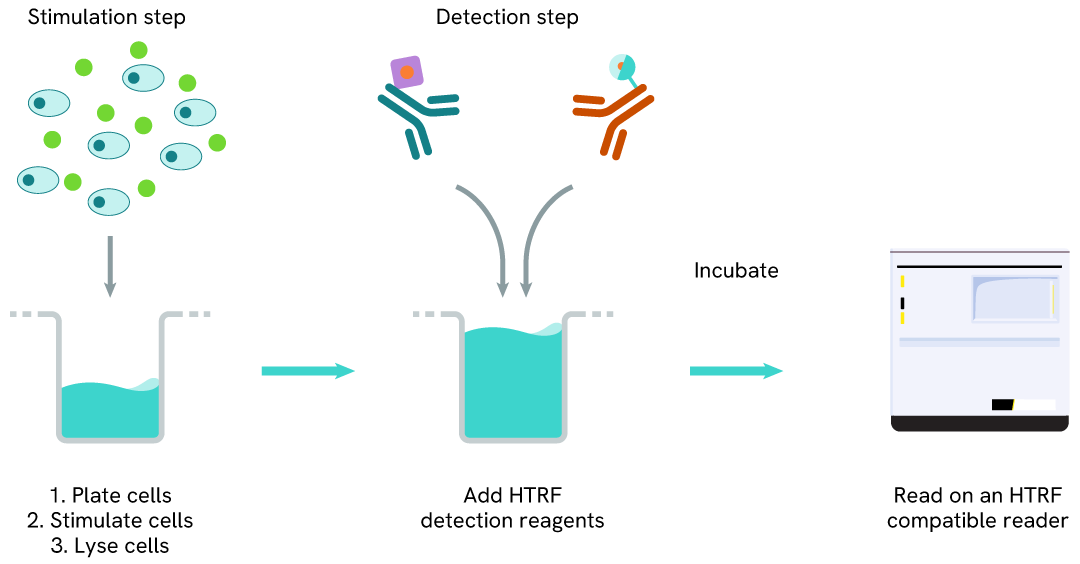
LC3B-II one-plate assay protocol
Detection of LC3B-II with HTRF reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, stimulation, and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS-designed protocol enables miniaturization while maintaining robust HTRF quality.
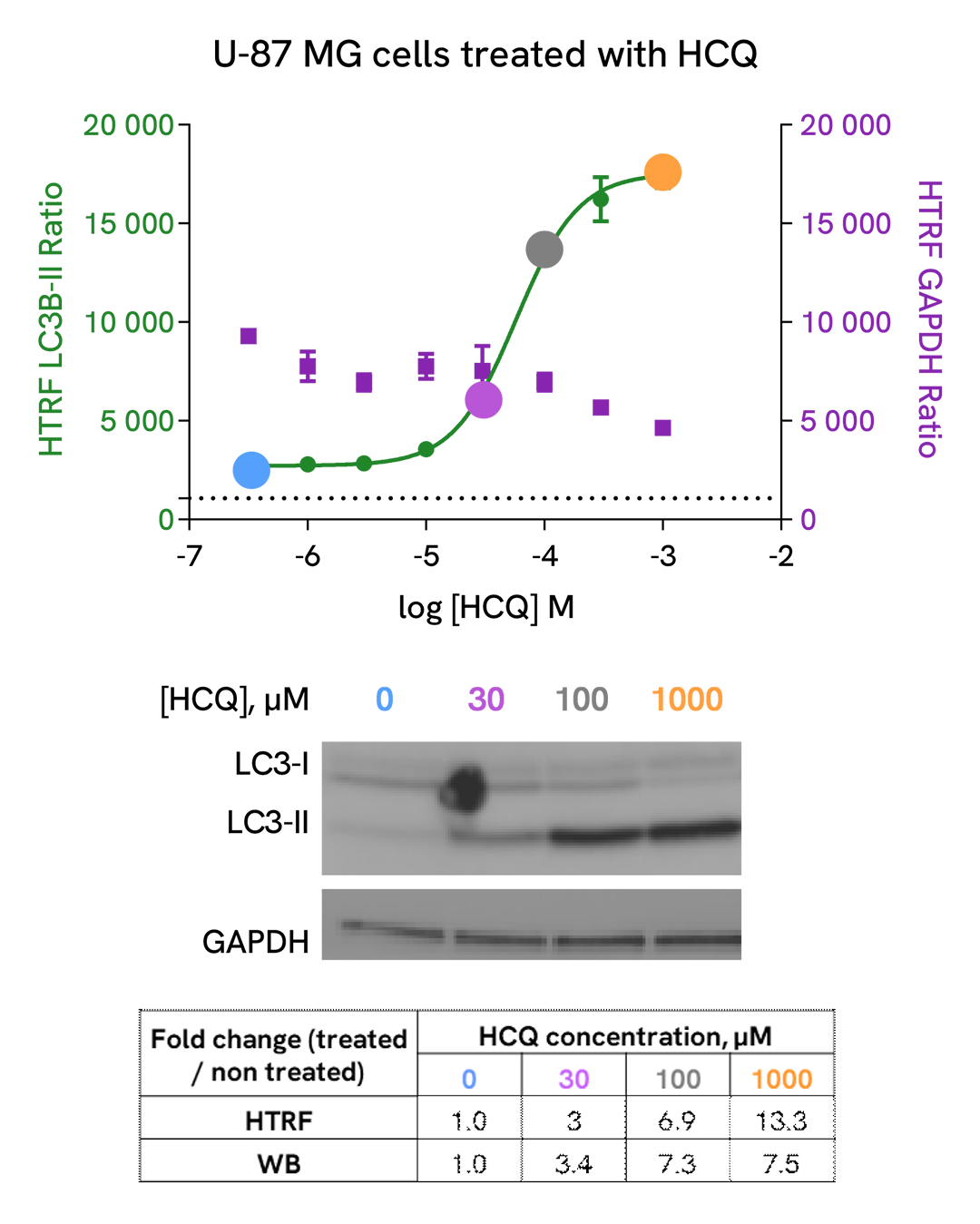
Assay validation
Detection of LC3B-II modulation with HTRF and Western Blot
U-87 MG cells were plated in a 96-well culture-treated plate (25,000 cells per well) in complete culture medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were then treated with increasing concentrations of Hydroxycholoroquine (HCQ), a late-stage autophagic inhibitor, for 4 h at 37 °C, 5% CO2. Following culture medium removal, cells were lysed with 3 mL of supplemented lysis buffer #3 (1X) + BR (1X) for 30 min at room temperature under gentle shaking.
After cell lysis, 16 µL of sample (cell lysate diluted by 2) were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate, then 4 µL of the HTRF LC3B-II detection antibodies were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation at room temperature.
In parallel, 16 µL of cell lysates were used for Western Blot (anti-LC3B, Sigma, #L7543).
HTRF and chemiluminescent signals were normalized with GAPDH Housekeeping protein (HTRF kit: Revvity®, #64GAPDHPEG)
Fold of change corresponds to LC3B-II normalized signal treated over untreated condition.
As evidenced, HTRF LC3B-II and Western Blot results are comparable demonstrating that these two methods are correlated.
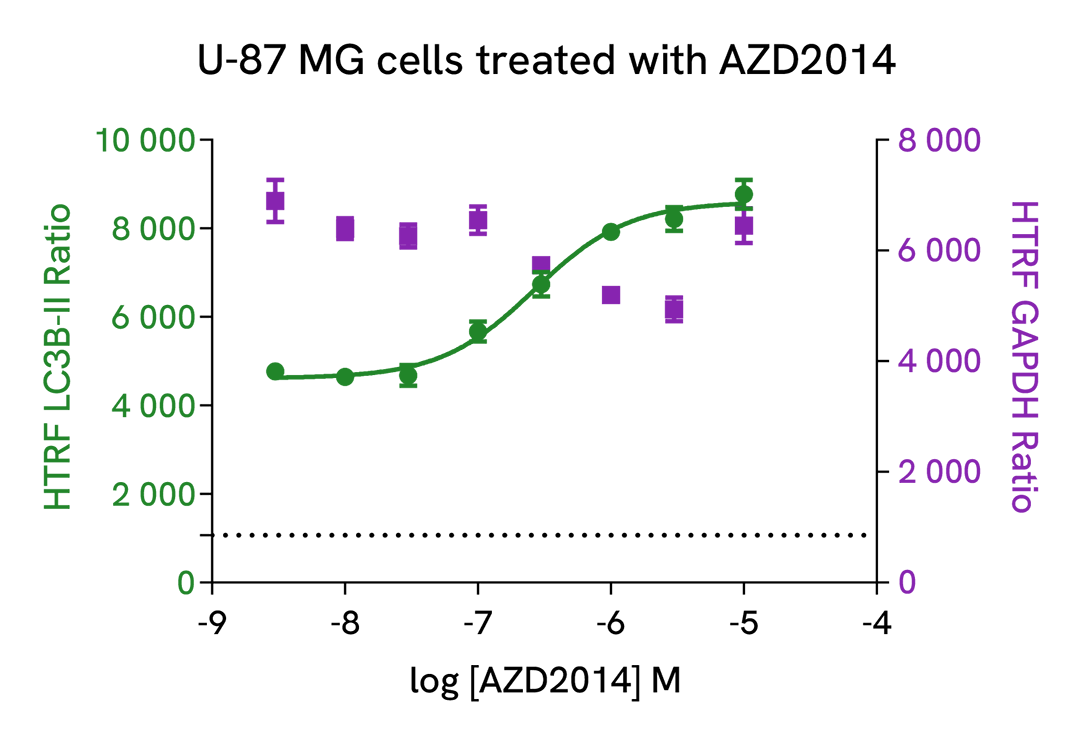
Induction of autophagy with AZD2014, a mTOR inhibitor
U-87 MG cells were plated in a 96-well culture-treated plate (50,000 cells per well) in complete culture medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. Then, cells were then treated with increasing concentrations of AZD2014 (Vistusertib), a mTOR inhibitor for 4 h at 37°C, 5%CO2. Following culture medium removal, cells were lysed with 50 µl of supplemented lysis buffer #3 (1X) + BR (1X) for 30 min at room temperature under gentle shaking. After cell lysis, 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate, then 4 µL of the HTRF LC3B-II detection antibodies were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation at room temperature.
As expected, AZD2014, a potent mTOR inhibitor, induced autophagy activation, leading to a dose-dependent increase of LC3B-II signal. In addition, no significant cytotoxic effects were observed with GAPDH Housekeeping Cellular Kit (Revvity®, Ref. 64GAPDHPEG) in the same experimental conditions.
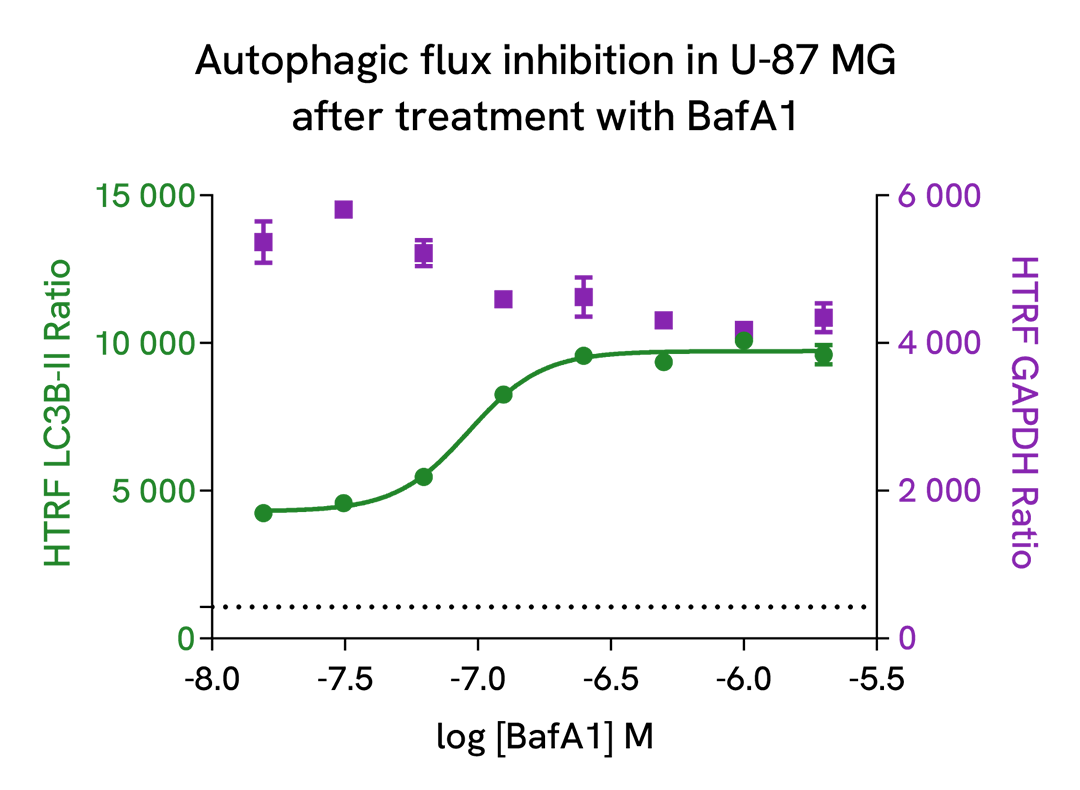
Autophagic flux inhibition with Bafimomycin A1, a vacuolar H(+)-ATPase inhibitor
U-87 MG cells were plated in a 96-well culture-treated plate (25,000 cells per well) in complete culture medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. Then, cells were then treated with increasing concentrations of Bafimomycin A1 (BafA1), a vacuolar H(+)-ATPase inhibitor, for 4 h at 37°C, 5% CO2. Following culture medium removal, cells were lysed with 50 µl of supplemented lysis buffer #3 (1X) + BR (1X) for 30 min at room temperature under gentle shaking. After cell lysis, 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate, then 4 µL of the HTRF LC3B-II detection antibodies were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation at room temperature.
As expected, Bafimomycin A1, a vacuolar H(+)-ATPase inhibitor, inhibited autophagic flux, leading to a dose-dependent increase of LC3B-II signal. In addition, no significant cytotoxic effects were observed with GAPDH Housekeeping Cellular Kit (Revvity®, #64GAPDHPEG) in the same experimental conditions.
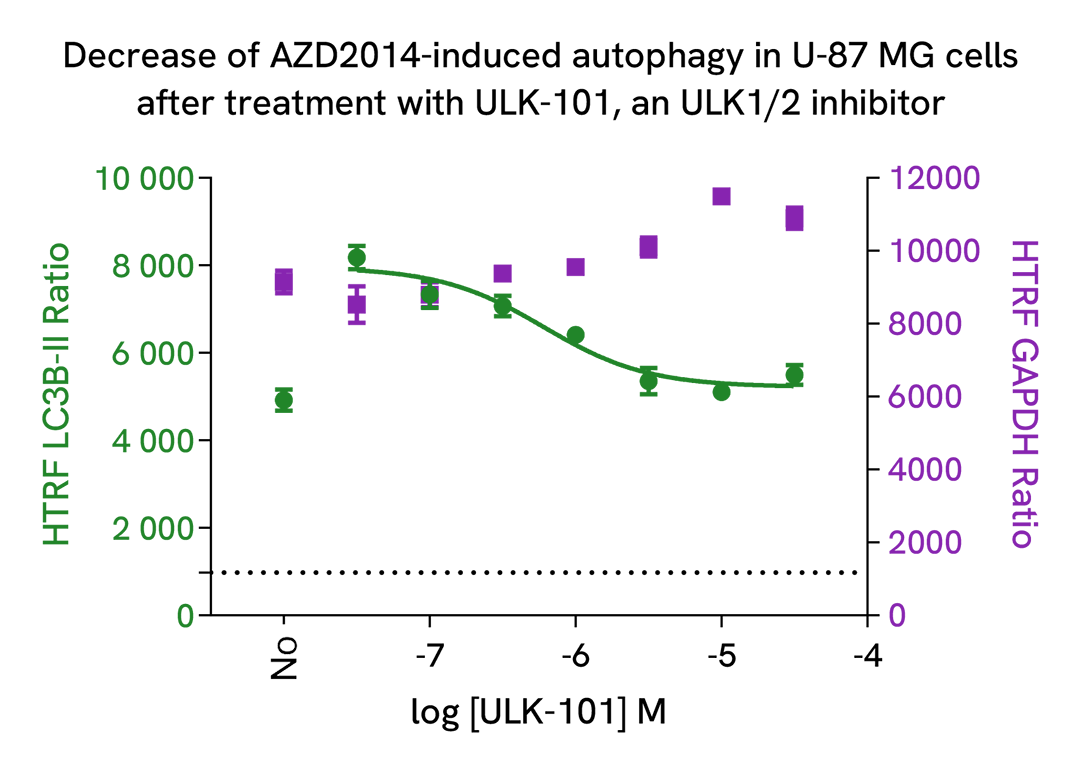
Autophagy inhibition with ULK-101, a potent and selective ULK1/2 inhibitor
U-87 MG cells were plated in a 96-well culture-treated plate (25,000 cells per well) in complete culture medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. Then, cells were then co-treated with 2.5 µM of AZD2014, a mTOR inhibitor, and increasing concentrations of ULK-101, a potent and selective ULK1/2 inhibitor, for 4 h at 37°C, 5%CO2. Following culture medium removal, cells were lysed with 50 µl of supplemented lysis buffer #3 (1X) + BR (1X) for 30 min at room temperature under gentle shaking. After cell lysis, 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate, then 4 µL of the HTRF LC3B-II detection antibodies were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation at room temperature.
As expected, ULK-101, a potent and dual autophagy kinase ULK1/2 inhibitor, repressed autophagy induced by AZD2014, leading to a dose-dependent decrease of LC3B-II signal. In addition, no significant cytotoxic effects were observed with GAPDH Housekeeping Cellular Kit (Revvity®, #64GAPDHPEG) in the same experimental conditions.
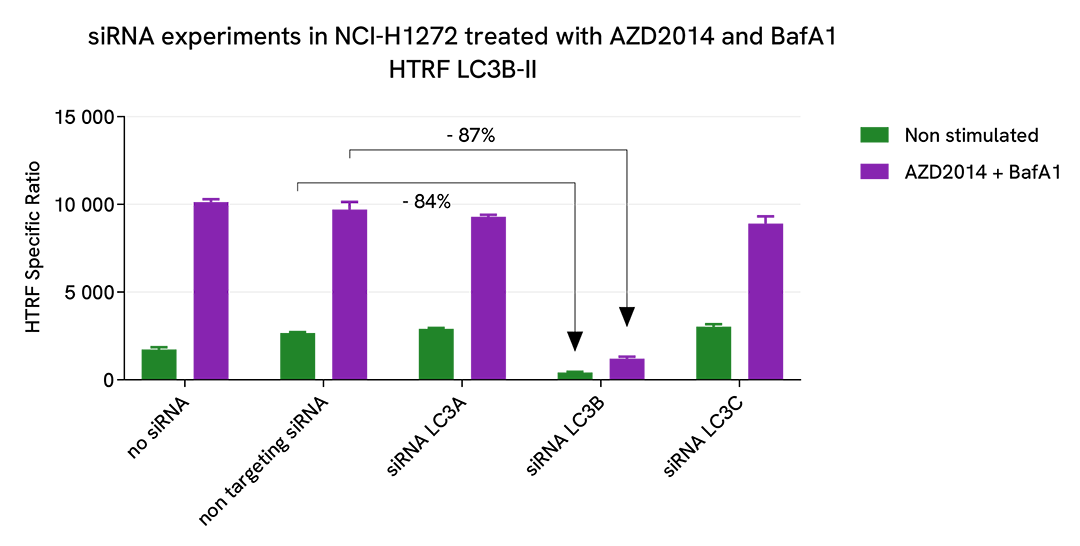
Specificity of LC3B-II assay
NCI-H1272 cells were plated in a 96-well culture plate (10,000 cells/well) in complete culture medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. The day after, the cells were transfected with ON-TARGETplus SMARTPool siRNAs (Horizon Discovery/Revvity) LC3A, LC3B and LC3C isoforms, as well as with a non-targeting siRNA used as negative control using DharmaFECT1 transfection reagent. After a 24h-incubation, the medium was replaced by fresh culture medium, and cells were incubated for an additional 24h-incubation. Then, cells were then treated with 2.5 µM AZD2014 (Vistusertib), a mTOR inhibitor, and 100 nM Bafimomycin A1 (BafA1), a vacuolar H(+)-ATPase inhibitor, for 4 h at 37°C, 5% CO2. Following culture medium removal, cells were lysed with 50 µl of supplemented lysis buffer #3 (1X) + BR (1X) for 30 min at room temperature under gentle shaking. After cell lysis, 16 µL of cell lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate, then 4 µL of the HTRF LC3B-II detection antibodies were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation at room temperature.
The siRNA experiments demonstrate that HTRF detection antibodies specifically measure LC3B isoform and do not recognize the other isoforms. It was found that treatment with the LC3B siRNA induced almost complete HTRF signal loss, while the knockdown of LC3A and LC3C genes did not lead to any significant signal modulation in this assay.
Versatility of LC3B-II assay using various human, mouse and rat cell lines
U-87 MG (human), NIH3T3 (mouse), H4-II-E (rat) cells were plated in a 96-well culture-treated plate (50,000 cells/well) in complete culture medium, and incubated 48 h at 37°C, 5% CO2. Then, cells were then treated with 2.5 µM AZD2014 (Vistusertib), a mTOR inhibitor, and 100 nM Bafimomycin A1 (BafA1), a vacuolar H(+)-ATPase inhibitor, for 4 h at 37°C, 5% CO2. Following culture medium removal, cells were lysed with 1 mL of supplemented lysis buffer #3 (1X) + BR (1X) for 30 min at room temperature under gentle shaking. After cell lysis, 16 µL of cell lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate, then 4 µL of the HTRF LC3B-II detection antibodies were added. The HTRF signal was recorded after an overnight incubation at room temperature.
The HTRF LC3B-II assay efficiently displayed significant positive signals in each tested cell lines, demonstrating its capability to detect LC3II-B protein in human, mouse and rat and its suitability for translational research.
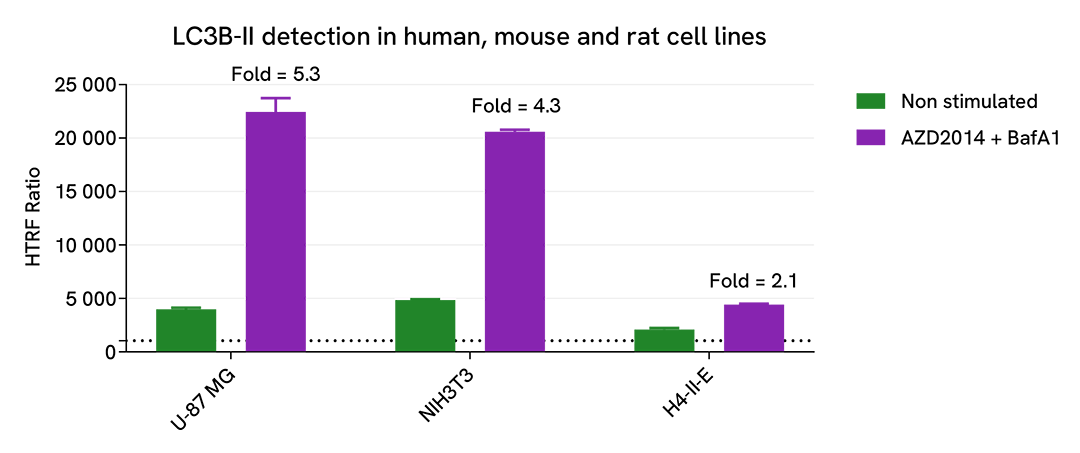
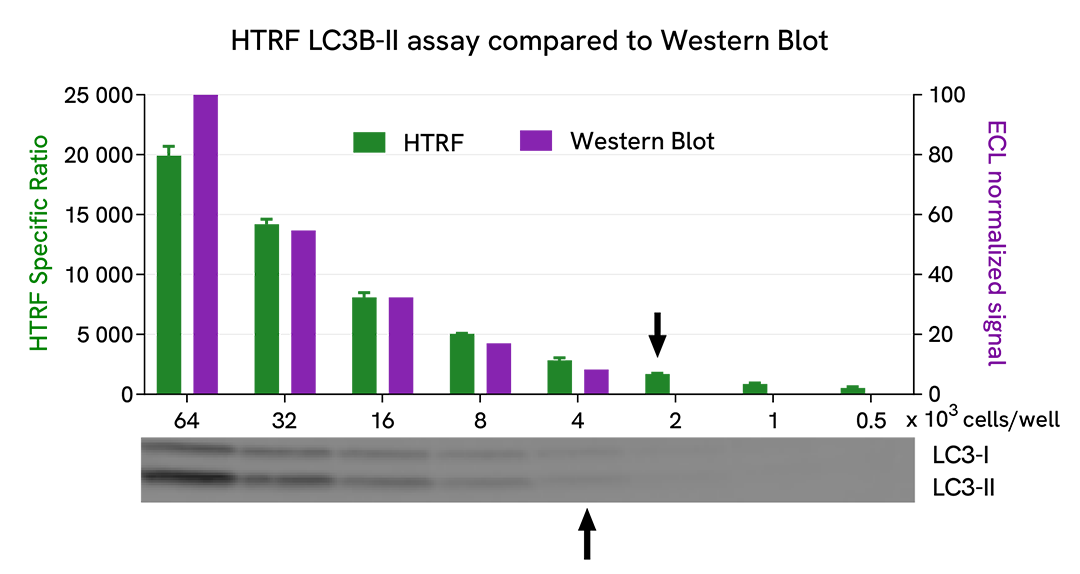
HTRF LC3B-II assay compared to Western Blot
U-87 MG cells were cultured in flasks and incubated 48 h at 37°C, 5% CO2. Then, cells were treated with 2.5 µM of AZD2014 (Vistusertib), a mTOR inhibitor, for 4 h at 37°C, 5% CO2. After culture medium removal, cells were lysed with supplemented lysis buffer #3 (1X) + BR (1X) for 30 min at RT under gentle shaking. Equal amounts of cell lysates (16 µL) were used for a side-by-side comparison of Western Blot and HTRF techniques.
Using the HTRF LC3B-II assay, 2,000 cells/well were enough to detect a significant signal, while 4,000 cells were needed to obtain a minimal chemiluminescent signal using Western Blot. Therefore, in these conditions, the HTRF LC3B-II assay is 2 times more sensitive than Western Blot technique.
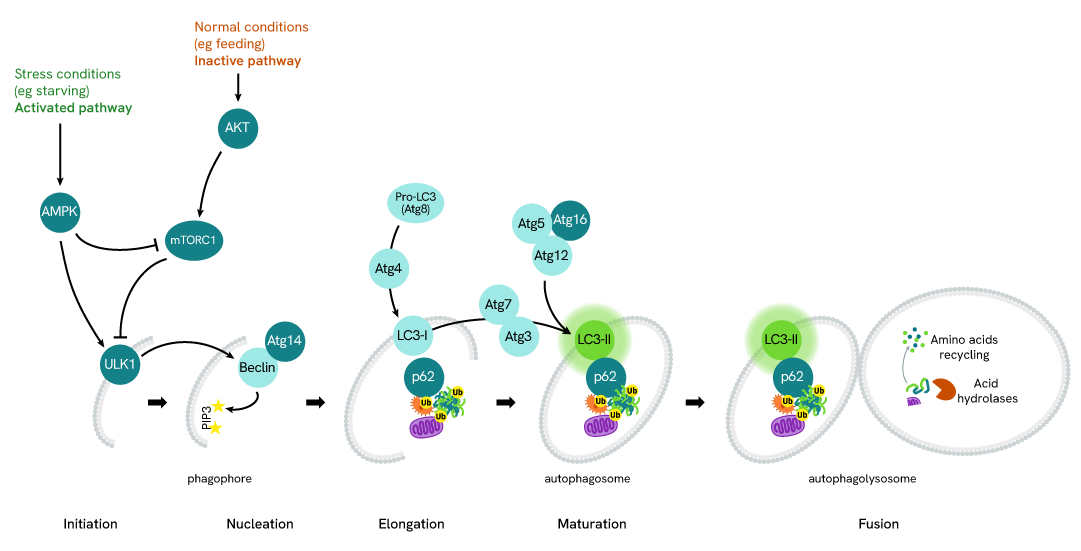
Simplified pathway
LC3B-II in Autophagy
Autophagy is an evolutionary conserved cellular process that occurs in virtually all eukaryotic cells, ranging from yeast to mammals. Autophagy is crucial in the maintenance of homeostasis, being involved in numerous physiological processes including stress responses (e.g. starvation, hypoxia, high temperature), cell growth, and aging. Conversely, dysfunctions in autophagic mechanisms have been associated with diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, infectious diseases, and cardiac and metabolic diseases.
During autophagy, cytoplasmic components, including cytosolic proteins and organelles, are engulfed by autophagosomes. Concomitantly, a cytosolic form of LC3 (LC3-I) is conjugated to phosphatidylethanolamine to form LC3-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate (LC3-II). This conjugate is recruited to autophagosomal membranes. Then, autophagosomes fuse with lysosomes to form autolysosomes, and intra-autophagosomal components are degraded by lysosomal hydrolases. At the same time, LC3-II in autolysosomal lumen is degraded. LC3-II level has been found to be proportional to the amount of autophagosomes and thus LC3-II detection has become the most reliable method for monitoring autophagy and autophagy-related processes.
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
Taking autophagy regulation research a step further
Autophagy regulation is a key molecular process involved in recycling long...
HTRF: unfamiliar territory?
This technical brochure reviews the general principles of HTRF™ and the associated Tag-lite™ technology...
Discover the versatility and precision of Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) technology. Our HTRF portfolio offers a...
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s, are complex disorders that affect millions...
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) offers a promising approach for treating neurodegenerative diseases by selectively degrading...
Your guide for improving cell signaling assay performance
This complete Revvity guide provides you with all the tools you need to...


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























