
AlphaLISA Human PICP (Pro-Collagen 1 C-Terminal Pro-Peptide) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points
AlphaLISA Human PICP (Pro-Collagen 1 C-Terminal Pro-Peptide) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points



The AlphaLISA™ kit enables the cell-based quantitative detection of PICP in cell supernatants. It can be used to measure the expression and secretion of all Pro-collagen type I in cell supernatants.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Protein Quantification |
| Dynamic Range | 21 - 100,000 pg/mL |
| Limit of Detection | 21 pg/mL |
| Limit of Quantification | 66 pg/mL |
| Protocol Time | 1h30 at RT |
| Sample Volume | 5 µL |
The AlphaLISA™ kit enables the cell-based quantitative detection of PICP in cell supernatants. It can be used to measure the expression and secretion of all Pro-collagen type I in cell supernatants.


AlphaLISA Human PICP (Pro-Collagen 1 C-Terminal Pro-Peptide) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points


AlphaLISA Human PICP (Pro-Collagen 1 C-Terminal Pro-Peptide) Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points


Product information
Overview
Collagen Type 1 is a protein present in abundance in the extracellular matrix, where forms cross-linking fibrils that associate in larger collagen fibers to play a role of structural support in connective tissues such as cartilage, bone, tendon, and skin. Due to its very unsoluble nature in its mature form, collagen is expressed and transported as a pro-collagen, in which the mature collagen sequence is flanked by two propetides respectively designated as PINP (Pro-collagen type 1 N-terminal Propeptide) and PICP (Pro-collagen type 1 C-terminal Propeptide). Mature collagen detection and quantification is not possible in immunoassays due to it being unsoluble and sticky. Instead, detection of the whole pro-collagen form or one of the propeptides is a good proxy to quantify the collagen expression in cells. In particular, targeting a propeptide like PICP allows to quantify both pro-collagen that have been expressed but not yet processed into mature collagen, and free PICP which have been cleaved from the mature sequence and are markers of collagen deposited in the extracellular matrix. The present kit is designed for the quantitative detection of Human PICP (Pro-Collagen 1 C-Terminal Pro-Peptide) in supernatants
Formats
- Our 100 assay point kit allows you to run 100 wells in 96-well format, using a 100 µL reaction volume (10 µL of sample).
- Our 500 assay point kit allows you to run 500 wells in 96-well or 384-well format, using a 50 µL reaction volume (5 µL of sample).
- Our 5,000 assay point kit allows you to run 5,000 wells in 96-well or 384-well format, using a 50 µL reaction volume (5 µL of sample).
Features
- No-wash steps, no separation steps
- ELISA alternative technology
- Broad sample compatibility
- Small sample volume
- Results in less than 3 hours
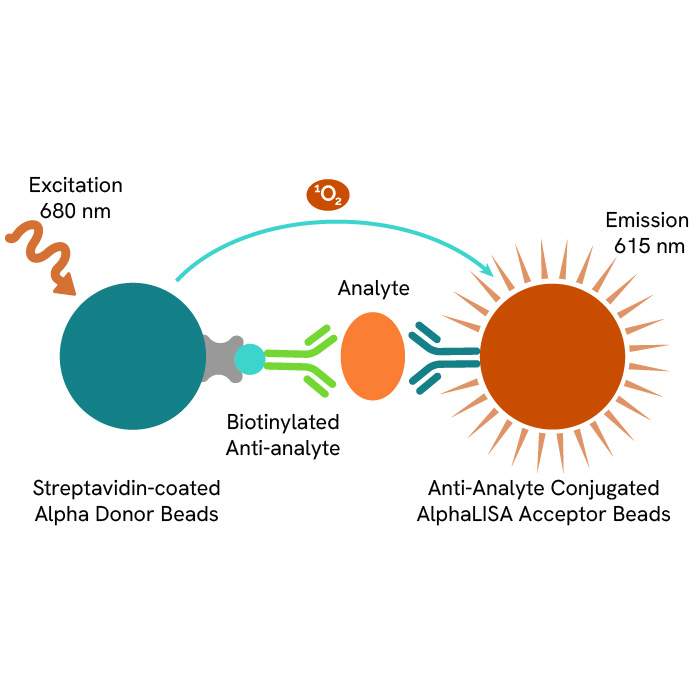
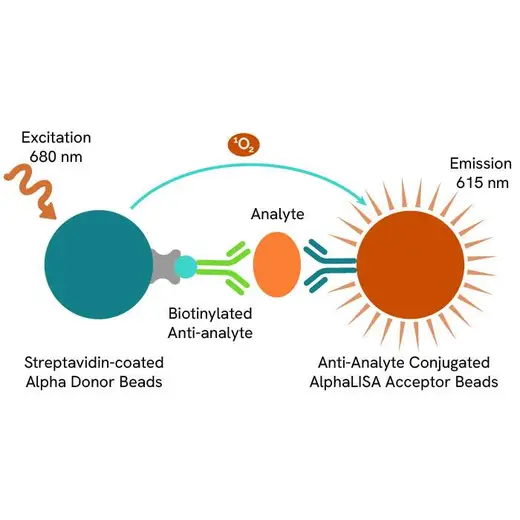
AlphaLISA technology allows the detection of molecules of interest in a no-wash, highly sensitive, quantitative assay. In an AlphaLISA assay, a biotinylated anti-analyte antibody binds to the Streptavidin-coated Donor beads while another anti-analyte antibody is conjugated to AlphaLISA Acceptor beads. In the presence of the analyte, the beads come into close proximity. The excitation of the Donor beads causes the release of singlet oxygen molecules that triggers a cascade of energy transfer in the Acceptor beads, resulting in a sharp peak of light emission at 615 nm.
Specifications
| Application |
Protein Quantification
|
|---|---|
| Automation Compatible |
Yes
|
| Brand |
AlphaLISA
|
| Detection Modality |
Alpha
|
| Dynamic Range |
21 - 100,000 pg/mL
|
| Limit of Detection |
21 pg/mL
|
| Limit of Quantification |
66 pg/mL
|
| Protocol Time |
1h30 at RT
|
| Sample Volume |
5 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Blue Ice
|
| Target |
PICP
|
| Target Class |
Biomarker
|
| Target Species |
Human
|
| Technology |
Alpha
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Oncology
|
| Unit Size |
500 assay points
|
How it works
Principle of the AlphaLISA human PICP assay
The AlphaLISA Human PICP assay is based on an AlphaLISA sandwich immunoassay involving a biotinylated anti-human PICP (hPICP) antibody bound to Streptavidin-coated AlphaLISA Donor beads and an anti-hPICP antibody conjugated to AlphaLISA Acceptor beads. Two antibodies are directed against the hPICP protein. In the presence of the hPICP, both antibodies bind to Human PICP and the beads come into proximity. The excitation of the Donor beads provokes the release of singlet oxygen molecules that triggers a cascade of energy transfer within the Acceptor beads, resulting in emission with λmax at 615 nm. The intensity of the signal is directly proportional to the concentration of hPICP present in the sample (recombinant protein or cell supernatant).

Protocol of the AlphaLISA human PICP assay
The AlphaLISA Human PICP assay can be run in a 96 - or 384-well detection plate (50 µL final). As described here, samples (cell supernatants) or standards are dispensed directly into the assay plate for the detection of human PICP by AlphaLISA reagents. No washing steps are needed. The protocol can be further miniaturized or upscaled by simply resizing each addition volume proportionally.
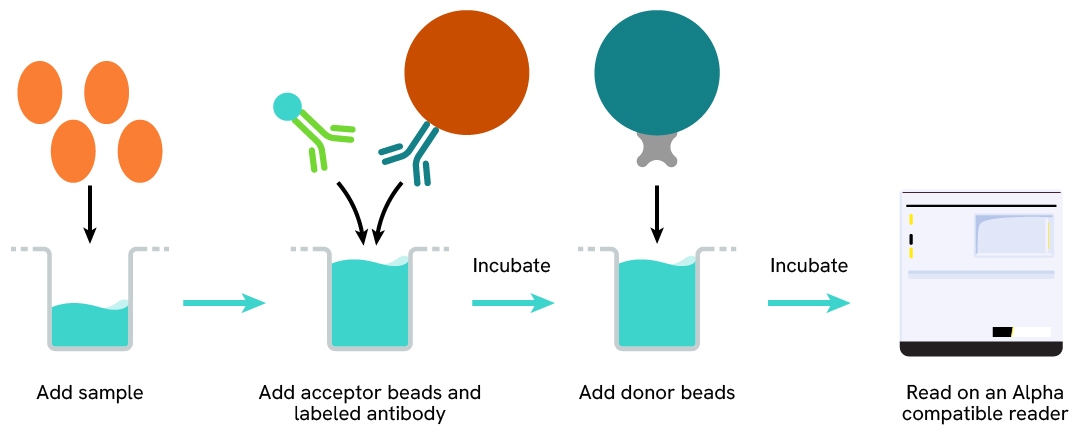
Assay details
Human PICP assay details
| Sample size | 5 µL |
|---|---|
| Final assay volume | 50 µL |
| Time to result | 1.5 hours at RT |
| Kit component | Lyophilized Human PICP, SA-Donor Beads, Biotinylated anti-hPICP, Anti-hPICP conjugated Acceptor Beads, AlphaLISA Immunoassay Buffer |
| Species | Human only |
| LDL | 21 pg/mL |
| LLOQ | 66 pg/mL |
| Dynamic Range | 0,3 – 100000 pg/mL |
Analytical performance
Intra-assay precision table
Samples were cell culture supernatants from fibroblast BJ cells. Each of the 3 samples was measured 24 times, and the % CV was calculated for each sample.
| Sample | [hPICP] (pg/mL) | CV |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 31000 | 9.8 % |
| 2 | 12800 | 5.3 % |
| 3 | 3600 | 4.6 % |
| Mean CV | 6.6 % |
Inter-assay precision table
Samples were cell culture supernatants from fibroblast BJ cells. Each of the samples was measured in 3 independent experiments, and the % CV was calculated for each sample.
| Sample | [hPICP] (pg/mL) | CV |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 43240 | 5.1 % |
| 2 | 14090 | 7.1 % |
| 3 | 4 690 | 5.0 % |
| Mean CV | 5.7 % |
Spike and recovery table
Three known amounts of hPICP protein (~25 822 – 1 442 and 166 pg/mL) were spiked to a dilution of native sample from neonatal foreskin BJ fibroblasts supernatants. The expected concentrations were compared to those measured in order to compute antigen recoveries (acceptance criteria: 80-120%). The results shown in the table below indicate that good recoveries were achieved for all three spikes tested.
| [hPICP] protein (pg/mL) | [hPICP] Spiked Sample (pg/mL) | Expected (pg/mL) | Measured (pg/mL) | Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 166 | 20796 | 20962 | 19054 | 91% |
| 1 442 | 20796 | 22238 | 17947 | 81% |
| 25 822 | 20796 | 46618 | 39994 | 86% |
| Mean Recovery | 86% |
Dilutional linearity table
Cell culture supernatants from fibroblast BJ cells and containing a known concentration of analyte were serially diluted in MEM without FBS. The recovery % obtained from these experiments show the good dilutional linearity of the assay.(dilution test acceptance criteria: 80-120%).
| Sample dilution factor (2) | Expected hPICP (pg/mL) | Measured hPICP (pg/mL) | Dilution Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neat | 35411 | 35411 | - |
| 1/2 | 17706 | 20278 | 115 % |
| 1/4 | 8853 | 10421 | 118 % |
| 1/8 | 4426 | 4865 | 110 % |
| 1/16 | 2213 | 2467 | 111 % |
| 1/32 | 1107 | 1287 | 116 % |
| 1/64 | 553 | 636 | 115 % |
Assay validation
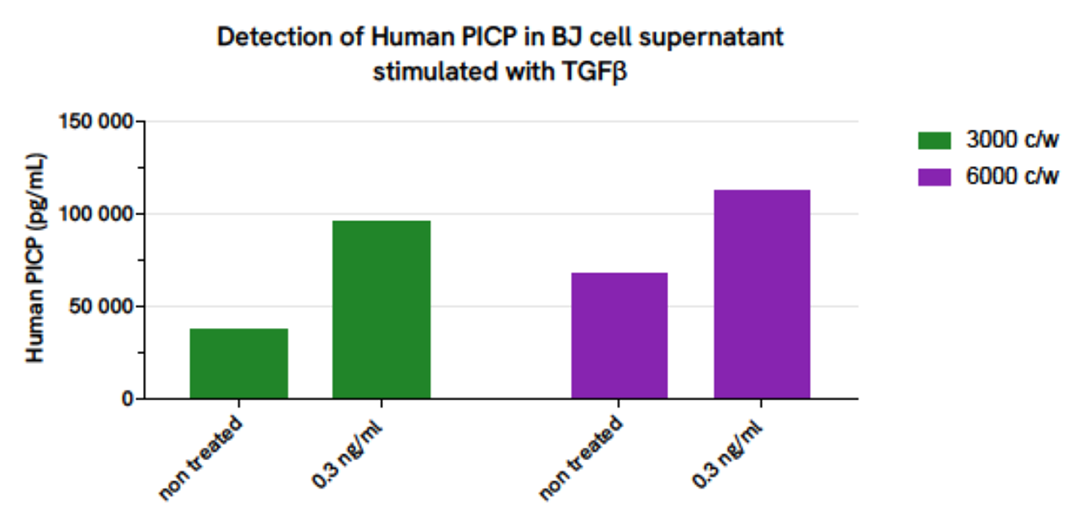
Validation of AlphaLISA Human PICP detection kit on BJ cell supernatant stimulated with TGFβ
BJ fibroblast cells were plated in a 96-well plate (3,000 and 6,000 cells/well) in MEM without FBS during 24 hours at 37°C + 5% CO2. The day after, cells were stimulated with 0,3ng/mL of TGFβ and incubated at 37°C + 5% CO2 during 60 hours. Cell supernatants were collected for the quantitative measurement of secreted hPICP levels.
The hPICP concentration in the sample was quantified using the AlphaLISA Human PICP Detection Kit. As expected, compare to basal hPICP level, a higher amount of hPICP after TGFβ stimulation, is detected.
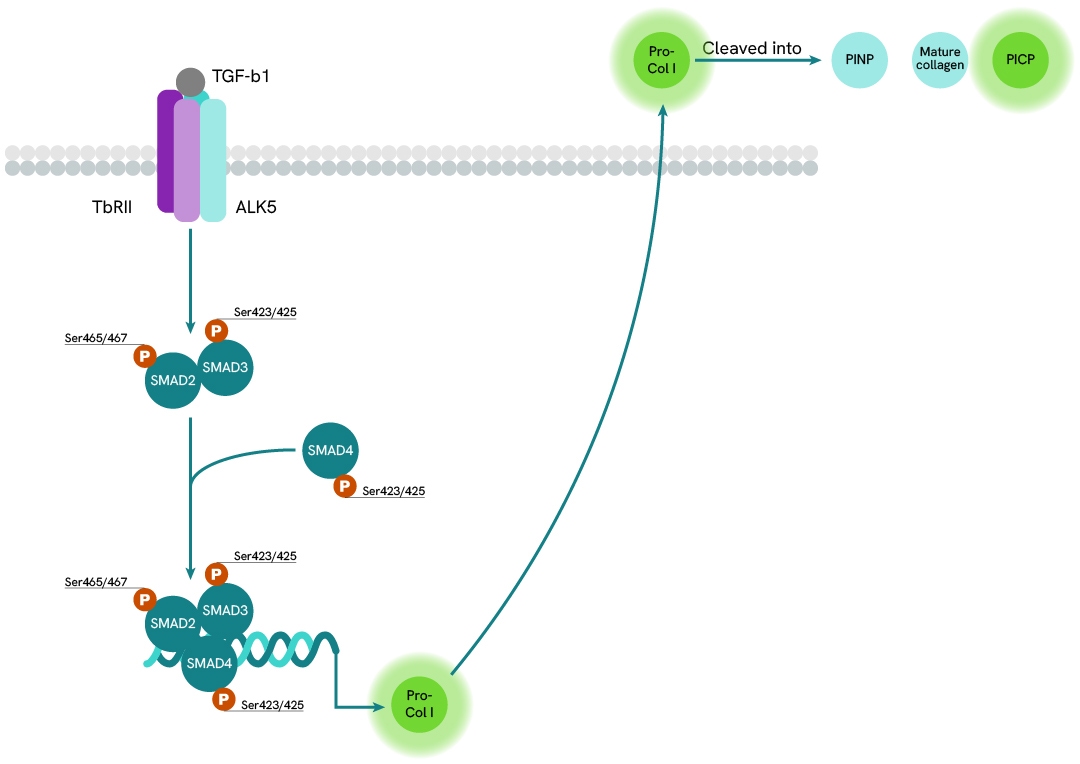
Simplified pathway
Collagen Expression Pathway
TGF-ß signaling is mediated by complexes of TßRI and TßRII which activate the intracellular SMAD3 by phosphorylation. The binding of the TGF-ß ligand on TßRII triggers the recruitment of TßRI into the ligand-receptor complex. TßRII autophosphorylates then transphosphorylates TßRI. Activated TßRI in turn phosphorylates SMAD3 on Ser423 and Ser425, enabling its oligomerization with SMAD4. This complex then translocates to the nucleus and acts as a transcription factor with coactivators and corepressors to regulate the expression of multiple genes involved in cell growth, apoptosis, proliferation, migration, and differentiation, as well as in extracellular matrix remodeling and immune/inflammatory responses. The most notable cellular secretion resulting from this pathway is that of pro-collagen I, a soluble precursor of collagen I flanked by N-terminal and C-terminal propeptides PINP and PICP. This pro-collagen is transported to the membrane and secreted in the extracellular environment where it is cleaved by specialized enzymes, thus acquiring its insolubility and ability to associate in fibers with other similar mature collagens.
SDS, COAs, Manuals and more
Are you looking for technical documents related to the product? We have categorized them in dedicated sections below. Explore now.
- LanguageEnglishCountryUnited States
- LanguageEnglishCountryEU
- Resource TypeManualLanguageEnglishCountry-


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























