
AlphaLISA Human CTLA4 / CD80 Binding Kit, 500 Assay Points
 View All
View All
AlphaLISA Human CTLA4 / CD80 Binding Kit, 500 Assay Points
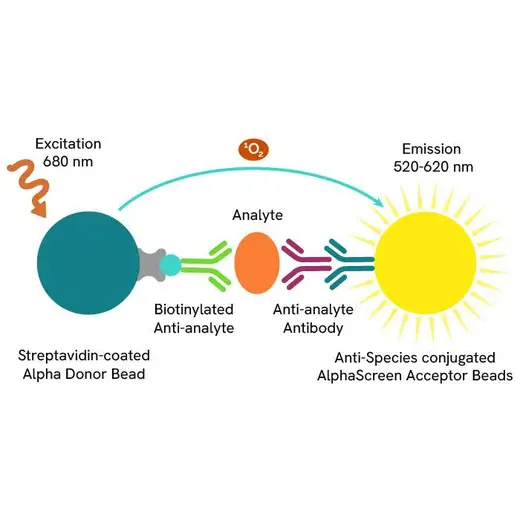



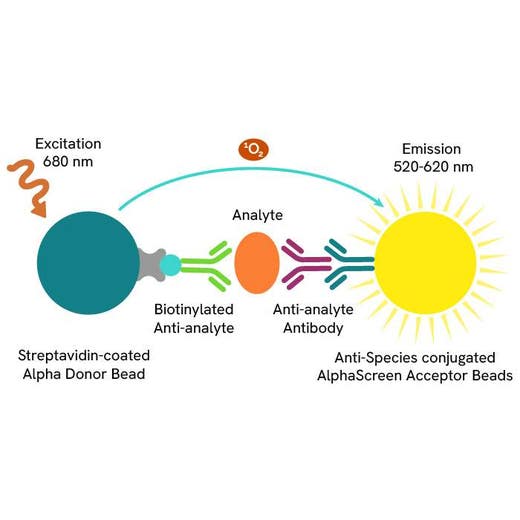



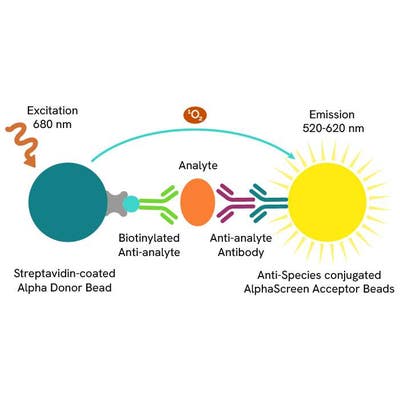
The AlphaLISA™ CTLA-4/CD80 binding kit is designed for the detection of binding activity between human CTLA-4 and CD80, using a fast and simple homogeneous AlphaLISA assay (no wash steps). This assay can be used to screen for small molecules that inhibit binding, as a competitive ligand binding (CLB) assay to screen therapeutic blocking antibodies, and for potency assays.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Protein-Protein Interaction |
| Sample Volume | 10 µL |
The AlphaLISA™ CTLA-4/CD80 binding kit is designed for the detection of binding activity between human CTLA-4 and CD80, using a fast and simple homogeneous AlphaLISA assay (no wash steps). This assay can be used to screen for small molecules that inhibit binding, as a competitive ligand binding (CLB) assay to screen therapeutic blocking antibodies, and for potency assays.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).





AlphaLISA Human CTLA4 / CD80 Binding Kit, 500 Assay Points





AlphaLISA Human CTLA4 / CD80 Binding Kit, 500 Assay Points





Product information
Overview
Features:
- No-wash steps, no separation steps
- ELISA alternative technology
- Sensitive detection
- Broad range of affinities
- High avidity
- Results in less than 3 hours
- Half the time of an ELISA assay
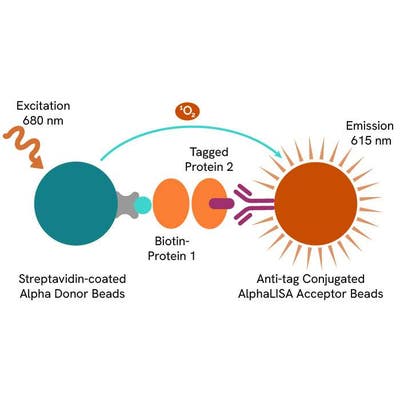
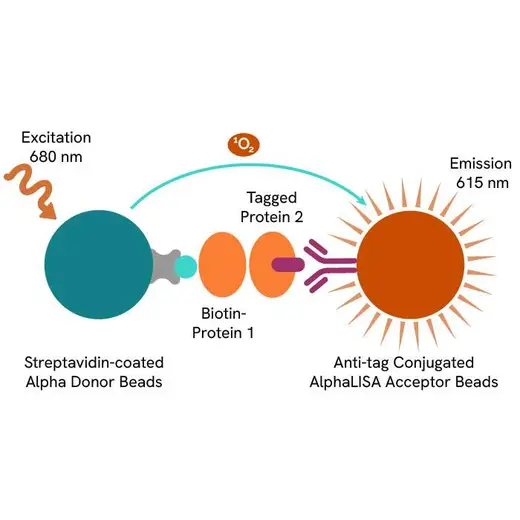
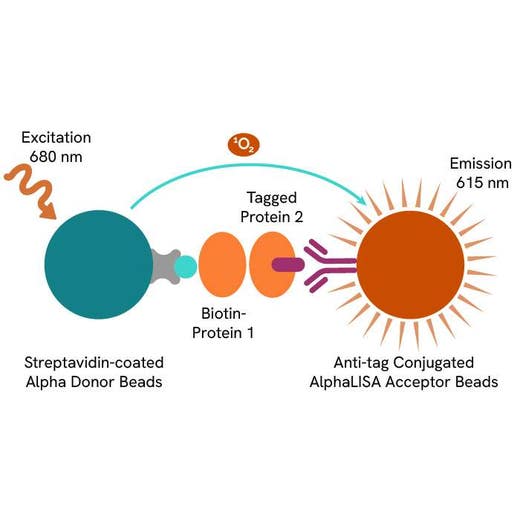
AlphaLISA technology allows the detection of molecules of interest in buffer, cell culture media, serum and plasma in a highly sensitive, quantitative, reproducible and user-friendly mode. In an AlphaLISA assay, a biotinylated CD80 binds to the Streptavidin-coated Alpha Donor beads, while His tagged CTLA-4 is captured by Anti-His AlphaLISA Acceptor beads. When CD80 binding to CTLA-4 happens, Donor beads and Acceptor beads come into close proximity. The excitation of the Donor beads provokes the release of singlet oxygen molecules that triggers a cascade of energy transfer in the Acceptor beads, resulting in a sharp peak of light emission at 615 nm.
Human Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), also known as CD152 (cluster of differentiation 152), is a cell membrane receptor and a member of immunoglobulin superfamily. CTLA-4 is expressed once a T cell becomes active and modulates T cell signals by blocking the CD80 (B7.1) and CD86 (B7.2) ligands from binding to CD28. CTLA-4, functioning as an immune checkpoint, downregulates T cell immune responses. Because of its profound inhibitory role blocking CTLA-4 and CD80 or CD86 binding has been considered as promising therapeutic target for human autoimmune disease and cancers.
Specifications
| Application |
Protein-Protein Interaction
|
|---|---|
| Automation Compatible |
Yes
|
| Brand |
AlphaLISA
|
| Detection Modality |
Alpha
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
10 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Blue Ice
|
| Target |
CTLA4,CD80
|
| Target Class |
Binding Assay
|
| Target Species |
Human
|
| Technology |
Alpha
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Immuno-oncology
|
| Unit Size |
500 Assay Points
|
Video gallery

AlphaLISA Human CTLA4 / CD80 Binding Kit, 500 Assay Points

AlphaLISA Human CTLA4 / CD80 Binding Kit, 500 Assay Points

Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
A single White Paper for a review of immuno-oncology
Immuno-oncology, the field which stimulates a individual's own immunity in...
Advance your autoimmune disease research and benefit from Revvity broad offering of reagent technologies
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has transformed the field of immuno-oncology providing a novel approach to treating...


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























