
AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human & Mouse Phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) Detection Kit, 100 Assay Points

 View All
View All
AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human & Mouse Phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) Detection Kit, 100 Assay Points
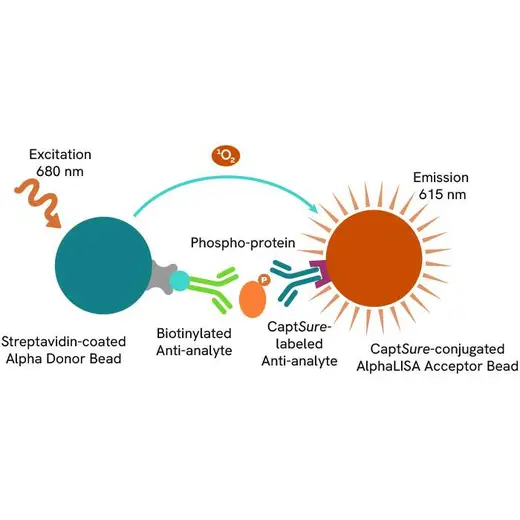











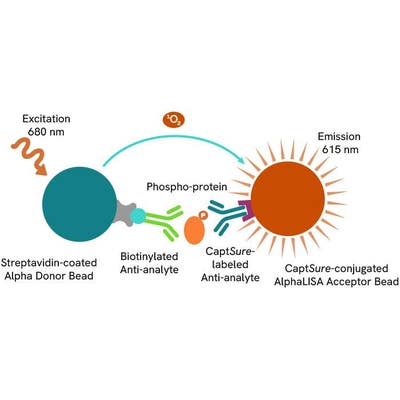
The AlphaLISA™ SureFire® Ultra™ Human and Mouse Phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) assay is a sandwich immunoassay for quantitative detection of phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) in cellular lysates using Alpha Technology.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Cell Signaling |
| Sample Volume | 30 µL |
The AlphaLISA™ SureFire® Ultra™ Human and Mouse Phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) assay is a sandwich immunoassay for quantitative detection of phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) in cellular lysates using Alpha Technology.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).







AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human & Mouse Phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) Detection Kit, 100 Assay Points







AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human & Mouse Phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) Detection Kit, 100 Assay Points







Product information
Overview
Sequestome-1 or ubiquitin binding protein p62 (SQSTM1 p62) is an autophagosome cargo protein that targets other proteins that bind to it for selective autophagy. SQSTM1 p62 is an adaptor protein that has an increased affinity for ubiquitin chains after phosphorylation, thus enabling SQSTM1 p62 to bind to ubiquitinated cargo proteins. Ubiquitinated proteins or ubiquitin-coated mitochondria associated with SQSTM1 p62 proteins are taken away in phagosomes, whose content is cleared out after lysosomal fusion. SQSTM1 p62 is implicated in Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, NASH, and numerous types of cancer.
The AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human and Mouse Phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) is a sandwich immunoassay for the quantitative detection of phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) in cellular lysates, using Alpha Technology.
Formats:
- The HV (high volume) kit contains reagents to run 100 wells in 96-well format, using a 60 μL reaction volume.
- The 500-point kit contains enough reagents to run 500 wells in 384-well format, using a 20 μL reaction volume.
- The 10,000-point kit contains enough reagents to run 10,000 wells in 384-well format, using a 20 μL reaction volume.
- The 50,000-point kit contains enough reagents to run 50,000 wells in 384-well format, using a 20 μL reaction volume.
AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra kits are compatible with:
- Cell and tissue lysates
- Antibody modulators
- Biotherapeutic antibodies
Alpha SureFire kits can be used for:
- Cellular kinase assays
- Receptor activation studies
- Screening
Specifications
| Application |
Cell Signaling
|
|---|---|
| Automation Compatible |
Yes
|
| Brand |
AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra
|
| Detection Modality |
Alpha
|
| Lysis Buffer Compatibility |
Lysis Buffer
|
| Molecular Modification |
Phosphorylation
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
30 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Blue Ice
|
| Target |
SQSTM1 p62
|
| Target Class |
Phosphoproteins
|
| Target Species |
Human
Mouse
|
| Technology |
Alpha
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Neuroscience
Oncology
|
| Unit Size |
100 Assay Points
|
Image gallery






AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human & Mouse Phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) Detection Kit, 100 Assay Points






AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human & Mouse Phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) Detection Kit, 100 Assay Points






Video gallery

AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human & Mouse Phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) Detection Kit, 100 Assay Points

AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human & Mouse Phospho-SQSTM1 p62 (Ser351) Detection Kit, 100 Assay Points

Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
Therapeutic antibodies directed to cell surface receptors are increasingly being developed as treatments for a variety of diseases...
The measurement of protein phosphorylation is a useful tool for measuring the modulation of receptor activation by both antibodies...


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























