
AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human Total Cyclin E1 Detection Kit, 500 Assay Points
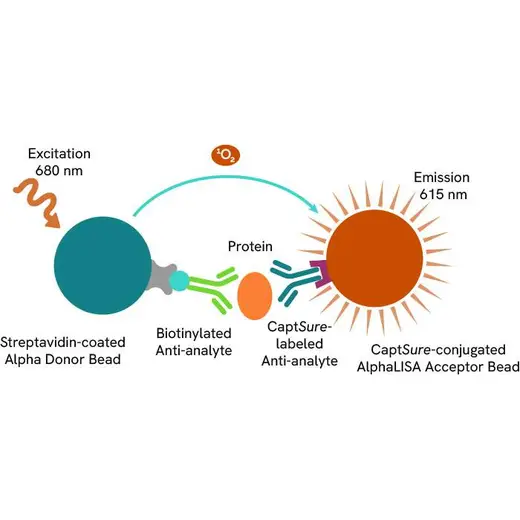





The AlphaLISA™ SureFire® Ultra™ Human Total Cyclin E1 assay is a sandwich immunoassay for quantitative detection of total cyclin E1 in cellular lysates using Alpha Technology.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).
Product information
Overview
Cyclin E1 (CCNE1) is a member of the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members have various roles in the cell cycle. CCNE1 forms a complex with cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) and acts as a regulatory subunit. CDK2 is required for cell cycle G1/S transition. Overexpression of CCNE1 has been observed in many tumors, such as breast, ovarian, endometrial, and bladder cancer.
The AlphaLISA SureFire Human Total Cyclin E1 Detection Kit is a sandwich immunoassay for the quantitative detection of total Cyclin E1 in cellular lysates, using Alpha Technology.
Formats
- The HV (high volume) kit contains reagents to run 100 wells in 96-well format, using a 60 μL reaction volume.
- The 500-point kit contains enough reagents to run 500 wells in 384-well format, using a 20 μL reaction volume.
- The 10,000-point kit contains enough reagents to run 10,000 wells in 384-well format, using a 20 μL reaction volume.
- The 50,000-point kit contains enough reagents to run 50,000 wells in 384-well format, using a 20 μL reaction volume.
AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra kits are compatible with
- Cell and tissue lysates
- Antibody modulators
- Biotherapeutic antibodies
Alpha SureFire kits can be used for
- Cellular kinase assays
- Receptor activation studies
- Screening
Specifications
| Application |
Protein Analysis & Detection
Protein Detection
|
|---|---|
| Assay Target |
Cyclin E1
|
| Assay Target Class |
Phospho-protein
|
| Assay Technology |
Alpha
|
| Automation Compatible |
Yes
|
| Brand |
AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra
|
| Detection Method |
Alpha
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Blue Ice
|
| Target Species |
Human
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Oncology
|
| Unit Size |
500 Assay Points
|
Video gallery


Resources
The cell cycle is tightly regulated by key proteins like Cyclin D1, which forms complexes to initiate progression through phases...
SDS, COAs, Manuals and more
Are you looking for technical documents related to the product? We have categorized them in dedicated sections below. Explore now.
-
LanguageEnglishCountryUnited States
-
LanguageEnglishCountryEU
-
Lot numberU18634Lot dateSeptember 24, 2024
-
Lot numberU17942Lot dateApril 16, 2024
-
Lot numberU17595Lot dateJanuary 24, 2024
-
Lot number-Lot date-
-
Resource typeManualLanguageEnglishCountry-


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.



































