
AlphaLISA Human Neurofilament L (NF-L) Detection Kit, 5,000 Assay Points
AlphaLISA Human Neurofilament L (NF-L) Detection Kit, 5,000 Assay Points



The AlphaLISA™ Human Neurofilament Light (NF-L) Kit is designed for the simple and rapid quantification of human NF-L in cell supernatants.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Protein Quantification |
The AlphaLISA™ Human Neurofilament Light (NF-L) Kit is designed for the simple and rapid quantification of human NF-L in cell supernatants.


AlphaLISA Human Neurofilament L (NF-L) Detection Kit, 5,000 Assay Points


AlphaLISA Human Neurofilament L (NF-L) Detection Kit, 5,000 Assay Points


Product information
Overview
Neurofilament Light chain protein, also known as Neurofilament Light polypeptide, NF-L, NFL or NEFL is a member of intermediate filament protein family, selectively expressed in neurons. NF-L (68 kDa) associated with neurofilament-heavy chain (NF-H, 200 kDa), medium chain (NF-M, 125 kDa) and alpha-internexin, forms the structure of axons. Depending on conditions, different levels of NF-L are released during brain development, maturation, aging and in numerous neurodegenerative diseases proportionally to the degree of axonal damage. Many studies have demonstrated that NF-L can be used as a biomarker for disease monitoring and more broadly as a neuronal damage marker but also to check the differentiation into neurons in IPSc models for example.
Formats
- Our 100 assay point kit allows you to run 100 wells in 96-well format, using a 100 µL reaction volume (10 µL of sample).
- Our 500 assay point kit allows you to run 500 wells in 96-well or 384-well format, using a 50 µL reaction volume (5 µL of sample).
- Our 5,000 assay point kit allows you to run 5,000 wells in 96-well or 384-well format, using a 50 µL reaction volume (5 µL of sample).
Features
- No-wash steps, no separation steps
- ELISA alternative technology
- Sensitive detection
- Broad sample compatibility
- Small sample volume
- Results in less than 3 hours
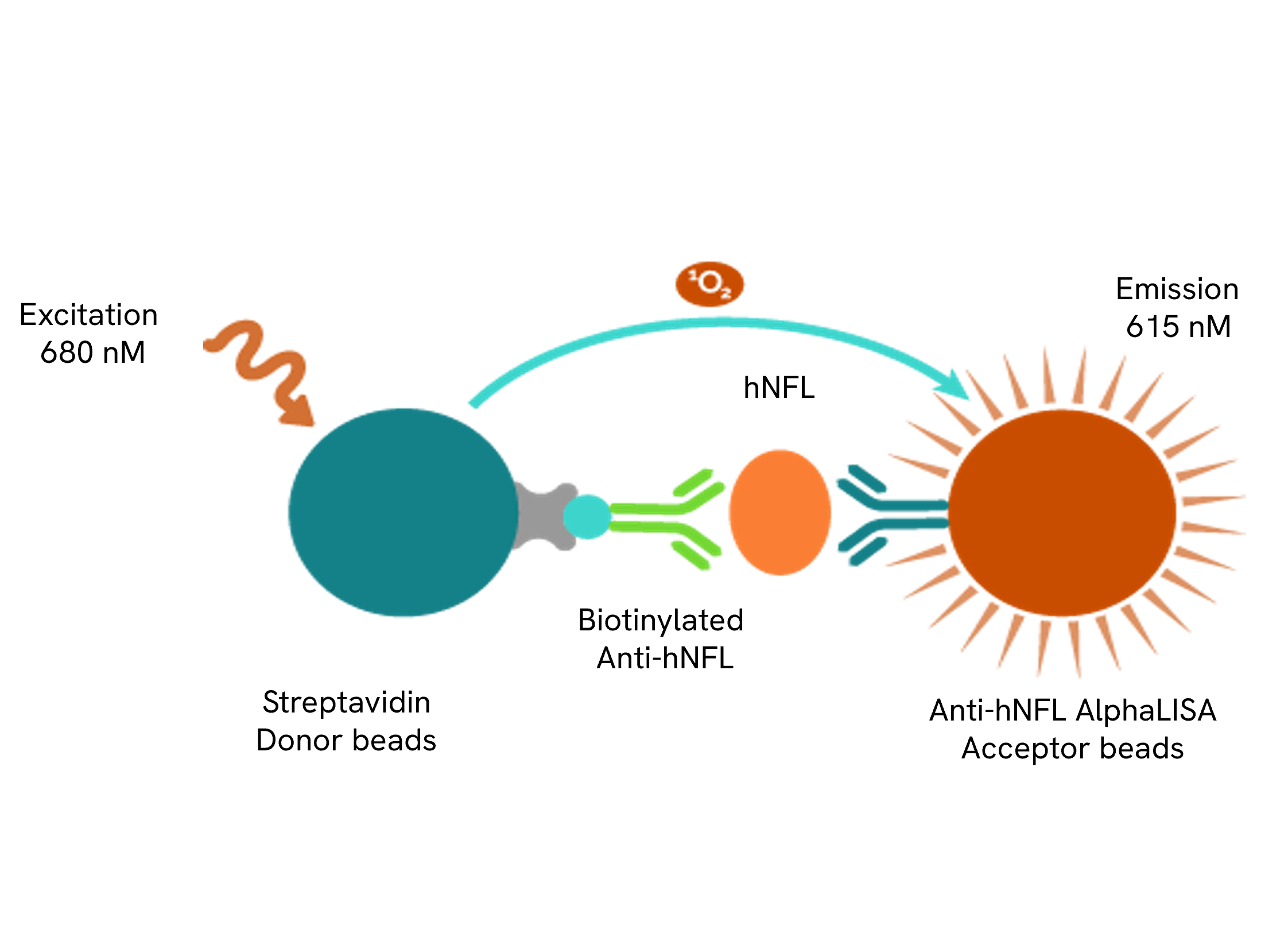
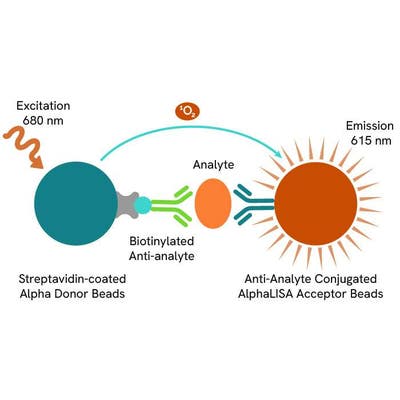
AlphaLISA technology allows the detection of molecules of interest in a no-wash, highly sensitive, quantitative assay. In an AlphaLISA assay, a biotinylated anti-analyte antibody binds to the Streptavidin-coated Donor beads while another anti-analyte antibody is conjugated to AlphaLISA Acceptor beads. In the presence of the analyte, the beads come into close proximity. The excitation of the Donor beads causes the release of singlet oxygen molecules that triggers a cascade of energy transfer in the Acceptor beads, resulting in a sharp peak of light emission at 615 nm.
Specifications
| Application |
Protein Quantification
|
|---|---|
| Automation Compatible |
Yes
|
| Brand |
AlphaLISA
|
| Detection Modality |
Alpha
|
| Host Species |
Human
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Blue Ice
|
| Target |
Neurofilament L
|
| Target Class |
Cytokines
|
| Target Species |
Human
|
| Technology |
Alpha
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Neuroscience
|
| Unit Size |
5,000 assay points
|
How it works
Principle of the AlphaLISA human Neurofilament Light chain assay
The AlphaLISA Neurofilament Light chain (NF-L) assay is based on an AlphaLISA sandwich immunoassay involving a biotinylated anti-hNF-L antibody bound to Streptavidin-coated AlphaLISA Donor beads and an anti-NF-L antibody conjugated to AlphaLISA Acceptor beads. Two antibodies are directed against the hNF-L protein. In the presence of the hNF-L, both antibodies bind to hNF-L and the beads come into proximity. The excitation of the Donor beads provokes the release of singlet oxygen molecules that triggers a cascade of energy transfer within the Acceptor beads, resulting in emission with λmax at 615 nm. The intensity of the signal is directly proportional to the concentration of hNF-L present in the sample (cell supernatant).

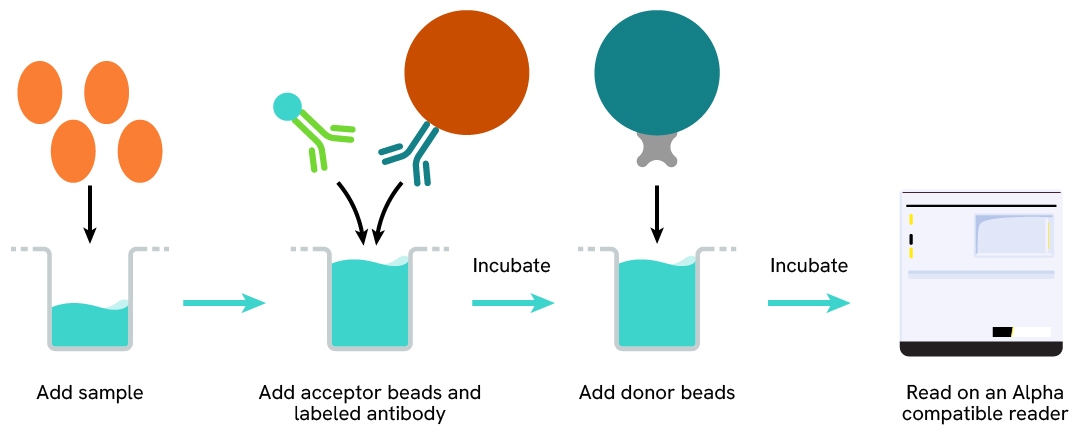
Protocol of the AlphaLISA human Neurofilament Light chain assay
The AlphaLISA Neurofilament Light chain (NF-L) assay can be run in a 96- or 384-well detection plate (50 µL final). As described here, samples (cell supernatants) or standards are dispensed directly into the assay plate for the detection of human NF-L by AlphaLISA reagents. No washing steps are needed. The protocol can be further miniaturized or upscaled by simply resizing each addition volume proportionally.
Assay details
Human Neurofilament Light chain assay details
| Sample size | 10 µL |
|---|---|
| Final assay volume | 100 µL |
| Time to result | 1.5 hours at RT |
| Kit component | Lyophilized hNF-L, SA-Donor Beads, Biotinylated anti-hNF-L, Anti-hNF-L conjugated Acceptor Beads, AlphaLISA Immunoassay Buffer |
| Species | Human only |
| LDL | 120.5 pg/mL |
| LLOQ | 356.6 pg/mL |
| Dynamic Range | 356.6 – 631,382 pg/mL |
Analytical performance
Intra-assay precision table
Each of the 3 samples was measured 24 times, and the % CV was calculated for each sample. Samples were cell culture supernatant of the neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y.
| Sample | [hNF-L] (pg/mL) | CV |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 28944 | 12.2% |
| 2 | 15517 | 5.4% |
| 3 | 3180 | 5.5% |
| Mean CV | 7,7% |
Inter-assay precision table
Each of the samples was measured in 3 independent experiments, and the % CV was calculated for each sample. Samples were cell culture supernatant of the neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y.
| Sample | [hNF-L] (pg/mL) | CV |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18144 pg/mL | 8.7% |
| 2 | 9827 pg/mL | 9.2% |
| 3 | 2556 pg/mL | 8.4% |
| Mean CV | 8.7% |
Spike and recovery table
Three known amounts of hNF-L were spiked into three SH-SY5Y supernatant 2330 -110925 and 783161 pg/mL). The spiked samples were diluted to 2- fold, using cell culture medium, resulting in 19676 -9562 and 5218 pg/mL in 2x diluted supernatant samples. The samples were assayed along with the standard prepared in cell culture medium and the expected concentrations were compared to those measured in order to compute antigen recoveries (acceptance criteria: 85-115%). The results shown in the table below indicate that excellent recoveries were achieved for all three spikes tested.
| [hNFL] Standard (pg/mL) | [hNF-L]Spiked sample (pg/mL) | Expected (pg/mL) | Measured (pg/mL) | Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2330 | 19676 | 22006 | 21016 | 96% |
| 9562 | 11892 | 12076 | 102% | |
| 5218 | 7547 | 7315 | 97% | |
| 110925 | 19676 | 130600 | 125936 | 96% |
| 9562 | 120487 | 113659 | 94% | |
| 5218 | 116142 | 110742 | 95% | |
| 783161 | 19676 | 802836 | 793628 | 99% |
| 9562 | 792723 | 770292 | 97% | |
| 5218 | 788378 | 787334 | 100% | |
| Mean CV | 99% |
Dilutional linearity table
A cell supernatant collected from SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells and containing a known concentration of analyte was serially diluted in DMEM + 10% FBS. The assay was performed on serially diluted samples, along with a standard curve prepared in the same cell culture medium. The recovery % obtained from these experiments show the good dilutional linearity of the assay.
| Sample dilution factor (2) | Expected hNF-L (pg/mL) | Observed hNF-L (pg/mL) | Dilution recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 | 3328.4 | 2825.9 | - |
| 1/4 | 1664.2 | 1361.9 | 96% |
| 1/8 | 832.1 | 675.2 | 96% |
| 1/16 | 416.0 | 296.2 | 84% |
| 1/32 | 208.0 | 163.5 | 93% |
| 1/64 | 88.3 | 97.0 | 110% |
Specificity table
Cross reactivities were assessed using recombinant proteins from the Neurofilament family (medium, heavy chains) or mouse neurofilament light chain from Neuro2a neuroblastoma cells. Proteins were tested up to 1,000,000 pg/mL or neat and standard curves were generated for each protein diluted in the kit diluent for recombinant proteins or cell culture medium for supernatant.
Percentage recovery was computed by comparing the measured Interpolated concentration versus the theoretical one. The assay is human specific for Neurofilament light chain.
| Proteins | Cross reactivity (%) |
|---|---|
| Human NF-L | 100% |
| Human NF-M | 0% |
| Human NF-H | 0% |
| Mouse NF-L | 0% |
Assay validation
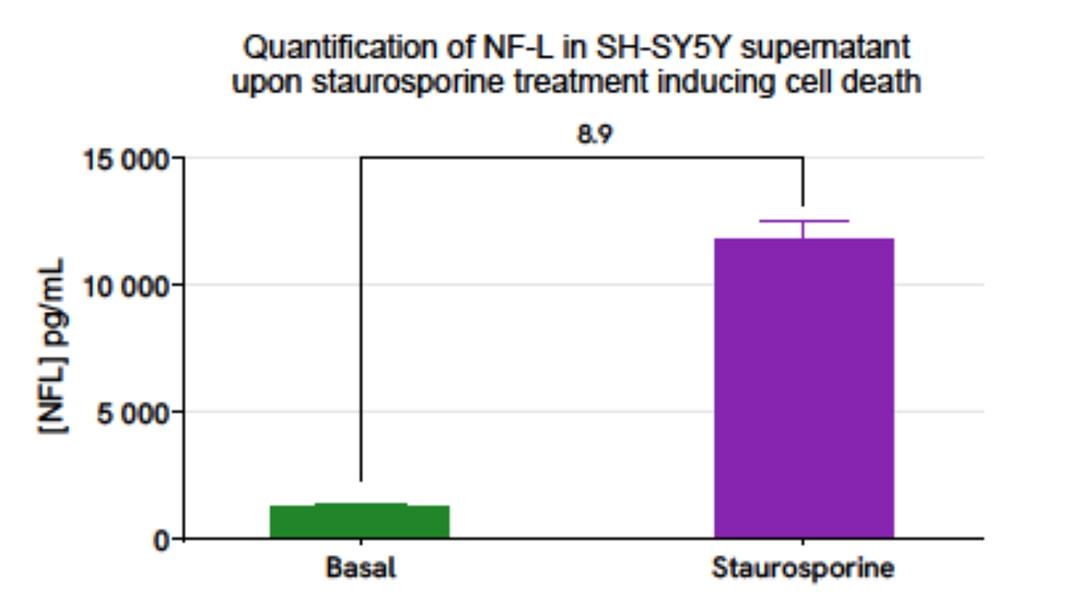
Validation of AlphaLISA Human NF-L detection kit on SH-SY5Y supernatant
The human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y was plated in a 96-well plate (25,000 cells/well). The day after, cells were treated overnight with 50 µL of Staurosporine (0.5 µM, Overnight) diluted in complete culture medium compared to control. Cell supernatants were collected for the quantitative measurement of secreted NF-L levels.
The NF-L concentration in the sample was estimated using the AlphaLISA Human NF-L Detection Kit. As expected, Staurosporine treatment resulted to cellular death, mimicking neurodegeneration, increasing NF-L release into the supernatant compared to basal condition.
SDS, COAs, Manuals and more
Are you looking for technical documents related to the product? We have categorized them in dedicated sections below. Explore now.
- LanguageEnglishCountryUnited States
- LanguageEnglishCountryEU
- Resource TypeManualLanguageEnglishCountry-


Recently viewed

How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























