
AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human and Mouse Phospho-BAD (Ser136) Detection Kit, 100 Assay Points
AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human and Mouse Phospho-BAD (Ser136) Detection Kit, 100 Assay Points



The AlphaLISA™ SureFire® Ultra™ Human and Mouse Phospho-BAD (Ser136) assay is a sandwich immunoassay for quantitative detection of phospho-BAD in cellular lysates using Alpha Technology.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Protein Quantification |
The AlphaLISA™ SureFire® Ultra™ Human and Mouse Phospho-BAD (Ser136) assay is a sandwich immunoassay for quantitative detection of phospho-BAD in cellular lysates using Alpha Technology.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. All products to be used in accordance with applicable laws and regulations including without limitation, consumption and disposal requirements under European REACH regulations (EC 1907/2006).


AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human and Mouse Phospho-BAD (Ser136) Detection Kit, 100 Assay Points


AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human and Mouse Phospho-BAD (Ser136) Detection Kit, 100 Assay Points


Product information
Overview
Bcl-2-associated death promoter (BAD) is a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family of proteins. BAD promotes apoptosis by binding to and neutralizing anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL, thereby promoting cell death. The function of BAD is regulated through phosphorylation; when phosphorylated, it is sequestered in the cytoplasm, becomes inactive and binds to 14-3-3 proteins, preventing it from inducing apoptosis. Dysregulation of BAD can contribute to cancer progression due to impaired apoptosis.
The AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra Human and Mouse Phospho-BAD (Ser136) Detection Kit is a sandwich immunoassay for the quantitative detection of phospho-BAD (Ser136) in cellular lysates, using Alpha Technology.
Formats:
- The HV (high volume) kit contains reagents to run 100 wells in 96-well format, using a 60 μL reaction volume.
- The 500-point kit contains enough reagents to run 500 wells in 384-well format, using a 20 μL reaction volume.
- The 10,000-point kit contains enough reagents to run 10,000 wells in 384-well format, using a 20 μL reaction volume.
- The 50,000-point kit contains enough reagents to run 50,000 wells in 384-well format, using a 20 μL reaction volume.
AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra kits are compatible with:
- Cell and tissue lysates
- Antibody modulators
- Biotherapeutic antibodies
Alpha SureFire Ultra kits can be used for:
- Cellular kinase assays
- Receptor activation studies
- Screening
Specifications
| Application |
Protein Quantification
|
|---|---|
| Automation Compatible |
Yes
|
| Brand |
AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra
|
| Detection Modality |
Alpha
|
| Host Species |
Human
Mouse
|
| Molecular Modification |
Phosphorylation
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Blue Ice
|
| Target |
BAD
|
| Target Class |
Phosphoproteins
|
| Target Species |
Human
|
| Technology |
Alpha
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Oncology
|
| Unit Size |
100 Assay Points
|
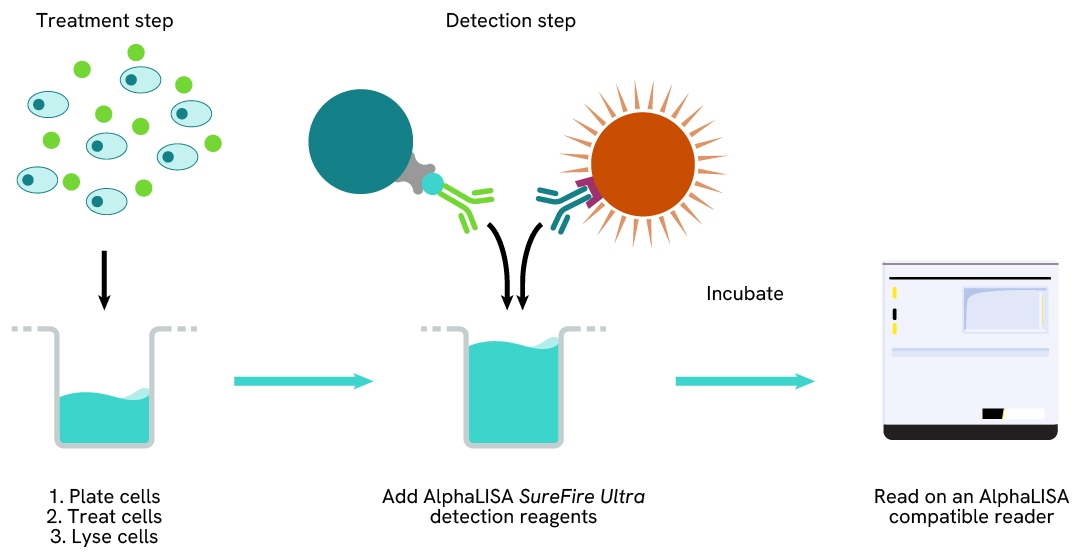
How it works
Phospho-AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra assay principle
The Phospho-AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra assay measures a protein target when phosphorylated at a specific residue.
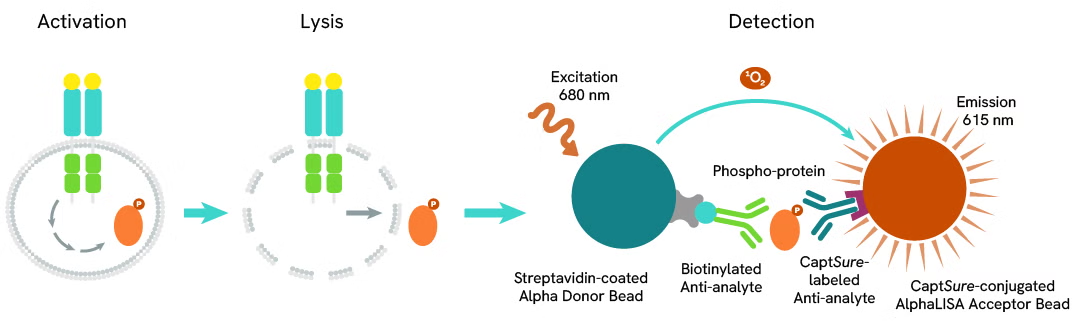
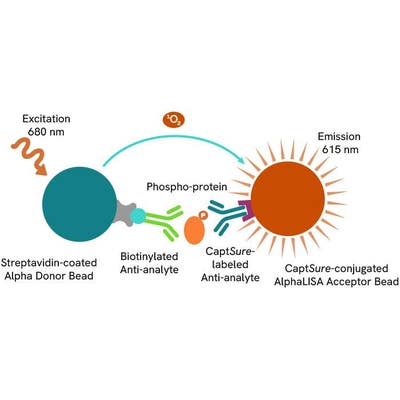
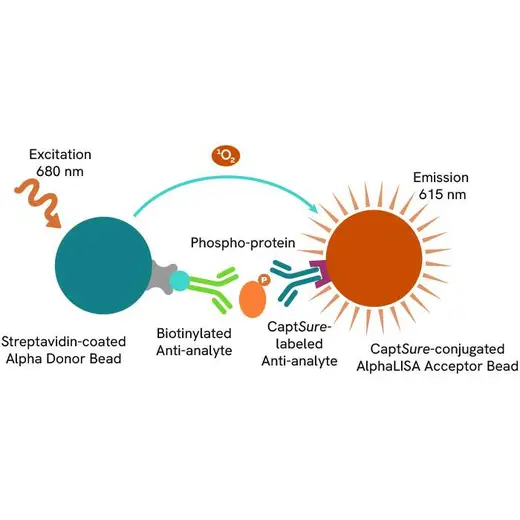
The assay uses two antibodies which recognize the phospho epitope and a distal epitope on the targeted protein. AlphaLISA assays require two bead types: Acceptor and Donor beads. Acceptor beads are coated with a proprietary CaptSure™ agent to specifically immobilize the assay specific antibody, labeled with a CaptSure™ tag. Donor beads are coated with streptavidin to capture one of the detection antibodies, which is biotinylated. In the presence of phosphorylated protein, the two antibodies bring the Donor and Acceptor beads in close proximity whereby the singlet oxygen transfers energy to excite the Acceptor bead, allowing the generation of a luminescent Alpha signal. The amount of light emission is directly proportional to the quantity of phosphoprotein present in the sample.

Phospho-AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra two-plate assay protocol
The two-plate protocol involves culturing and treating the cells in a 96-well plate before lysis, then transferring lysates into a 384-well OptiPlate™ plate before the addition of Phospho-AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra detection reagents. This protocol permits the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored. In addition, lysates from a single well can be used to measure multiple targets.
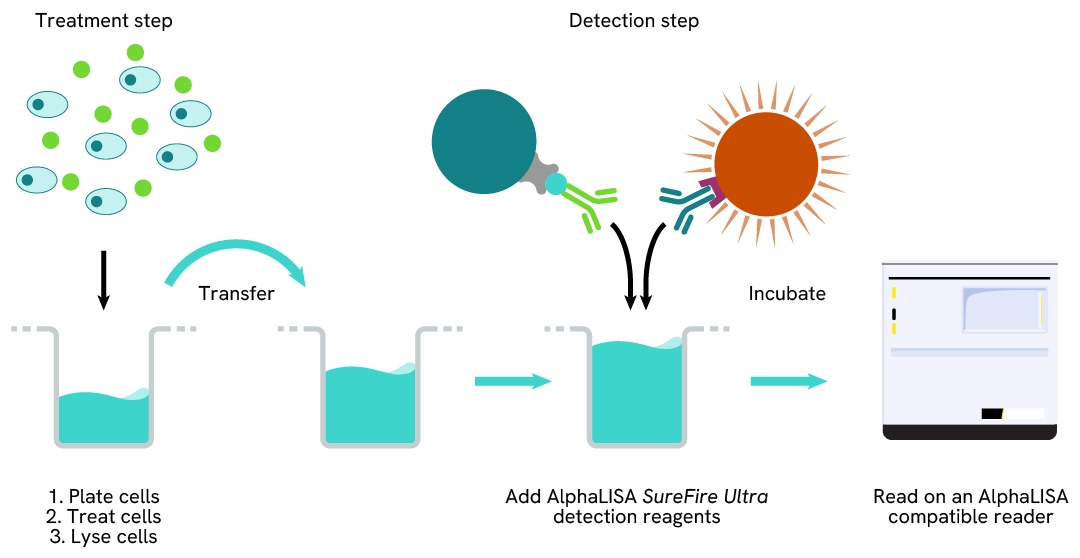
Phospho-AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra one-plate assay protocol
Detection of Phosphorylated target protein with AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, treatment, and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS designed protocol allows for miniaturization while maintaining AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra quality.
Assay validation
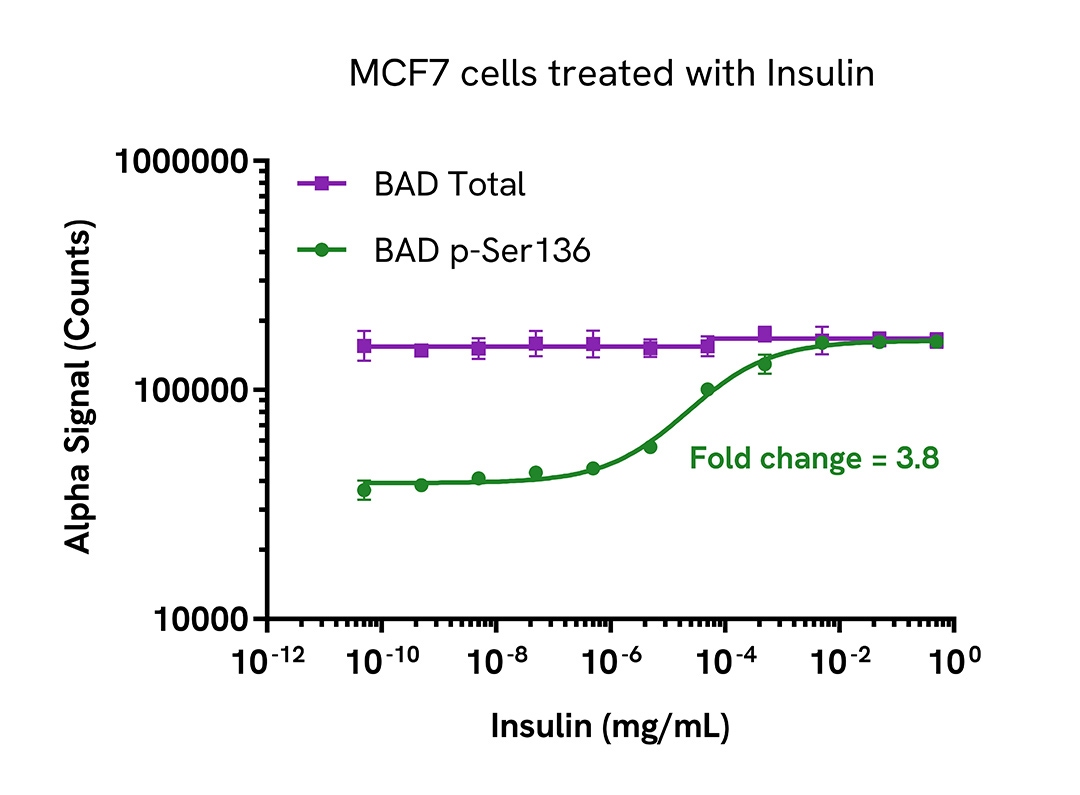
Activation of Phospho BAD (Ser136) in Insulin treated cells
MCF7 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate (40,000 cells/well) in complete medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were starved for 2 hours and then treated with increasing concentrations of Insulin for 5 minutes.
After treatment, the cells were lysed with 100 µL of Lysis Buffer for 10 minutes at RT with shaking (350 rpm). BAD Phospho (Ser136) and Total levels were evaluated using respective AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra assays. For the detection step, 10 µL of cell lysate (approximately 4,000 cells) was transferred into a 384-well white OptiPlate, followed by 5 µL of Acceptor mix and incubated for 1 hour at RT. Finally, 5 µL of Donor mix was then added to each well and incubated for 1 hour at RT in the dark. The plate was read on an EnVision XCite™ using standard AlphaLISA settings.
As expected, Insulin triggered a dose-dependent increase in the levels of Phospho BAD (Ser136) while Total BAD levels remained unchanged.
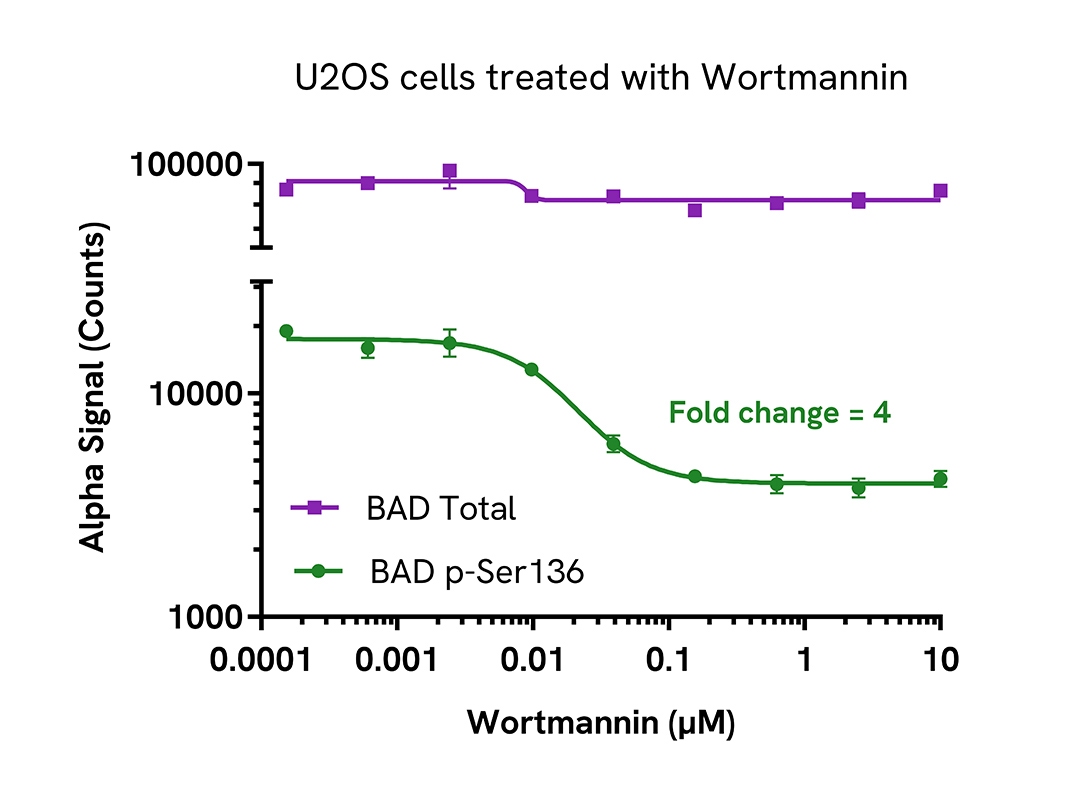
Decrease of Phospho BAD (Ser136) levels in Wortmannin treated cells
U2OS cells were seeded in a 96-well plate (40,000 cells/well) in complete medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were treated for 2 hours with increasing concentrations of Wortmannin.
After treatment, the cells were lysed with 100 µL of Lysis Buffer for 10 minutes at RT with shaking (350 rpm). BAD Phospho (Ser136) and Total levels were evaluated using respective AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra assays. For the detection step, 10 µL of cell lysate (approximately 4,000 cells) was transferred into a 384-well white OptiPlate, followed by 5 µL of Acceptor mix and incubated for 1 hour at RT. Finally, 5 µL of Donor mix was then added to each well and incubated for 1 hour at RT in the dark. The plate was read on an EnVision XCite using standard AlphaLISA settings.
As expected, Wortmannin triggered a dose-dependent decrease in the levels of Phospho BAD (Ser136) while Total BAD levels remained unchanged.
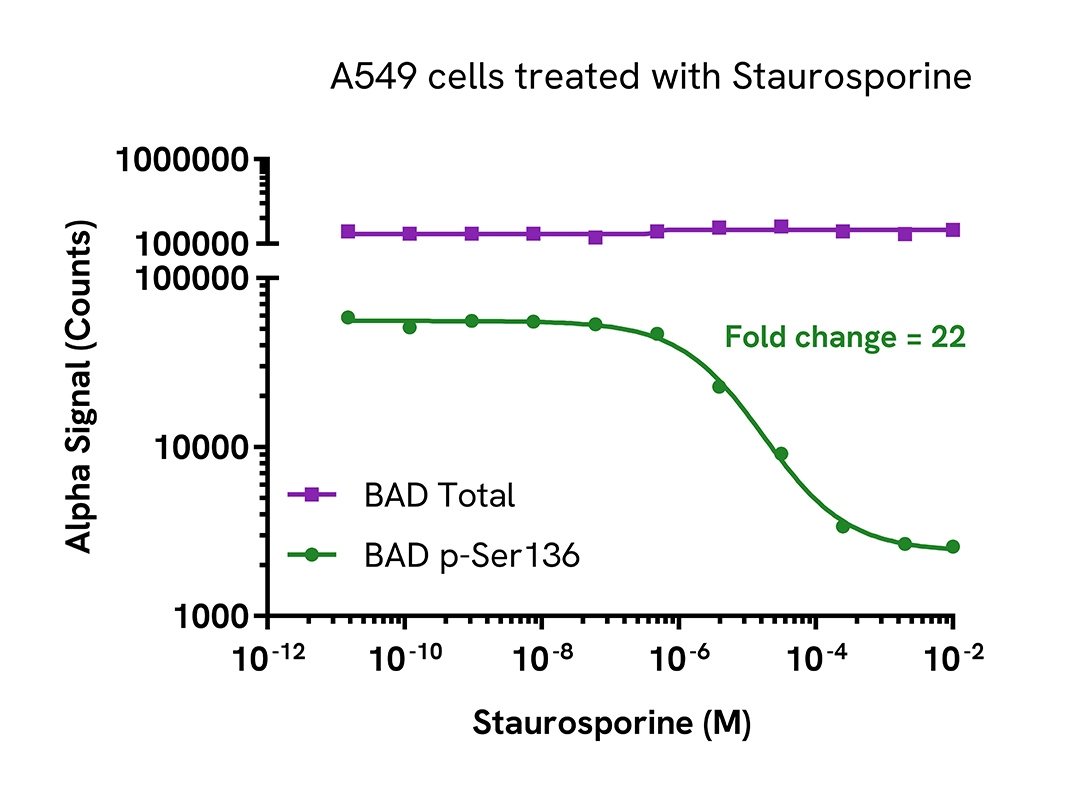
Decrease of Phospho BAD (Ser136) levels in Staurosporine treated cells
A549 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate (40,000 cells/well) in complete medium, and incubated overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were treated for 1 hour with increasing concentrations of Staurosporine.
After treatment, the cells were lysed with 100 µL of Lysis Buffer for 10 minutes at RT with shaking (350 rpm). BAD Phospho (Ser136) and Total levels were evaluated using respective AlphaLISA SureFire Ultra assays. For the detection step, 10 µL of cell lysate (approximately 4,000 cells) was transferred into a 384-well white OptiPlate, followed by 5 µL of Acceptor mix and incubated for 1 hour at RT. Finally, 5 µL of Donor mix was then added to each well and incubated for 1 hour at RT in the dark. The plate was read on an EnVision XCite using standard AlphaLISA settings.
As expected, Staurosporine triggered a dose-dependent decrease in the levels of Phospho BAD (Ser136) while Total BAD levels were unchanged.
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























