
NEXTFLEX Unique Dual Index Barcodes (8NT index, 1-24)

NEXTFLEX Unique Dual Index Barcodes (8NT index, 1-24)


| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Automation Compatible | Yes |
| Product Group | Barcodes |



Loading...
Product information
Overview
- UDI full length adapters for multiplexing up to 384 libraries for Illumina® and Element® sequencing platforms
- Compatible with all PCR-free and amplified TruSeq-style T-overhang library preps as drop in replacement
- Unique Dual Index design with ≥3 hamming distance reduces index hopping and sample mis-assignment on patterned flow cells
- Each lot is sequence-verified for index purity (QC by sequencing)
- Compatible with the NEXTFLEX Universal Blockers
Additional product information
For labs interested in increasing their multiplexing capabilities, a set of 1536 NEXTFLEX Unique Dual Index Barcodes is also available.
Index architecture and error robustness
The NEXTFLEX Unique Dual Index Barcodes contain full length adapters with unique dual 8NT index pairs. Every index in the set is separated by ≥ 3 Hamming distance. This design allows detection of single-base substitution errors during demultiplexing, limits index collisions and lowers false assignment on patterned flow cells where index hopping can occur. When using the NEXTFLEX Unique dual index pairs (i7 + i5) a read is assigned only when both indices match the same dedicated pair, greatly reducing misassignment from single-end index hopping or low-level contamination.

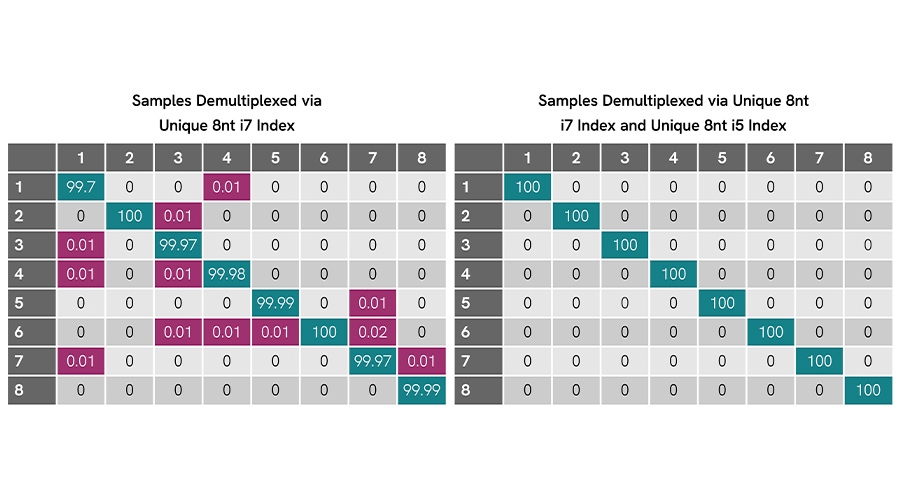
Figure 1. Dual unique indexing removes residual misassignment on MiSeq® sequencer. Eight libraries with NEXTFLEX 8 nt UDIs show low off-diagonal cross assignment (≤0.02%) when demultiplexed by i7 only (left). Demultiplexing with the paired unique i7 + i5 indices (right) yields 100% correct assignment for all samples (no detectable misassignment).
Demultiplexing confidence and data quality
A ≥3 base Hamming distance between indices makes it extremely unlikely that a single base miscall converts one valid index into another. Standard demultiplexing tools (bcl-convert, bcl2fastq, DRAGEN) can therefore confidently assign reads with one mismatch without risking misassignment. This preserves usable read counts, maintains balanced sample representation, and reduces cross-sample index bleed in applications such as rare variant detection, low-input RNA sequencing, and metagenomics.
Workflow integration and flexibility
NEXTFLEX Adapters can act as drop-in replacements for any TruSeq-style library prep with T-overhang ligation steps in both PCR-free and amplified library preps. Our plate format supports partial use while maintaining performance of remaining wells (with proper storage), accommodating both high-throughput batches and occasional low-plex runs.
Barcode design, quality control and traceability
Sequence-based QC verifies index purity with spike-in libraries so that each barcode maps only to its intended sequence, while proprietary contamination-reduction steps lowers index crosstalk to ~0.1%. Indices are engineered with a ≥3 base Hamming distance, avoid homopolymers longer than two bases, and are color balanced even in low-plex pools, design choices that limit misassignment from sequencing errors, reduce base-calling bias, and maintain balanced signal. Automated plating with controlled volumes supports consistent handling and traceability. Together these design and manufacturing controls deliver high usable read percentages with very low misassigned reads, supporting sensitive low-frequency variant detection.
Scalability, Universal blockers, and UMIs
Start with 24 or 96 unique dual indices, scale to 384, then up to 1,536 while keeping the same ≥3 base spacing so demultiplex parameters stay unchanged. NEXTFLEX® Universal Blockers block non-specific hybridization between adapter sequences, enhancing specificity and reducing sequencing costs. For workflows needing molecular counting or error suppression, NEXTFLEX® UDI-UMI adapters layer a molecular identifier onto the UDI framework to enable duplicate collapsing and more accurate quantitation.
Specifications
| Automation Compatible |
Yes
|
|---|---|
| Barcodes |
1 - 24
|
| Product Group |
Barcodes
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Unit Size |
48 rxns
|
References
- Estermann, M. (2020). Mouse embryonic stem cells self-organize into trunk-like structures with neural tube and somites. doi:10.1242/prelights.18906.
- Gardner, E. J., Prigmore, E., Gallone, G., Danecek, P., Samocha, K. E., Handsaker, J., . . . Hurles, M. E. (2019). Contribution of retrotransposition to developmental disorders. Nature Communications, 10(1). doi:10.1038/s41467-019-12520-y.
- Gaeta, N. C., Bean, E., Miles, A. M., Daniel Ubriaco Oliveira Gonçalves De Carvalho, Alemán, M. A., Carvalho, J. S., . . . Ganda, E. (2020). A Cross-Sectional Study of Dairy Cattle Metagenomes Reveals Increased Antimicrobial Resistance in Animals Farmed in a Heavy Metal Contaminated Environment. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.590325.
- Hirose, K., Chang, S., Yu, H., Wang, J., Barca, E., Chen, X., . . . Huang, G. N. (2019). Loss of a novel striated muscle-enriched mitochondrial protein Coq10a enhances postnatal cardiac hypertrophic growth. doi:10.1101/755793.
- Leon, K. E., et al. (2020) DOT1L modulates the senescence-associated secretory phenotype through epigenetic regulation of IL1A. bioRxiv 2020.08.21.258020; doi: 10.1101/2020.08.21.258020.
- Miura, H., Takahashi, S., Shibata, T. et al. Mapping replication timing domains genome wide in single mammalian cells with single-cell DNA replication sequencing. Nat Protoc 15, 4058–4100 (2020).
- Starr, T. N., Greaney, A. J., Hilton, S. K., Crawford, K. H., Navarro, M. J., Bowen, J. E., . . . Bloom, J. D. (2020). Deep mutational scanning of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain reveals constraints on folding and ACE2 binding. doi:10.1101/2020.06.17.157982.
- Veenvliet, J. V., et al. (2020) Mouse embryonic stem cells self-organize into trunk-like structures with neural tube and somites. bioRxiv 2020.03.04.974949; doi: 10.1101/2020.03.04.974949
- Dubey SK et al. (2025). Deciphering age-related transcriptomic changes in the mouse retinal pigment epithelium. Aging (Albany NY) 17(3):657–684. DOI: 10.18632/aging.206219
- Pujari & Cullen (2024) Modulators of MAPK pathway activity during filamentous growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. G3 14(6):jkae072
- Kant et al. (2023) High-quality full genome assembly of historic Xylella fastidiosa strains… Microbiol Resour Announc. 12(11):e00536-23.
- Arras et al. (2023) Characterisation of an E. coli line that completely lacks ribonucleotide reduction… eLife 12:e83845.
- Larkin et al. (2025) Climate-driven succession in marine microbiome biodiversity and biogeochemical function. Nat Commun. 16:3926.
- Klauer et al. (2024) Hydrophobins from Aspergillus mediate fungal interactions with microplastics. bioRxiv preprint 2024.11.05.622132.
FAQs
-
Which library preps are compatible with the NEXTFLEX® Unique Dual Index Barcodes?
-
How do NEXTFLEX Unique Dual Indices (UDI) reduce index hopping compared with combinatorial dual indices on patterned Illumina flow cells?
-
What demultiplex mismatch setting (0 vs 1) is recommended for an 8 nt UDI set with a ≥ 3 base Hamming distance and why?
-
Can I combine any of the NEXTFLEX UDI (8NT) kits with other NEXTFLEX UDI sets in the same run?
-
Are NEXTFLEX UDI adapters compatible with PCR-free library preps and low input or degraded samples such as cfDNA or FFPE?
-
What is the difference between NEXTFLEX UDI adapters and NEXTFLEX UDI-UMI adapters, and when should I choose a UDI-UMI design for molecular counting?
-
How is index purity verified for NEXTFLEX UDI lots and what read level QC metrics should I monitor after demultiplexing?
Resources
Are you looking for resources, click on the resource type to explore further.
This excel file includes the sequences of the indexes for the 384 NEXTFLEX UDI Barcodes.
Loading...
Loading...


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.






























