Overview
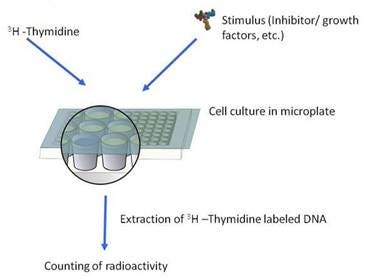
Cell proliferation studies based on the thymidine incorporation assay are employed frequently in immunological, cancer, stem cells, and pharmaceutical research to assess the ability both of natural and synthetic compounds to stimulate or inhibit the proliferation of lymphocytes and other cells.
Cell proliferation assays measure the incorporation of a radiolabeled DNA precursor, 3H- or 14C- thymidine, into the replication strands of DNA produced during cell division. Cultures are typically set up in microplates. The labeled DNA is usually captured with a cell harvester on glass fiber filters discs, which are then placed in liquid scintillation counting vials or directly harvested into a filter plate for counting on a scintillation beta-counter. The assay can also be performed using a scintillating Cytostar-T® plate, which requires no filtration step or scintillation cocktail.

What do I need to run this assay
Filtration format
Reagents available from Revvity:
- Radiolabeled thymidine (see next section)
- TC-treated microplates for cell culturing
- Glass fiber filters (UniFilter plates or Filtermat)
- Scintillation cocktail or Meltilex™ solid scintillant (Cat. No. 1450-441) (if using Filtermat)
- Scintillation vials (if using filter discs)
- Cell harvester
- TopSeal™-A (Cat. No. 6050185) and BackSeal (Cat. No. 6005199) (if using UniFilter plates)
- Radiometric detector (such as a Tri-Carb™ liquid scintillation counter, or a high-throughput detector such as the MicroBeta2™)
Reagents available from other suppliers:
- Stimulation factors
- Trypsin
- Wash buffer (e.g., PBS)
Cytostar-T format
- Cytostar-T plates (Cat. No. RPNQ0162 for 96-well, RPNQ0165 for 384-well)
- TopSeal-A adhesive plate seal (Cat. No. 6050185)
- White BackSeal, if counting from the top (Cat. No. 6005199)
- Radiolabeled thymidine (see next section)
- High-throughput radiometric detector
- Cell culture medium, buffer for labeling
- Stimulation factors
Products and catalog numbers
Thymidine radiochemicals
(Sample list of thymidine products. Visit our website for our complete listing)
| Radiochemical | Specific activity | Rad. conc. (mCi/mL) | Packaging buffer | Storage temp. | Cat. number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thymidine, [Methyl-3H]- | 2 mCi | 250 Ci/mmol | Steri-packaged, aqueous solution | 5°C | NET027A |
| 250 uCi | 20 Ci/mmol | Steri-packaged, aqueous solution | 5°C | NET027X | |
| 1 mCi | 20 Ci/mmol | Ethanol solution | -20°C | NET027E | |
| 1 mCi | 40-60 Ci/mmol | 2% Ethanol solution | 5°C | NET027W | |
| 250 uCi | 70-90 Ci/mmol | Steri-packaged, aqueous solution | 5°C | NET027Z | |
| Thymidine, [2-14C] | 10 uCi | >50 mCi/mmol | Steri-packaged, aqueous solution | 5°C | |
| Thymidine, [6-3H] | 1 mCi | >10 Ci/mmol | Steri-packaged, aqueous solution | 5°C | NET355 |
| Deoxythymidine 5'-Triphosphate, [Methyl-3H]- | 250 uCi | 10-25 Ci/mmol | Steri-packaged, aqueous solution | -5°C | NET221H |
| 1 mCi | 70-90 Ci/mmol | 50% ethanol solution | -20°C | NET221X | |
| 250 uCi | 70-90 Ci/mmol | Steri-packaged, aqueous solution | -5°C | NET221A |
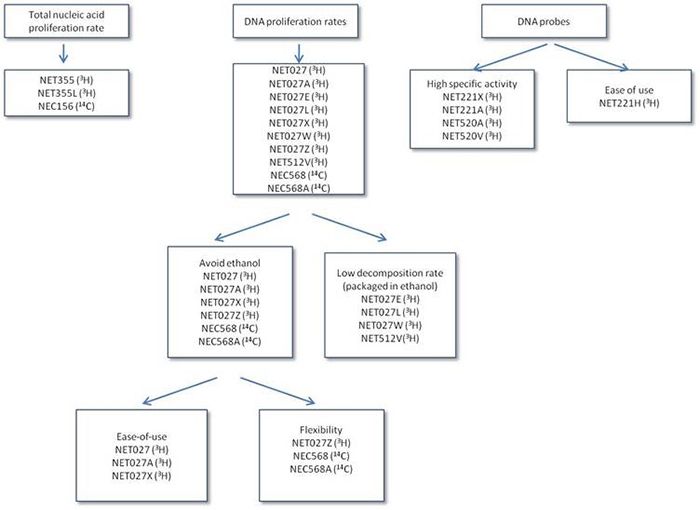
Choose the right thymidine
Notes
- Total vs. DNA only proliferation: Thymidine will label both DNA and RNA. 3H-methyl-thymidine (thymidine labeled on the methyl group) will only label DNA.
- Stability vs. toxicity: Formulations containing ethanol will last longer in storage, however, may kill cells. Formulations without ethanol are less toxic to cells but have a shorter shelf life.
- Ease vs. flexibility: fixed specific activity means that the same volume can be used every time. Products with variable specific activities tend to have higher specific activities (and therefore more signal); however, the volume needs to be calculated each time.
- Level of proliferation: high specific activity will give more signal, but will be less stable in storage
- Proliferation vs. probes: Thymidine and methyl thymidine are used for proliferation studies, while thymidine triphosphate is used for probe labeling, because triphosphate is unable to penetrate the cell membrane.
Radiolabeled thymidine table
Protocol-in-brief
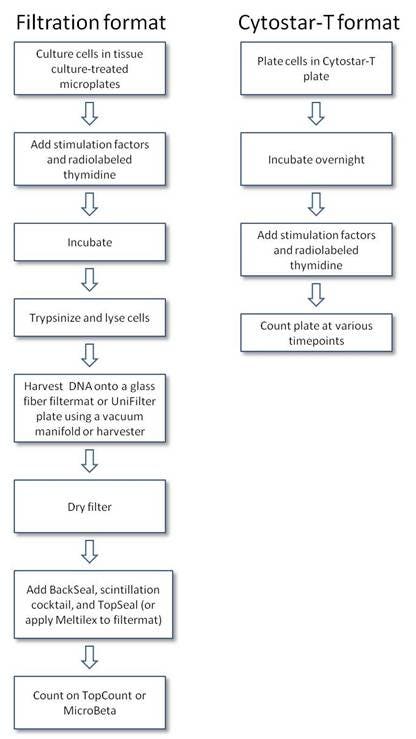
Protocol
Typical protocol for CytoStar-T assay
Sample protocol for 384-well CytoStar-T Plate
- Grow cells to subconfluence in complete medium. Grow cells at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 in 162 cm2 flasks. Passage cells at 1:10. Exponentially growing cells exhibit best uptake.
- Release the cells by trypsinization and estimate cell density in the resulting suspension.
- Dilute the suspension in complete medium to the selected seeding density and dispense 40 μL/well. Incubate overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2.
- Remove overnight media from the wells and wash with 50 μL sterile PBS/well. Dilute [methyl-14C] thymidine to 0.625 μCi/mL in assay medium. Add 80 μL [methyl-14C] thymidine to the wells to give a final concentration of 0.05 μCi/mL.
- Add [methyl-14C] thymidine to medium-only for solution control wells (background counts).
- Cover the plates with a clear plastic plate seal and count the plates immediately.
- Remove plate seal carefully and replace with plate lid. Return counted plate to the incubator. Count plate at appropriate intervals (e.g. every 24 hours up to 72 hours).
- Check cells regularly under the microscope for growth and morphology.
- Optional: Cells from individual wells may be trypsin released and counted at intervals to determine cell numbers (Cytostar-T signal is cell density dependent).
- Optional: At termination of the experiment, uptake may be confirmed by liquid scintillation counting of cells.
Application notes
- Kivelä, P. et al. Filter counting applications with the MicroBeta2 Microplate Counter. Cell Proliferation Assay on MicroBeta²
- Härkönen, P.L. et al. Cell Proliferation Assay by Using MicroBeta 3H-Thymidine Incorporation. Cell Proliferation Assay by Using MicroBeta 3H-Thymidine Incorporation
Citations
- Inglis, J.J., Simelyte, E., McCann, F.E., Criado, G. & Williams, R.O. Protocol for the induction of arthritis in C57BL/6 mice. Nat Protoc 3, 612-618 (2008). Link
- Liu, S. & Yamauchi, H. p27-Associated G1 arrest induced by hinokitiol in human malignant melanoma cells is mediated via down-regulation of pRb, Skp2 ubiquitin ligase, and impairment of Cdk2 function. Cancer Lett 286, 240-249 (2009). Link
- Munier, C.M.L., Zaunders, J.J., Ip, S., Cooper, D.A. & Kelleher, A.D. A culture amplified multi-parametric intracellular cytokine assay (CAMP-ICC) for enhanced detection of antigen specific T-cell responses. J. Immunol. Methods 345, 1-16 (2009). Link
- Lee-Hoeflich, S.T. et al. A central role for HER3 in HER2-amplified breast cancer: implications for targeted therapy. Cancer Res 68, 5878-5887 (2008). Link
- Sommerfeld, M.R. et al. In vitro metabolic and mitogenic signaling of insulin glargine and its metabolites. PLoS ONE 5, e9540 (2010). Link
Other Revvity cell proliferation technologies
- DELFIA fluorescent cell proliferation assay
- ATPLite™ 1-step luminescent assay
- ATPLite luminescent assay
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures