Overview
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is the standard in kidney function assessment and is used to determine progression of kidney disease and drug-induced kidney toxicity. One of the most accepted ways to assess GFR is by measuring the rate of disappearance of labeled inulin from the blood; as inulin is completely filtered at the kidneys’ glomeruli (but neither secreted nor reabsorbed by the tubules), this rate of disappearance is directly proportional to GFR.
IVISense™ GFR 680 (formerly GFR-Vivo) is a near infrared fluorescent inulin-based probe that, in combination with fluorescence tomography heart imaging, enables quantitative assessment of renal Glomerular Filtration Rate, as an indicator of renal toxicity or injury.
Products and catalog numbers
| Product | Catalog Number | Ex/Em wavelength (nm) | Molecular weight (g/mol) | Validated Experiments | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVISense GFR 680 | NEV30000 | 670/685 | 6,000 | In vivo | Renal (kidney) disease, toxicity or injury |
Using IVISense GFR 680 probe for in vivo studies
In Vivo imaging
The generally recommended procedure for in vivo imaging with IVISense GFR 680 is administration via either tail vein intravenous injection or retro orbital injection and imaging the chest area immediately at various times points (1, 5, 15, 30, and 45 min) following injection.
The blood half-life of IVISense GFR 680 in normal mice are approximately 0.5 and 8.0 min, respectively, for T 1/2 Alpha and T 1/2 Beta. Repeat injection and heart imaging may be performed as early as 24 hours for longitudinal studies, although there is longer term retention in the kidneys.
| Route of Injection | Mouse Dose (25 g) | Blood t 1/2 | Optimal imaging time | Optimal Re-injection Time (complete clearance) | Route of Metabolism/ background tissue | FMT and IVIS settings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IV | 100 µL | 0.5 min (t ½ Alpha) | 1, 5, 15, 30, and 45 min post-injection | 24 hours | Kidneys | - FMT 680/700 |
| 8 min (t ½ Beta) | - IVIS 675/720 |

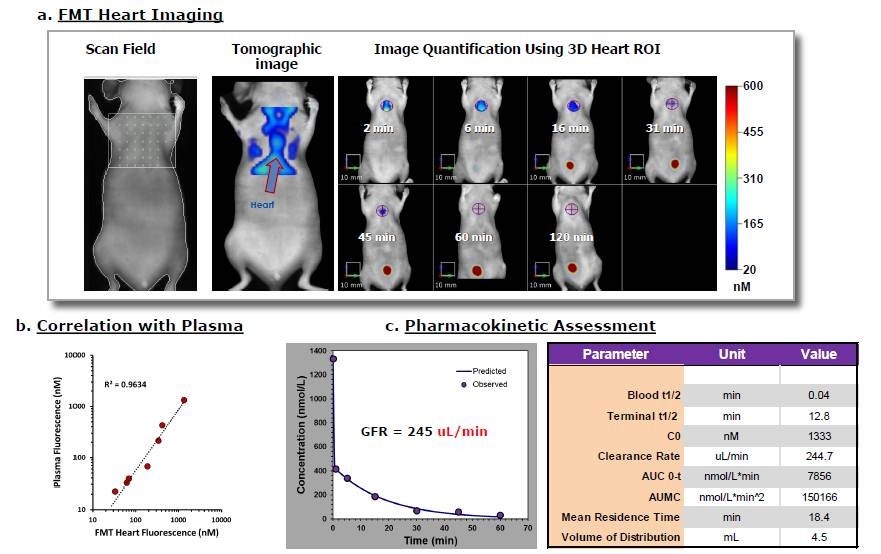
Figure 1. Kinetic imaging of the heart region of mice after IVISense GFR 680 IV injection offers a noninvasive approach to quantifying circulating fluorescence. A) A representative mouse scanned using fluorescence molecular tomography yields heart and blood vessel signal throughout the body. Heart fluorescence is identified and quantified at the indicated imaging times. B) Quantitative results established noninvasively using tomography imaging can be correlated to a parallel study in which mice were serially bled and samples assayed ex vivo in comparison to a standard curve. C) Various pharmacokinetic parameters were assessed using the MicroSoft Excel Add-In PK Solver 2.0.
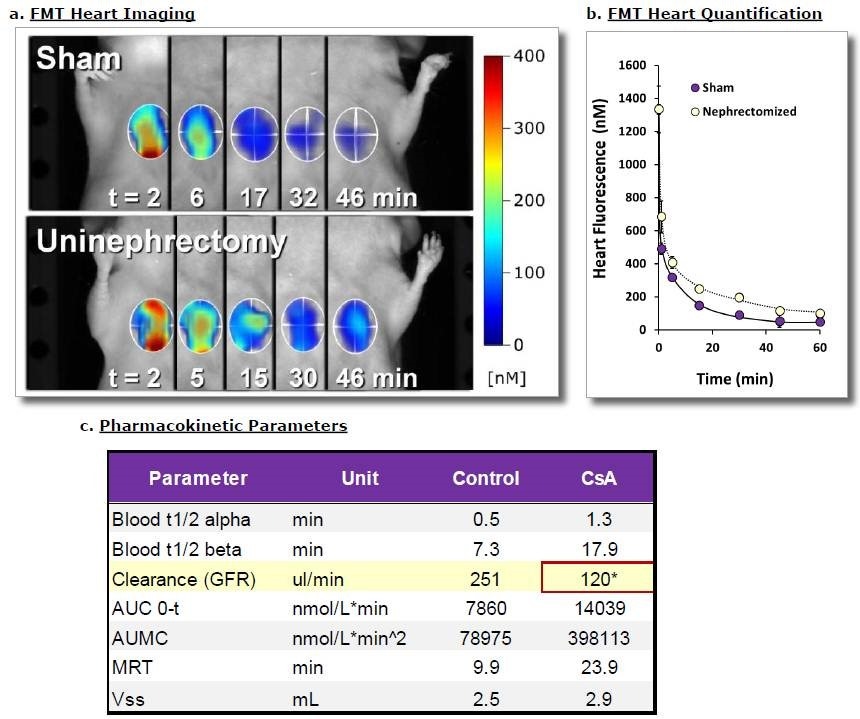
Figure 2. SKH-1E mice underwent either sham surgery or removal of one kidney to alter total GFR capability. After 3-4 days of recovery, mice were injected IV with 2 nmol of IVISense GFR 680. A) Fluorescence tomography imaging of representative mice (i.e. representative of the mean of each group) show defined changes in heart region signal over time. B) Quantitative heart results for all mice, established noninvasively fluorescence tomography imaging, yielded kinetic curves showing delayed clearance of IVISense GFR 680 in uninephrectomized mice. C) Various pharmacokinetic parameters were assessed, revealing qantitative differences in GFR. Asterisk indicates statistically significant difference between Sham and Uninephrectomy groups (p < 0.005).
Application notes and posters
- Application Note: An in vivo non-invasive method to determine glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- Poster: Novel near Infrared probe for Noninvasive Imaging and Quantification of Glomerular Filtration Rate in Mice
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.




























