Overview
The determination of chloroamphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) enzyme activity is a standard method for assessing promotor expression in transfected cell lines. In such assays the promoter sequence of interest is fused to a DNA sequence encoding the bacterial CAT enzyme, an enzyme which is not expressed in trhe mammalian cell line. The enzyme catalyzes acylation of chloramphenicol, primarily at the 3-hydroxyl position. Quantification of the acetyl-chloramphenicol (AcCAM) generated provides a convenient measure of promoter activity.
The rapid two-phase CAT assay described here utilizes acetyl-1-14C Acetyl Coenzyme A or acetyl-3H Acetyl Coenzyme A as the labeled substrate. In this method the enzymatic reaction components are combined directly in a mini scintillation vial and then immediately overlaid with 5 mL of a water-immiscible counting cocktail. The 14C or 3H AcCAM generated by the reaction diffuses linearly over time into the organic phase of the cocktail. Direct liquid scintillation counting (LSC) of the two-phase reaction mix in the vial provides quantitative data reflecting the CAT activity. The rate of the enzymatic reaction, as determined by the rate of increase in cpm/min, is directly proportional to the concentration of CAT in the reaction.
This method does not require any extractions or TLC autoradiography. The assay provides a continuous data stream from a single reaction, as opposed to the data from an end-point reaction. Other advantages are that the specific activity and radiochemical concentration is constant and preadjusted for direct use in the assay. No additional concentration adjustments are required, and lot-to-lot variation is thus eliminated.
What do I need to run this assay?
Reagents available from Revvity:
- Scintillation cocktail
- Pico Glass Vials, 7 mL (Cat. No. 6000167)
Reagents available from other suppliers:
- Chloramphenicol (Sigma Aldrich Cat. No. C0378)
- E.coli chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (Promega Cat. No. E1051)
- CAT assay buffer (100 mM Tris buffer, pH 7.8)
Instrumentation/Equipment:
- A Liquid scintillation counting-capable reader (We recommend the Tri-Carb® or MicroBeta2™ counters)
Protocol-in-brief

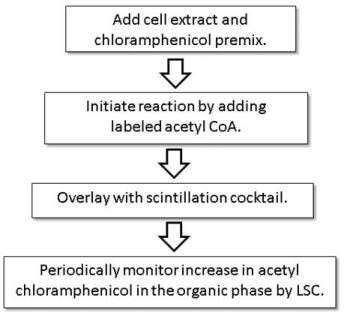
Step-by-step protocol
- To each 7 mL glass vial, add 50 μL of cell extract or CAT enzyme standard in CAT assay buffer (100 mM Tris buffer, pH 7.8).
- To this sample add 200 μL of premix containing 1.25 mM Chloramphenicol in CAT assay buffer.
- Initiate the reaction by adding the radiolabeled substrate containing 0.1 μCi of 14C Acetyl Coenzyme A or 0.5 μCi of 3H Acetyl Coenzyme A in 22.5 μL of 1 mM unlabeled acetyl Coenzyme A. These additions result in a 0.1 mM final concentration of acetyl CoA.
- Gently overlay the reaction with 5 mL of Insta-Fluor Plus scintillation cocktail.
- Close the vials and incubate at room temperature.
- At timed intervals, count the vials sequentially in a liquid scintillation counter for 0.10 min. Final experimental resulats are obtained in 1-2 hours, although the assay can be terminated at any point at which counts above background are obtained.
- Plot cpm vs. time for each reaction.
- Determine CAT enzyme activity by comparison to a standard curve, with the data expressed as the increase in cpm/min.
Citations
- Crabb, D. and Dixon, J. A method for increasing the sensitivity of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase assays in extracts of transfected cultured cells Anal. Biochem. 163, 88-92 (1987) Link
- Hsu, J.C. et al. Indole-3-carbinol inhibition of androgen receptor expression and downregulation of androgen responsiveness in human prostate cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 26, 1896 -1904 (2005). Link
- Neumann, J. et al. A novel rapid assay for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene expression Biotechniques 5,444-448 (1987)
- Tsumaki, N., Liu, Y., Yamada, Y. & Krebsbach, P. Enhancer analysis of the alpha 1(II) and alpha 2(XI) collagen genes in transfected chondrocytes and transgenic mice. Methods Mol. Biol 139, 187-195 (2000). Link
- Zhang, S., Jonklaas, J. & Danielsen, M. The glucocorticoid agonist activities of mifepristone (RU486) and progesterone are dependent on glucocorticoid receptor levels but not on EC50 values. Steroids 72, 600-608 (2007). Link
Tips and troubleshooting
Tips
- To generate a continuous data stream, the scintillation cocktail should be added to the vial immediately after initiation of the CAT reaction. Adding the cocktail later point does not significantly reduce the diffusion time but will extend the overall assay time.
- Note that the cell extract samples in step 1 of the protocol may require a 15 min heat treatment at 70 °C to destroy interfering acylases. The need for this step is cell-line dependent.
FAQs
Q. Do I need to shake or vortex the sample?
A. To maintain linearity and reproducibility of experimental results, mixing of the two phases should be avoided. Shaking or vortexing the sample disperses the aqueous phase and adequate time must be allowed for complete phase separation to occur prior to counting the samples.
Q. Can I incubate at temperatures other than room temperature?
A. Yes, incubation at 37 °C is possible if acceleration of the reaction is desired.
Q. What is the sensitivity of the assay?
A. Experiments utilizing 5 μCi of 3H Acetyl CoA have shown linearity down to CAT levels of 0.0025 units.
Other reporter gene assays available from Revvity
Luciferase reporter gene assay reagents
Custom conjugation and custom assay development at Revvity
Revvity offers custom radiochemical services as well as custom assay development. If you are interested in having your biomolecule custom-radiolabeled or in custom assay development, please contact our custom teams:
Radiosynthesis and Labeling Custom Services
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. The information provided above is solely for informational and research purposes only. Revvity assumes no liability or responsibility for any injuries, losses, or damages resulting from the use or misuse of the provided information, and Revvity assumes no liability for any outcomes resulting from the use or misuse of any recommendations. The information is provided on an "as is" basis without warranties of any kind. Users are responsible for determining the suitability of any recommendations for the user’s particular research. Any recommendations provided by Revvity should not be considered a substitute for a user’s own professional judgment.




























